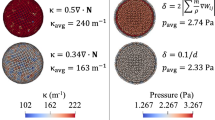
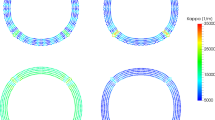
Abstract
Surface tension plays a significant role in fluid simulation, especially small-scale fluid. In this paper, we present a novel surface tension formulation for smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) to simulate interfacial fluid flow. The surface tension formulation is decomposed into three main processes: (1) volume-preserved mesh smoothing, (2) surface tension computation and (3) surface tension transfer. Firstly, we exploit a Lagrangian operator to smooth an initial three-dimensional discrete interfacial surface mesh generated from fluid particles; and then the surface mesh is scaled in a volume-preserved way and the center is translated to its original position to get a smoothed mesh. Secondly, surface tension strengths on the vertices of the interfacial surface mesh are computed according to the offsets from the original surface mesh to the smoothed mesh. Finally, we transfer the surface tension strengths from the mesh vertices onto their neighbor fluid particles in a conservative way. The proposed surface tension solver is simple and straightforward to be plugged into a standard SPH solver. Experimental results show that it is effective and efficient to produce realistic fluid simulations, especially for the phenomena with strong surface tension.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, M., Zhang, S., Zhang, H., Zheng, L.: Simulation of surface tension driven interfacial flow with Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics method. Comput. Fluids. 59, 61–71 (2012)
Calagrossi, A., Landrini, M.: Numerical simulation of interfacial flows by smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Comput. Phys. 191, 448–475 (2003)
Morris, J.P.: Simulating surface tension with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. IntjNumer Meth Fluids. 33, 333–353 (2000)
Monagehan, J.J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 1703–1759 (2005)
Nugent, S., Posch.: Liquid drops and surface tension with smoothed particle applied mechanics. Phys. Rev. E. 62, 4968–4975 (2000)
Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A.: A multi-phase SPH method for macroscopic and mesoscopic flows. Comput. Phys. 213, 844–861 (2006)
Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A.: An incompressible multi-phase SPH method. Comput. Phys. 227, 264–278 (2007)
Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A.: A constant-density approach for incompressible multiphase SPH. Comput. Phys. 228, 2082–2091 (2009)
Nils, T., Chris, W., Markus, G., Greg, T.: A multi-scale approach to Mesh-based surface tension flows. ACM. Trans. Graph. 29(3), 48:1–48, 10 (2010)
Muller, M., Charypar, D., Gross, M.: Particle-based fluid simulation for interactive applications. InL Proceedings of Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 154159 (2003)
Becker, M., Teschner, M.: Weakly compressible SPH for free surface flows. In: Proceedings of Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 6372 (2007)
Adams, B., Pauly, M., Keiser, R., Guibas. L.J.: Adaptively sampled particle fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 26(3), Article no 48 (2007)
Markus, I., Jens, O., Barbara, S., Andreas, K., Matthias, T., Markus, I., Jens, O., Barbara, S., Andreas, K., Matthias, T.: SPH fluids in computer graphics. In: Proceedings of Eurographics (Strasbourg, France), Computer Graphics Forum, pp. 21–42 (2014)
Rackbill, J.U.B., Kothe, D.B., Zemach, C.: A continuum method for modeling surface tension. J. Comput. Phys. 2(100), 335354 (1992)
Muller, M., Charypar, D.ee., Gross, M.: Particle-based fluid simulation for interactive applications. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 154159 (2003)
Muller, M., Olenthaler, B.S., Keiser, R., Gross, M.: Particle-based fluid-fluid interaction. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 237244 (2005)
Olenthaler, B.S., Pajarola, R.: Density contrast SPH interfaces. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 211218 (2008)
Nugent, S., Posch, H.: Liquid drops and surface tension with smoothed particle applied mechanics. Phys. Rev. E. 62(4), 49684975 (2000)
Tartakovsky, A., Meakin, P.: Modeling of surface tension and contact angles with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. E. 72(2), 026301 (2005)
Akinci, N., Akinci, G., Teschner, M.: Versatile surface tension and adhesion for SPH fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. SIGGRAPH Asia). 32(6), 182:1182:8 (2013)
Zheng, Q., Yong, J.H., Paul, J.C.: Simulation of bubbles. In: Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation (SCA ’06). Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland, Switzerland, pp. 325–333 (2006)
Hong, J.M., Kim, C.H.: Discontinuous fluids. In: Gross, Markus (ed.) ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Papers (SIGGRAPH ’05), pp. 915–920. ACM, New York (2005)
Sussman, M., Ohta, M.: A stable and efficient method for treating surface tension in incompressible two-phase flow. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31(4), 2447–2471 (2009)
Lorensen, W.E., Cline, H.E.: Marching cubes: a high-resoulution 3D suface construction algorithm. Comput. Graph. 21(4), 163–169 (1987)
Yu J., Wojtan, C., Turk, G., Yap, C.: Explicit mesh surfaces for particle based fluids. Comput. Graph. Forum. 31(2pt4), 815–824 (2012)
Betchelor, G.: An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1967)
Monaghan, J.: Simulating free surface flows with SPH. J. Computat. Phys. 110, 399–406 (1994)
Fujiwara, K.: Eigenvalues of Laplacians on a closed riemannian manifold and its nets. Proc. AMS 123, 2585–2594 (1995)
Desbrun, M., Meyer, M., Schrder, P., Alan, H.: Barr. Implicit fairing of irregular meshes using diffusion and curvature flow. In Proceedings of the 26th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques (SIGGRAPH ’99), ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, pp. 317–324 (1999)
Kang, Myungjoo, Fedkiw, Ronald P., Liu, Xu-Dong: A boundary condition capturing method for multiphase incompressible flow. J. Sci. Comput. 15(3), 323–360 (2000)
Losasso, Frank, Gibou, Frdric, Fedkiw, Ron: Simulating water and smoke with an octree data structure. ACM Trans. Graph. 23(3), 457–462 (2004)
Misztal, M., Bridson, R., Erleben, K., Brentzen, J., Anton, F.: Optimization-based fluid simulation on unstructured meshes. In: Proc. of Virtual Reality Interactions and Physical Simulations, pp. 1120. 2, 3 (2010)
Erleben, K., Misztal, M., Brentzen, J.: Mathematical foundation of the optimization-based fluid animation method. In: Proc. of Symp. on Comput. Anim, pp. 101110. 3. ACM (2011)
Brochu, T., Batty, C., Bridson, R.: Matching fluid simulation elements to surface geometry and topology. ACM Trans. Graph. 29(4), Article 47, 9 (2010)
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers for their kind suggestions. The authors also thank Xuemin Liu and Cheng Wang at the School of Information Science and Technology, Beijing Forestry University, for their hard work on the final result rendering and to Dong Li for his careful grammar revision. The work in this paper has been supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. BLX2012049, 2015ZCQ-XX), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61402038, 61100132), CCF-Tencent Open Fund in 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Li, X., Liu, Y. et al. A novel surface tension formulation for SPH fluid simulation. Vis Comput 33, 597–606 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-016-1274-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-016-1274-4