Abstract
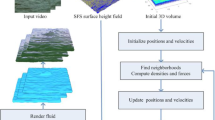
Conventional methods to create fluid animation primarily resort to physically based simulation via numerical integration, whose performance is dominantly hindered by large amount of numerical calculation and low efficiency. Alternatively, video-based methods could easily reconstruct fluid surfaces from videos, yet they are not able to realize two-way dynamic interaction with their surrounding environment in a physically correct manner. In this paper, we propose a hybrid method that combines video-based fluid surface reconstruction and popular fluid animation models to compute and re-animate fluid surface. First, the fluid surface’s height field corresponding to each video frame is estimated by using the shape-from-shading method. After denoising, hole-filling, and smoothing operations, the height field is utilized to calculate the velocity field, where the shallow water model is adopted. Then we treat the height field and velocity field as real data to drive the simulation. Still, only one layer of surface particles is not capable of driving the smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) system. The surface particles (including 3D position and its velocity) are then employed to guide the spatial sampling of the entire volume underneath. Second, the volume particles corresponding to each video frame are imported into the SPH system to couple with other possible types of particles (used to define interacting objects), whose movement is dictated by the direct forcing method, and fluid particles’ geometry information is then corrected by both physical models and real video data. The resulting animation approximates the reconstruction surface from the input video, and new physically based coupling behaviors are also appended. We document our system’s detailed implementation and showcase visual performance across a wide range of scenes.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinci, N., Ihmsen, M., Akinci, G., Solenthaler, B., Teschner, M.: Versatile rigid-fluid coupling for incompressible sph. ACM Trans. Graph. 31(4), 62:1–62:8 (2012)
Becker, M., Teschner, M.: Weakly compressible sph for free surface flows. In: Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 209–217 (2007)
Besl, P.J., McKay, N.D.: Method for registration of 3-d shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 14(2), 239–256 (1992)
Chao, J., Mei, R., Singh, R., Shyy, W.: A filter-based, mass-conserving lattice boltzmann method for immiscible multiphase flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 66(5), 622–647 (2011)
Chen, S., Doolen, G.D.: Lattice Boltzmann method for fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30(1), 329–364 (1998)
Chentanez, N., Müller, M.: Real-time eulerian water simulation using a restricted tall cell grid. ACM Trans. Graph. 30(4), 82:1–82:10 (2011)
Foster, N., Metaxas, D.: Realistic animation of liquids. Graph. Models Image Process. 58(5), 471–483 (1996)
Gregson, J., Ihrke, I., Thuerey, N., Heidrich, W.: From capture to simulation-connecting forward and inverse problems in fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 33(4), 139:1–139:11 (2014)
He, X., Wang, H., Zhang, F., Wang, H., Wang, G., Zhou, K.: Robust simulation of sparsely sampled thin features in sph-based free surface flows. ACM Trans. Graph. 34(1), 7:1–7:9 (2014)
Ihmsen, M., Akinci, N., Becker, M., Teschner, M.: A parallel sph implementation on multi-core cpus. Comput. Graph. Forum 30(1), 99–112 (2011)
Ihmsen, M., Orthmann, J., Solenthaler, B., Kolb, A., Teschner, M.: Sph fluids in computer graphics. In: Eurographics, pp. 21–42 (2014)
Kutulakos, K., Steger, E.: A theory of refractive and specular 3d shape by light-path triangulation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 76(1), 13–29 (2007)
Kwatra, V., Mordohai, P., Narain, R., Penta, S.K., Carlson, M., Pollefeys, M., Lin, M.C.: Fluid in video: augmenting real video with simulated fluids. Comput. Graph. Forum 27(2), 487–496 (2008)
Ladický, L., Jeong, S., Solenthaler, B., Pollefeys, M., Gross, M.: Data-driven fluid simulations using regression forests. ACM Trans. Graph. 34(6), 199:1–199:9 (2015)
Lentine, M., Zheng, W., Fedkiw, R.: A novel algorithm for incompressible flow using only a coarse grid projection. ACM Trans. Graph. 29(4), 114:1–114:9 (2010)
Li, C., Pickup, D., Saunders, T., Cosker, D., Marshall, D., Hall, P., Willis, P.: Water surface modeling from a single viewpoint video. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graphics 19(7), 1242–1251 (2013)
Low, K.L.: Linear Least-squares Optimization for Point-to-plane ICP Surface Registration. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill (2004)
Monaghan, J.J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 30, 543–574 (1992)
Müller, M., Charypar, D., Gross, M.: Particle-based fluid simulation for interactive applications. In: Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 154–159 (2003)
Ojeda, J., Susín, A.: Enhanced lattice boltzmann shallow waters for real-time fluid simulations. Eurographics 2013, 25–28 (2013)
Pan, Z., Huang, J., Tong, Y., Bao, H.: Wake synthesis for shallow water equation. Comput. Graph. Forum 31, 2029–2036 (2012)
Péteri, R., Fazekas, S., Huiskes, M.J.: Dyntex: a comprehensive database of dynamic textures. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 31(12), 1627–1632 (2010)
Pickup, D., Li, C., Cosker, D., Hall, P., Willis, P.: Reconstructing mass-conserved water surfaces using shape from shading and optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 10th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Volume Part IV, pp. 189–201 (2011)
Ping-Sing, T., Shah, M.: Shape from shading using linear approximation. Image Vis. Comput. 12(8), 487–498 (1994)
Quan, H., Wang, C., Song, Y.: Fluid re-simulation based on physically driven model from video. The Visual Computer, pp. 1–14 (2015)
Robert Bridson, A.K.P.: Fluid simulation for computer animation (2008)
Shao, X., Zhou, Z., Magnenat-Thalmann, N., Wu, W.: Stable and fast fluid-solid coupling for incompressible sph. Comput. Graph. Forum 34(1), 191–204 (2015)
Solenthaler, B., Mller, M., Gross, M.H., Bucher, P., Chentanez, N.: Sph based shallow water simulation. Virtual Reality Interactions and Physical Simulations, pp. 39–46 (2011)
Stam, J.: Stable fluids. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, pp. 121–128 (1999)
Tan, P., Zeng, G., Wang, J., Kang, S.B., Quan, L.: Image-based tree modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 26(3) (2007)
Thurey, N., Müller-Fischer, M., Schirm, S., Gross, M.: Real-time breaking waves for shallow water simulations. In: Proceedings of the 15th Pacific Conference on Computer Graphics and Applications, pp. 39–46 (2007)
Wang, H., Liao, M., Zhang, Q., Yang, R., Turk, G.: Physically guided liquid surface modeling from videos. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(3), 341–352 (2009)
Zhang, R., Tsai, P.S., Cryer, J.E., Shah, M.: Shape-from-shading: a survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 21(8), 690–706 (1999)
Zhu, B., Lu, W., Cong, M., Kim, B., Fedkiw, R.: A new grid structure for domain extension. ACM Trans. Graph. 32(4), 63:1–63:12 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This paper is partially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61532002, 61272199, National High-tech R&D Program of China (863 Program) under Grant 2015AA016404, the Specialized Research Fund for Doctoral Program of Higher Education under Grant 20130076110008, and Open Funding Project of State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems of Beihang University under Grant BUAA-VR-15KF-14. The authors would like to thank all reviewers for their very helpful and constructive comments and suggestions. We also thank Dyntex Dataset for the support of rich fluid videos for our study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Wang, C., Qin, H. et al. Video-based fluid reconstruction and its coupling with SPH simulation. Vis Comput 33, 1211–1224 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-016-1284-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-016-1284-2