Abstract
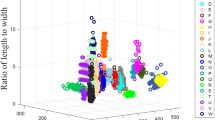
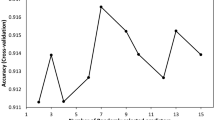
The present paper reports an automated approach for the characterization and analysis of the behavioral of sand flies; the method used is based on Gaussian mixture model and Kalman filter for the detection and tracking of sand flies, and then the extraction of an optimized set of features from the trajectory of flight is performed for the classification process. So, we propose here two optimized sets of features; the first one is used to identify sand flies among other insects, and the second is employed for the characterization of the behavioral change in the sand flies in the presence of a repulsive odor. These features are tested on three different classifiers; artificial neural network, support vector machine and K-nearest neighbor (KNN), and the results show an important improvement in the classification accuracy and confirm the effectiveness of our approach; the accuracy rate of the proposed method reached 88.6% for the identification of sand flies and 93.4% for the detection of their behavior change. Instead of the excessive use of pesticides over wide areas, the presented investigation is a key pillar of the development of an ecological way for a statistical information gathering about sand flies in order to fight against disease carried by those insects especially leishmaniosis and pappataci fever.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
www.who.int/whr/1996/media_centre/executive_summary1/en/index9.html. Accessed 20 Aug 2017
Fry, S., Bichsel, M., Muller, P., Robert, D.: Tracking of flying insects using pan-tilt cameras. J. Neurosci. Methods 101, 59–67 (2000)
Müller, P., Robert, D.: Death comes suddenly to the unprepared: singing crickets, call fragmentation, and parasitoid flies. Behav. Ecol. 13, 598–606 (2002)
Frye, M., Tarsitano, M., Dickinson, M.: Odor localization requires visual feedback during free flight in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Exp. Biol. 206, 843–855 (2003)
Poiesi, F., Cavallaro, A.: Tracking multiple high-density homogeneous targets. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol. 25(4), 623–637 (2015)
Solis-Sánchez, L.O., García-Escalante, J.J., Castaneda-Miranda, R., Torres-Pacheco, I., Guevara-González, R.G.: Machine vision algorithm for whiteflies (BemisiatabaciGenn.) scouting under greenhouse environment. J. Appl. Entomol. 133((7), 546–552 (2009)
Solis-Sánchez, L.O., Castañeda-Miranda, R., García-Escalante, J.J., Torres-Pacheco, I., Guevara-González, R.G., Castañeda-Miranda, C.L., Alaniz-Lumbreras, P.D.: Scale invariant feature approach for insect monitoring. Comput. Electron. Agric. 75, 92–99 (2011)
Qing, Y., Jun, L.V., Qing-jie, L.I.U., Guang-qiang, D., Bao-jun, Y., Hong-ming, C., Jian, T.: An insect imaging system to automate rice light-trap pest identification. J. Integr. Agric. 11(6), 978–985 (2012)
Potamitis, I.: Classifying insects on the fly. Ecol. Inf. 21, 40–49 (2014)
Feng, L., Bhanu, B., Heraty, J.: A software system for automated identification and retrieval of moth images based on wing attributes. Pattern Recogn. 51, 225–241 (2016)
Kaya, Y., Kayci, L.: Application of artificial neural network for automatic detection of butterfly species using color and texture features. Vis. Comput. 30, 71–79 (2014)
Li, F., Xiong, Y.: Automatic identification of butterfly species based on HoMSC and GLCMoIB. Vis Comput (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-017-1426-1
Chiu, C., En-Cheng, Y., Joe-Air, J., Ta-Te, L.: An imaging system for monitoring the in-and-out activity of honey bees. Comput. Electron. Agric. 89, 100–109 (2012)
Qing, Y., Jun, L.V., Qing-jie, L., Guang-qiang, D., Bao-jun, Y., Hong-ming, C., Jian, T.: Automatic behavior analysis system for honeybees using computer vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 122, 10–18 (2016)
Cullinan, V.I., Matzner, S., Duberstein, C.A.: Classification of birds and bats using flight tracks. Ecol. Inf. 27, 55–63 (2015)
Handoko, Yeffry, Nazaruddin, Yul Y., Hu, Huosheng: Using echo ultrasound from schooling fish to detect and classify fish types. J. Bionic Eng. 6(3), 264–269 (2009)
Dutta, M.K., Sengar, N., Kamble, N., Banerjee, K., Minhas, N., Sarkar, B.: Image processing based technique for classification of fish quality after cypermethrine exposure. Food Sci. Technol. 68, 408–417 (2016)
Jhuang, H., Garrote, E., Yu, X., Khilnani, V., Poggio, T.D., Steele, A., Serre, T.: Automated home-cage behavioral phenotyping of mice. Nat. Commun. 1(5), 1–9 (2010)
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs375/en/. Accessed 20 Aug 2017
Dube, S., Upadhyay, P.D., Tripathi, S.C.: Antifungal, physicochemical, and insect-repelling activity of the essential oil of Ocimumbasilicum. Can. J. Bot. 67(7), 2085–2087 (1989)
Umerie, S.C., Anaso, H.U., Anyasoro, L.J.C.: Insecticidal potentials of Ocimum basilicum leaf-extract. Bioresour. Technol. 64(3), 237–239 (1998)
Machraoui, A.N., Diouani, M.F., Ghrab, J., Sayadi, M.: Accurate detection and complete shape extraction of sand-flies using Gaussian mixture model. In: IEEE IPAS’14: International Image Processing Applications and Systems Conference. Hamamet, Tunisia (2014)
Dempster, A.P., Laird, N.M., Rubin, D.B.: Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. 39(1), 1–38 (1977). Series B
Kuhn, H.W.: The Hungarian method for the assignment problem. Naval Res. Log. Q. 2, 83–97 (1955)
Munkres, J.: Algorithms for the assignment and transportation problems. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 5(1), 32–38 (1957)
Beyan, C., Fisher, R.B.: Detection of Abnormal Tish Trajectories Using a Clustering Based Hierarchical Classifier. BMVC, Bristol (2013)
Bashir, F.I., Khokhar, A.A., Schonfeld, D.: View-invariant motion trajectory-based activity classification and recognition. Multimed. Syst. 12(1), 45–54 (2006)
Liwicki, M., Bunke, H., et al.: Hmm-based on line recognition of handwritten white board notes. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition (2006)
Beyan, C.: Detection of Unusual Fish Trajectories from Underwater Videos. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Edinburgh (2015)
Tlig, L., Sayadi, M., Fnaiech, F.: A new fuzzy segmentation approach based on SFCM type 2 using LBP-GCO features. Signal Process. Image Commun. 27, 694–708 (2012)
Zhang, G.P.: Neural networks for classification: a survey. IEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 30(4), 451–462 (2000)
Berbar, M.A.: Three robust features extraction approaches for facial gender classification. Vis. Comput. 30(1), 19–31 (2014)
Zanaty, E.A.: Support vector machines (SVMs) versus multilayer perception (MLP) in data classification. Egypt. Inf. J. 13(3), 177–183 (2012)
Munisami, T., Ramsum, M., Kishnah, S., Pudaruth, S.: Plant leaf recognition using shape features and colour histogram with K-nearest neighbors classifiers. Proc. Comput. Sci. 58, 740–747 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Tropsense Project, ref: 645 758, H2020-MSCA-2014 RISE Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machraoui, A.N., Diouani, M.F., Mouelhi, A. et al. Automatic identification and behavioral analysis of phlebotomine sand flies using trajectory features. Vis Comput 35, 721–738 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1506-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1506-x