Abstract
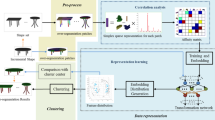
Unsupervised co-segmentation for a set of 3D shapes is a challenging problem as no prior information is provided. The accuracy of the current approaches is necessarily restricted by the accuracy of the unsupervised face classification, which is used to provide an initialization for the following optimization to improve the consistency between adjacent faces. However, it is exceedingly difficult to obtain a satisfactory initialization pre-segmentation owing to variation in topology and geometry of 3D shapes. In this study, we consider the unsupervised 3D shape co-segmentation as an exemplar-based clustering problem, aimed at simultaneously discovering optimal exemplars and obtaining co-segmentation results. Therefore, we introduce a novel exemplar-based clustering method based on affinity propagation for 3D shape co-segmentation, which can automatically identify representative exemplars and patterns in 3D shapes considering the high-order statistics, yielding consistent and accurate co-segmentation results. Experiments using various datasets, especially large sets with 200 or more shapes that would be challenging to manually segment, demonstrate that our method exhibits a better performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belongie, S., Malik, J., Puzicha, J.: Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts. IEEE TPAMI 24(4), 509–522 (2002)
Chaudhuri, S., Kalogerakis, E., Guibas, L., Koltun, V.: Probabilistic reasoning for assembly-based 3D modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 30(4), 35:1–35:10 (2011)
Chen, K., Xu, K., Yu, Y., Wang, T.Y., Hu, S.M.: Magic decorator: automatic material suggestion for indoor digital scenes. ACM Trans. Graph. 34(6), 232:1–232:11 (2015)
Chen, X., Golovinskiy, A., Funkhouser, T.: A benchmark for 3D mesh segmentation. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(3), 73:1–73:12 (2009)
Frey, B.J., Dueck, D.: Clustering by passing messages between data points. Science 315, 972–976 (2007)
Gal, R., Cohen-Or, D.: Salient geometric features for partial shape matching and similarity. ACM Trans. Graph. 25(1), 130–150 (2006)
Golovinskiy, A., Funkhouser, T.: Consistent segmentation of 3D models. Comput. Graph. 33(3), 262–269 (2009)
Hilaga, M., Shinagawa, Y., Kohmura, T., Kunii, T.L.: Topology matching for fully automatic similarity estimation of 3D shapes. In: Proceedings of SIGGRAPH, pp. 203–212 (2001)
Hu, R., Fan, L., Liu, L.: Co-segmentation of 3D shapes via subspace clustering. CGF 31(5), 1703–1713 (2012)
Huang, Q., Koltun, V., Guibas, L.: Joint shape segmentation with linear programming. ACM Trans. Graph. 30(6), 125:1–125:12 (2011)
Jain, S., Neal, R.: A split-merge Markov chain Monte Carlo procedure for the Dirichlet process mixture model. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 13, 158–182 (2000)
Johnson, A.E., Hebert, M.: Using spin images for efficient object recognition in cluttered 3D scenes. IEEE TPAMI 21(5), 433–449 (1999)
Kalogerakis, E., Averkiou, M., Maji, S., Chaudhuri, S.: 3D shape segmentation with projective convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2017)
Kalogerakis, E., Hertzmann, A., Singh, K.: Learning 3D mesh segmentation and labeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 29(4), 102:1–102:12 (2010)
Kim, V.G., Li, W., Mitra, N.J., Chaudhuri, S., DiVerdi, S., Funkhouser, T.: Learning part-based templates from large collections of 3D shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. 32(4), 70:1–70:12 (2013)
Kim, V.G., Lipman, Y., Funkhouser, T.: Blended intrinsic maps. ACM Trans. Graph. 30(4), 79:1–79:12 (2011)
Kohli, P., Pawan Kumar, M., Torr, P.H.S.: P3 & beyond: move making algorithms for solving higher order functions. IEEE TPAMI 31(9), 1645–56 (2009)
Krähenbühl, P., Koltun, V.: Efficient inference in fully connected CRFS with Gaussian edge potentials. CoRR arXiv:1210.5644 (2012)
Laga, H., Mortara, M., Spagnuolo, M.: Geometry and context for semantic correspondences and functionality recognition in man-made 3D shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. 32(5), 150:1–150:16 (2013)
Liu, R., Zhang, H., Shamir, A., Cohen-Or, D.: A part-aware surface metric for shape analysis. Comput. Graph. Forum 28(2), 397–406 (2009)
Luo, P., Wu, Z., Xia, C., Feng, L., Ma, T.: Co-segmentation of 3D shapes via multi-view spectral clustering. Vis. Comput. 29(6–8), 587–597 (2013)
Lv, J., Chen, X., Huang, J., Bao, H.: Semi-supervised mesh segmentation and labeling. CGF 31(7), 2241–2248 (2012)
MacQueen, J.: Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In: Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, pp. 281–297 (1967)
Shamir, A.: A survey on mesh segmentation techniques. CGF 27(6), 1539–1556 (2008)
Shao, T., Monszpart, A., Zheng, Y., Koo, B., Xu, W., Zhou, K., Mitra, N.J.: Imagining the unseen: stability-based cuboid arrangements for scene understanding. ACM Trans. Graph. 33(6), 209:1–209:11 (2014)
Shapira, L., Shalom, S., Shamir, A., Cohen-Or, D., Zhang, H.: Contextual part analogies in 3D objects. IJCV 89(2–3), 309–326 (2010)
Shi, J., Malik, J.: Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE TPAMI 22(8), 888–905 (2000)
Sidi, O., van Kaick, O., Kleiman, Y., Zhang, H., Cohen-Or, D.: Unsupervised co-segmentation of a set of shapes via descriptor-space spectral clustering. ACM Trans. Graph. 30(6), 126:1–126:10 (2011)
van Kaick, O., Tagliasacchi, A., Sidi, O., Zhang, H., Cohen-Or, D., Wolf, L., Hamarneh, G.: Prior knowledge for part correspondence. CGF 30(2), 553–562 (2011)
Wang, F., Huang, Q., Guibas, L.: Functional map networks for analyzing and exploring large shape collections. ACM Trans. Graph. 33(4), 36:1–37:11 (2014)
Wang, Y., Asafi, S., van Kaick, O., Zhang, H., Cohen-Or, D., Chen, B.: Active co-analysis of a set of shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. 31(6), 165 (2012)
Wang, Y., Gong, M., Wang, T., Cohen-Or, D., Zhang, H., Chen, B.: Projective analysis for 3D shape segmentation. ACM Trans. Graph. 32(6), 192:1–192:12 (2013)
Wu, Z., Wang, Y., Shou, R., Chen, B., Liu, X.: Unsupervised co-segmentation of 3D shapes via affinity aggregation spectral clustering. Comput. Graph. 37(6), 628–637 (2013)
Xie, Z., Xu, K., Liu, L., Xiong, Y.: 3D shape segmentation and labeling via extreme learning machine. CGF 33, 85–95 (2014)
Xu, K., Li, H., Zhang, H., Cohen-Or, D., Xiong, Y., Cheng, Z.Q.: Style-content separation by anisotropic part scales. ACM Trans. Graph. 29(6), 184:1–184:10 (2010)
Xu, K., Zhang, H., Cohen-Or, D., Chen, B.: Fit and diverse: set evolution for inspiring 3D shape galleries. ACM Trans. Graph. 31(4), 57:1–57:10 (2012)
Yang, Y., Xu, W., Guo, X., Zhou, K., Guo, B.: Boundary-aware multidomain subspace deformation. IEEE TVCG 19(10), 1633–1645 (2013)
Yu, Y., Zhou, K., Xu, D., Shi, X., Bao, H., Guo, B., Shum, H.Y.: Mesh editing with poisson-based gradient field manipulation. ACM TOG 23(3), 644–651 (2004)
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61502023) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1736217).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Zhou, B., Wang, Z. et al. Efficiently consistent affinity propagation for 3D shapes co-segmentation. Vis Comput 34, 997–1008 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1538-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1538-2