Abstract
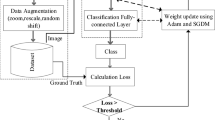
Sign language is a visual language used by persons with hearing and speech impairment to communicate through fingerspellings and body gestures. This paper proposes a framework for automatic sign language recognition without the need of hand segmentation. The proposed method first generates three different types of motion templates: motion history image, dynamic image and our proposed RGB motion image. These motion templates are used to fine-tune three ConvNets trained on ImageNet dataset. Fine-tuning avoids learning all the parameters from scratch, leading to faster network convergence even with a small number of training samples. For combining the output of three ConvNets, we propose a fusion technique based on Kernel-based extreme learning machine (KELM). The features extracted from the last fully connected layer of trained ConvNets are used to train three KELMs, and the final class label is predicted by averaging their scores. The proposed approach is validated on a number of publicly available sign language as well as human action recognition datasets, and state-of-the-art results are achieved. Finally, an Indian sign language dataset is also collected using a thermal camera. The experimental results obtained show that our ConvNet-based deep features along with proposed KELM-based fusion are robust for any type of human motion recognition.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This dataset can be downloaded from our website: https://www.iitr.ac.in/mvlab/research.html.
References
Ahad, M.A.R., Tan, J.K., Kim, H., Ishikawa, S.: Motion history image: its variants and applications. Mach. Vis. Appl. 23(2), 255–281 (2012)
Baraldi, L., Paci, F., Serra, G., Benini, L., Cucchiara, R.: Gesture recognition in ego-centric videos using dense trajectories and hand segmentation. In: IEEE CVPR (2014)
Bauer, B., Kraiss, K.F.: Video-based sign recognition using self-organizing subunits. In: IEEE ICPR, pp. 434–437 (2002)
Bi, L., Feng, D., Kim, J.: Dual-path adversarial learning for fully convolutional network (fcn)-based medical image segmentation. Vis. Comput. 34, 1–10 (2018)
Bilen, H., Fernando, B., Gavves, E., Vedaldi, A., Gould, S.: Dynamic image networks for action recognition. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 3034–3042 (2016)
Bobick, A.F., Davis, J.W.: The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23(3), 257–267 (2001)
Carreira, J., Zisserman, A.: Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 4724–4733 (2017)
Chen, C., Liu, K., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Real-time human action recognition based on depth motion maps. J. Real-Time Image Process. 23, 1–9 (2013)
Chen, C., Jafari, R., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Action recognition from depth sequences using depth motion maps-based local binary patterns. In: WACV, IEEE, pp. 1092–1099 (2015)
Choi, H., Park, H.: A hierarchical structure for gesture recognition using RGB-D sensor. In: ACM HAI, pp. 265–268 (2014)
Cirujeda, P., Binefa, X.: 4DCov: A nested covariance descriptor of spatio-temporal features for gesture recognition in depth sequences. In: IEEE 3DV, vol. 1, pp 657–664 (2014)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 248–255 (2009)
Donahue, J., Anne Hendricks, L., Guadarrama, S., Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan, S., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 2625–2634 (2015)
Dreuw, P., Deselaers, T., Keysers, D., Ney, H.: Modeling image variability in appearance-based gesture recognition. In: ECCVW, pp. 7–18 (2006)
Duan, J., Zhou, S., Wan, J., Guo, X., Li, S.Z.: Multi-modality fusion based on consensus-voting and 3D convolution for isolated gesture recognition (2016). arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.06689
Escalera, S., Baró, X., Gonzalez, J., Bautista, M.A., Madadi, M., Reyes, M., Ponce-López, V., Escalante, H.J., Shotton, J., Guyon, I.: Chalearn looking at people challenge 2014: dataset and results. In: ECCVW, pp. 459–473 (2014)
Feichtenhofer, C., Pinz, A., Zisserman: Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: IEEE CVPR (2016)
Gao, Z., Zhang, H., Liu, A.A., Xue, Yb, Xu, Gp: Human action recognition using pyramid histograms of oriented gradients and collaborative multi-task learning. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. (TIIS) 8(2), 483–503 (2014)
Gao, Z., Zhang, H., Xu, G., Xue, Y.: Multi-perspective and multi-modality joint representation and recognition model for 3D action recognition. Neurocomputing 151, 554–564 (2015)
Gao, Z., Zhang, H., Liu, A.A., Xu, G., Xue, Y.: Human action recognition on depth dataset. Neural Comput. Appl. 27(7), 2047–2054 (2016)
Geng, L., Ma, X., Wang, H., Gu, J., Li, Y.: Chinese sign language recognition with 3D hand motion trajectories and depth images. In: IEEE WCICA, pp. 1457–1461 (2014)
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 580–587 (2014)
Gogić, I., Manhart, M., Pandžić, I.S., Ahlberg, J.: Fast facial expression recognition using local binary features and shallow neural networks. Vis. Comput. 1–16 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1585-8
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Heilbron, F.C., Escorcia, V., Ghanem, B., Niebles, J.C.: Activitynet: a large-scale video benchmark for human activity understanding. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 961–970 (2015)
Howard, A.G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D., Wang, W., Weyand, T., Andreetto, M., Adam, H.: Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Weinberger, K.Q., van der Maaten, L.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: IEEE ICPR, vol. 1, p. 3 (2017)
Huang, G.B., Zhu, Q.Y., Siew, C.K.: Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1–3), 489–501 (2006)
Huang, G.B., Zhou, H., Ding, X., Zhang, R.: Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 42(2), 513–529 (2012)
Imran, J., Kumar, P.: Human action recognition using RGB-D sensor and deep convolutional neural networks. In: IEEE ICACCI, pp. 144–148 (2016)
Jiang, T., Zhang, Z., Yang, Y.: Modeling coverage with semantic embedding for image caption generation. Vis. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1565-z
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Li, X., Huang, H., Zhao, H., Wang, Y., Hu, M.: Learning a convolutional neural network for propagation-based stereo image segmentation. Vis. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1582-y
Lin, Y.C., Hu, M.C., Cheng, W.H., Hsieh, Y.H., Chen, H.M.: Human action recognition and retrieval using sole depth information. In: ACMMM, pp. 1053–1056 (2012)
Liu, H., Tian, L., Liu, M., Tang, H.: SDM-BSM: a fusing depth scheme for human action recognition. In: IEEE ICIP, pp. 4674–4678 (2015)
Liu, L., Shao, L.: Learning discriminative representations from RGB-D video data. IJCAI 1, 1493–1500 (2013)
Liu, M., Liu, H.: Depth context: a new descriptor for human activity recognition by using sole depth sequences. Neurocomputing 175, 747–758 (2016)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Ma, C., Wang, A., Chen, G., Xu, C.: Hand joints-based gesture recognition for noisy dataset using nested interval unscented Kalman filter with LSTM network. Vis. Comput. 34(6–8), 1053–1063 (2018)
Nishida, N., Nakayama, H.: Multimodal gesture recognition using multi-stream recurrent neural network. In: Springer PSIVT, pp. 682–694 (2015)
Pigou, L., Dieleman, S., Kindermans, P.J., Schrauwen, B.: Sign language recognition using convolutional neural networks. In: ECCVW, pp. 572–578 (2014)
Ronchetti, F., Quiroga, F., Estrebou, C.A., Lanzarini, L.C., Rosete, A.: LSA64: an Argentinian sign language dataset. In: CACIC (2016)
Shahroudy, A., Liu, J., Ng, T.T., Wang, G.: Ntu rgb+ d: A large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 1010–1019 (2016)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: NIPS, pp. 568–576 (2014a)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-image recognition. (2014b). arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556
Smola, A.J., Schölkopf, B.: A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 14(3), 199–222 (2004)
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., Rabinovich, A.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 1–9 (2015)
Tanwar, V.K., Buckchash, H., Raman, B., Bhargava, R.: Dense motion analysis of German finger spellings. Multimed. Tools Appl. 78, 1–26 (2018)
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 4489–4497 (2015)
Tung, P.T., Ngoc, L.Q.: Elliptical density shape model for hand gesture recognition. In: ACM SoICT, pp. 186–191 (2014)
Varol, G., Laptev, I., Schmid, C.: Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40, 1510–1517 (2017)
Wan, J., Zhao, Y., Zhou, S., Guyon, I., Escalera, S., Li, S.Z.: Chalearn looking at people RGB-D isolated and continuous datasets for gesture recognition. In: IEEE CVPRW, pp. 56–64 (2016)
Wang, H., Kläser, A., Schmid, C., Liu, C.L.: Action recognition by dense trajectories. In: IEEE CVPR, pp. 3169–3176 (2011)
Wang, P., Li, W., Gao, Z., Tang, C., Zhang, J., Ogunbona, P.: Convnets-based action recognition from depth maps through virtual cameras and pseudocoloring. In: ACMMM, pp. 1119–1122 (2015)
Wang, P., Li, W., Gao, Z., Zhang, J., Tang, C., Ogunbona, P.O.: Action recognition from depth maps using deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Hum.–Mach. Syst. 46(4), 498–509 (2016a)
Wang, P., Li, W., Liu, S., Gao, Z., Tang, C., Ogunbona, P.: Large-scale isolated gesture recognition using convolutional neural networks. In: IEEE ICPR, pp. 7–12 (2016b)
Yu, Z., Liu, Q., Liu, G.: Deeper cascaded peak-piloted network for weak expression recognition. Vis. Comput. 34, 1–9 (2017)
Zheng, J., Feng, Z., Xu, C., Hu, J., Ge, W.: Fusing shape and spatio-temporal features for depth-based dynamic hand gesture recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 76(20), 20525–20544 (2017)
Zhou, F., Hu, Y., Shen, X.: MSANet: multimodal self-augmentation and adversarial network for RGB-D object recognition. Vis. Comput. 1–12 (2018)
Zhu, G., Zhang, L., Shen, P., Song, J.: Multimodal gesture recognition using 3-D convolution and convolutional LSTM. IEEE Access 5, 4517–4524 (2017)
Funding
This project was funded by SMILE Project, IIT Roorkee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imran, J., Raman, B. Deep motion templates and extreme learning machine for sign language recognition. Vis Comput 36, 1233–1246 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01725-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01725-3