Abstract
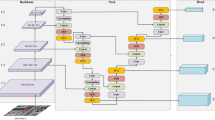
Visual tracking for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is a hot research topic for the wide applications of UAVs. As UAVs are high-altitude and high-freedom platforms, small targets in UAV tracking sequences are often under the attribute of large-scale location change due to the abrupt motion of the platform. Currently, many visual tracking methods based on the local search hypothesis have been widely researched on low-speed moving platforms. However, these methods cannot be directly used on the UAV platform, because targets will appear in any position of the new frame. To address this problem, we propose an abrupt-motion-aware visual tracking method in this paper. Because of the high power consumption of deep learning models, the proposed method is a lightweight tracker for small UAVs without the deep learning framework. Our method consists of three major components: abrupt motion estimation, object tracking and model updating. Abrupt motion often leads to abnormal changes in the response map of trackers. Thus, by analyzing the changes of tracking response maps, the abrupt motion can be detected efficiently. When abrupt motion happens, keypoint matching will be adaptively implemented to estimate the ego-motion and skipped otherwise. Then, the target location is predicted by the correlation filter tracker in a local search region. Moreover, according to the confidence analysis, an adaptive model update strategy is designed to alleviate the model noise caused by the short-term occlusion. Experimental results confirm the robustness and the accuracy of our method on challenging sequences and show the comparative performance of the proposed method against several state-of-the-art lightweight methods.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The proposed method focuses on visual tracking under the attribute of the abrupt motion, where two adjacent frames have enough point pairs for image registration.
References
Floreano, D., Wood, R.J.: Science, technology and the future of small autonomous drones. Nature 521(7553), 460–466 (2015)
Henriques, J.F., Caseiro, R., Martins, P., Batista, J.: High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(3), 583–596 (2015)
Avidan, Shai: Ensemble tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(2), 261–271 (2007)
Belagiannis, V., Schubert, F., Navab, N., Ilic, S.: Segmentation based particle filtering for real-time 2d object tracking. Comput. Vis. ECCV 2012, 842–855 (2012)
Liu, T., Wang, G., Wang, L., Chan, K.L.: Visual tracking via temporally smooth sparse coding. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(9), 1452–1456 (2015)
Xing, J., Gao, J., Li, B., Hu, W., Yan, S.: Robust object tracking with online multi-lifespan dictionary learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 665–672 (2013)
Lin, S.D., Lin, J.-J., Chuang, C.-Y.: Particle filter with occlusion handling for visual tracking. IET Image Process. 9(11), 959–968 (2015)
Hare, S., Golodetz, S., Saffari, A., Vineet, V., Cheng, M.-M., Hicks, S.L., Torr, P.H.S.: Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(10), 2096–2109 (2016)
Cheng, M., Zhang, Z., Lin, W.Y., Philip, T.: Bing: Binarized normed gradients for objectness estimation at 300fps. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3286–3293 (2014)
Zitnick, C.L., Dollár, P.: Edge boxes: Locating object proposals from edges. 8693, 391–405 (2014)
Fang, Z., Cao, Z., Xiao, Y., Zhu, L., Yuan, J.: Adobe boxes: locating object proposals using object adobes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(9), 4116–4128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2579311. ISSN 1057-7149
Zhu, G., Porikli, F., Li, H.: Beyond local search: tracking objects everywhere with instance-specific proposals. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 943–951 (2016)
Liang, P., Pang, Y., Liao, C., Mei, X., Ling, H.: Adaptive objectness for object tracking. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(7), 949–953 (2016)
Huang, D.: Enable scale and aspect ratio adaptability in visual tracking with detection proposals. In: British Machine Vision Conference (2015)
Danelljan, M., Häger, G., Khan, F.S., Felsberg, M.: Discriminative scale space tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(8), 1561–1575 (2017)
Ma, C., Yang, X., Zhang, C., Yang, M.-H.: Long-term correlation tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5388–5396, (2015)
Ma, C., Yang, X., Zhang, C., Yang, M.-H.: Long-term correlation tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5388–5396 (2015)
Liu, T., Wang, G., Yang, Q.: Real-time part-based visual tracking via adaptive correlation filters. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4902–4912 (2015)
Bolme, D.S., Beveridge, J.R., Draper, B.A., Lui, Y.M.: Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2544–2550. IEEE (2010)
Henriques, J.F., Caseiro, R., Martins, P., Batista, J.: Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 702–715. Springer (2012)
Wu, Y., Lim, J., Yang, M.-H.: Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(9), 1834–1848 (2015)
Danelljan, M., Hager, G., Shahbaz Khan, F., Felsberg, M.: Adaptive decontamination of the training set: a unified formulation for discriminative visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1430–1438 (2016)
Zitnick, C. L., Dollár, P.: Edge boxes: locating object proposals from edges. In: ECCV (2014)
Zhang, K., Li, X.Z., Zhang, J.X.: A robust point-matching algorithm for remote sensing image registration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 11(2), 469–473 (2014)
Wu, Y., Ma, W., Gong, M., Su, L., Jiao, L.: A novel point-matching algorithm based on fast sample consensus for image registration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 12(1), 43–47 (2017)
Fang, Z., Cao, Z., Xiao, Y.: Structured output tracking guided by keypoint matching. In: Electro-Optical Remote Sensing X, volume 9988, page 99880Y. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2016)
Grandvalet, Y., Bengio, Y.: Semi-supervised learning by entropy minimization. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp. 529–536 (2005)
Zhang, J., Ma, S., Sclaroff, S.: Meem: robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 188–203. Springer (2014)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
Rosten, E., Porter, R., Drummond, T.: Faster and better: a machine learning approach to corner detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(1), 105–119 (2010)
Bay, H., Ess, A., Tuytelaars, T., Van Gool, L.: Speeded-up robust features (surf). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 110(3), 346–359 (2008)
Fischler, M.A., Bolles, R.C.: Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 24(6), 381–395 (1981)
Bian, J., Lin, W.-Y., Matsushita, Y., Yeung, S.-K., Nguyen, T.-D., Cheng, M.-M.: Gms: grid-based motion statistics for fast, ultra-robust feature correspondence. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017)
Wang, M., Liu, Y., Huang, Z.: Large margin object tracking with circulant feature maps. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.05020 (2017)
Hare, S., Saffari, A., Torr, P.H.S : Efficient online structured output learning for keypoint-based object tracking. In 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1894–1901. IEEE (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work is jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61702182) and the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2018JJ3254).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, K., Cao, Z., Xiao, Y. et al. Abrupt-motion-aware lightweight visual tracking for unmanned aerial vehicles. Vis Comput 37, 371–383 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01805-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01805-9