Abstract
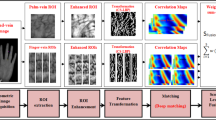
This paper addresses the problem of poor biometric recognition performance that is caused by greatly increased variations among the hand vein patterns of the same individuals as a result of using different imaging devices under different acquisition conditions and presents a novel solution based on two-stage coarse-to-fine matching. In particular, a global pattern descriptor is proposed as a geometrical reference for optimum image segmentation of vein patterns without significant over-segmentation and under-segmentation. In order to accommodate large cross-device variations, a control parameter is introduced to allow adjustment of segmented vein patterns, thereby enabling not only intra-class pattern similarities but also inter-class pattern dissimilarities to be increased. Furthermore, overlapping of principal vein patterns is proposed as a criterion for global coarse matching to reduce the number of candidates for identification, and distinctive efficient robust features are employed to provide a biological vision-based descriptor of salient local pattern characteristics for fine matching. Using a large dataset of 2000 cross-device hand vein images captured from two different near-infrared imaging devices and 100 hands, the efficacy of the proposed approach for a cross-device biometric system is demonstrated, with a recognition performance shown to be compatible to that of a single-device biometric system.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleites, F.C., Wang, H., Chen, S.C.: Enabling enriched TV shopping experience via computational and temporal aware view-centric multimedia abstraction[J]. IEEE Trans. Multimed 17(7), 1068–1080 (2015)
Wu, G., Kang, W.: Robust fingertip detection in a complex environment[J]. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 18, 1–1 (2016)
Tsai, T.J., Stolcke, A., Slaney, M.: A study of multimodal addressee detection in human-human-computer interaction[J]. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 17(9), 1550–1561 (2015)
Raja K B, Auksorius E, Raghavendra R, et al. Robust verification with subsurface fingerprint recognition using full field optical coherence tomography[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops. 2017: 144–152.
Ding, C., Tao, D.: Robust face recognition via multimodal deep face representation[J]. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 17(11), 2049–2058 (2015)
Jiang, J., Chen, C., Ma, J., et al.: SRLSP: a face image super-resolution algorithm using smooth regression with local structure prior[J]. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 19(1), 27–40 (2016)
Ramaiah, N., Kumar, A.: Toward more accurate iris recognition using cross-spectral matching[J]. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 99, 1–1 (2016)
Tan, C.W., Kumar, A.: Accurate iris recognition at a distance using stabilized iris encoding and Zernike moments phase features[J]. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(9), 3962–3974 (2014)
Zhang, L., Li, L., Li, H., et al.: 3D Ear identification using block-wise statistics based features and LC-KSVD[J]. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 18(8), 1–1 (2016)
Pan, Z., Wang, J., Shen, Z., et al.: Multi-layer convolutional features concatenation with semantic feature selector for vein recognition[J]. IEEE Access 7, 90608–90619 (2019)
Cross J M, Smith C L. Thermographic imaging of the subcutaneous vascular network of the back of the hand for biometric identification[C]// Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 1995 International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology, 1995. Proceedings. IEEE, 1995:20–35.
Wang, L., Leedham, G., Cho, S.Y.: Infrared imaging of hand vein patterns for biometric purposes[J]. Iet. Computer Vision 1, 113–122 (2007)
Kumar, A., Prathyusha, K.V.: Personal authentication using hand vein triangulation and knuckle shape[J]. IEEE Trans. Image Process. Publ. IEEE Signal Process. Soc. 18(9), 2127–2136 (2009)
Standring, S.: Gray’s anatomy, 39th edn. Elsevier Churchill Livingston, Edinburgh (2005)
Yan L, Zhang J, Pan J S, et al. Bilinear Feature Line Analysis for Face Recognition[C]// 2015 International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing (IIH-MSP). IEEE, 2015.
Si-Jung, R., Jun-Seuk, , G., et al.: Feature-based hand gesture recognition using an FMCW radar and its temporal feature analysis[J]. IEEE Sensors J 18, 7593–7602 (2018)
Khan, M.H.M., Subramanian, R.K., Khan, N.A.M.: Low dimensional representation of dorsal hand vein features using principle component analysis (PCA) [J]. Proc. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 37(1), 1091–1097 (2009)
Ojala, T., Pietikäinen, M., Mäenpää, T.: Multiresolution grayscale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns[J]. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 7(24), 971–987 (2002)
Lowe D G. Object Recognition from Local Scale-Invariant Features[C].IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 1999:1150.
Mo, D., Lai, Z., Wong, W.K.: Locally joint sparse marginal embedding for feature extraction[J]. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 21, 3038–3052 (2019)
Zhong, D., Shao, H., et al.: Towards application of dorsal hand vein recognition under uncontrolled environment based on biometric graph matching[J]. IET Biometr. 8, 159–167 (2019)
Dexing, Z., Huikai, Z., et al.: A hand-based multi-biometrics via deep hashing network and biometric graph matching[J]. Inf. Forensic. Secur. IEEE Trans. 14(12), 3140–3150 (2019)
Wang Y, Wang H. Gradient Based Image Segmentation for Vein Pattern[C]. International Conference on Computer Sciences and Convergence Information Technology. IEEE,2009:1614–1618
Weng, D., Wang, Y., Gong, M., et al.: DERF: distinctive efficient robust features from the biological modeling of the P ganglion cells [J]. IEEE Trans. Image Process. Publ. IEEE Signal Process. Soc. 24(8), 2287–2302 (2015)
Ding Y,Zhuang D,Wang K. A study of hand vein recognition method. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation,2005:2106–2110
Ohtsu, N.: A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 9(1), 62–66 (2007)
Niblack, W.: An introduction to image processing. Prentice-Hall (1986)
Sauvola, J., Pietikäinen, M.: Adaptive document image binarization[J]. Pattern Recogn. 33(2), 225–236 (2000)
Wang K,Guo Q,Zhuang D,et al. The Study of Hand Vein Image Processing Method[C]. Intelligent Control and Automation,2006. WCICA 2006. The Sixth World Congress on. IEEE,2006:10197–10201
Rodieck, R.W.: Quantitative analysis of cat retinal ganglion cell response to visual stimuli[J]. Vision. Res. 5(12), 583–601 (1965)
Daubechies, I., et al.: Ten lectures on wavelets, vol. 61. SIAM, Philadelphia (1992)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Fund Committee of China (NSFC no. 61673021).
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant 61,271,368.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Cao, X. & Miao, X. Cross-device recognition of dorsal hand vein images by two-stage coarse-to-fine matching. Vis Comput 38, 3595–3610 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02190-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02190-7