Abstract
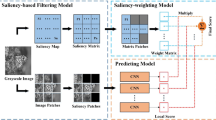
We propose a no-reference image quality assessment (NR-IQA) approach to predict the perceptual quality score of a given image without using any reference image. Our model consists of two steps and trains two similar convolutional neural networks (CNN) progressively. In order to consider the quality of different blocks in the whole picture, the first CNN takes the weighted average of the FR-IQA score of each patch and the differential mean opinion scores of the whole image as target output. The second CNN considers the interaction of the adjacent patches in an image. This paper not only uses visual saliency to address the importance of different patches, but also considers the spatial interaction of adjacent patches using Gaussian function. We compare the prediction results with several up-to-date proposed methods in six databases, and demonstrate the advance of our method. The source code can be found in https://github.com/busigushen/SCVS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, N., Saba, T., Khan, S., Mehmood, Z., Rehman, A., Tabasum, R.: Reduced reference image quality assessment technique based on dwt and path integral local binary patterns. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45(4), 3387–3401 (2020)
Abdul, R., Rehman, Z.: Reduced-reference image quality assessment by structural similarity estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(8), 3378–3389 (2012)
Ali, B., Sihite, D.N., Laurent, I.: Quantitative analysis of human-model agreement in visual saliency modeling: a comparative study. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(1), 55–69 (2013)
Anush Krishna, M., Alan Conrad, B.: Blind image quality assessment: from natural scene statistics to perceptual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(12), 3350–3364 (2011)
Bianco, S., Celona, L., Napoletano, P., Schettini, R.: On the use of deep learning for blind image quality assessment. SIViP 12(2), 355–362 (2018)
Cheon, M., Yoon, S.J., Kang, B., Lee, J.: Perceptual image quality assessment with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 433–442 (2021)
Fan, D.P., Li, T., Lin, Z., Ji, G.P., Zhang, D., Cheng, M.M., Fu, H., Shen, J.: Re-thinking co-salient object detection. IEEE Trans.Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2021)
Ghadiyaram, D., Bovik, A.: Massive online crowdsourced study of subjective and objective picture quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(1), 372–387 (2015)
Ghadiyaram, D., Bovik, A.C.: Perceptual quality prediction on authentically distorted images using a bag of features approach. J. Vis. 17(1), 32 (2017)
Harel, J., Koch, C., Perona, P.: Graph-based visual saliency. Proc. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 19, 545–552 (2006)
Hosu, V., Lin, H., Sziranyi, T., Saupe, D.: Koniq-10k: an ecologically valid database for deep learning of blind image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 4041–4056 (2020)
Hou, X., Zhang, L.: Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach. In: 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2007)
Huang, K., Gao, S.: Image saliency detection via multi-scale iterative cnn. Vis. Comput. 36(7), 1355–1367 (2020)
Huang, Z., Chen, H.X., Zhou, T., Yang, Y.Z., Wang, C.Y., Liu, B.Y.: Contrast-weighted dictionary learning based saliency detection for vhr optical remote sensing images. Pattern Recogn. 113, 107757 (2021)
Huang, Z., Liu, S.: Perceptual hashing with visual content understanding for reduced-reference screen content image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. (2020)
Itti, L., Koch, C., Niebur, E.: A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20(11), 1254–1259 (1998)
Jayaraman, D., Mittal, A., Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: Objective quality assessment of multiply distorted images. In: 2012 Conference Record of the Forty Sixth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), pp. 1693–1697 (2012)
Jie, L., Lian, Z., Jia, Y., Deng, D., Tao, Q., Xie, G.: No-reference image quality assessment using prewitt magnitude based on convolutional neural networks. Signal Image Video Process. 10(4), 609–616 (2016)
Joshi, P., Prakash, S., Rawat, S.: Continuous wavelet transform-based no-reference quality assessment of deblocked images. Vis. Comput. 34(12), 1739–1748 (2018)
Kang, L., Ye, P., Li, Y., Doermann, D.: Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1733–1740 (2014)
Kim, J., Hui, Z., Ghadiyaram, D., Lee, S., Lei, Z., Bovik, A.C.: Deep convolutional neural models for picture-quality prediction: challenges and solutions to data-driven image quality assessment. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 34(6), 130–141 (2017)
Kim, J., Lee, S.: Fully deep blind image quality predictor. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 11(1), 206–220 (2017)
Larson, E.C., Chandler, D.M.: Most apparent distortion: full-reference image quality assessment and the role of strategy. J. Electron. Imaging 19(1), 011006 (2010)
Lin, H., Hosu, V., Saupe, D.: Kadid-10k: A large-scale artificially distorted iqa database. In: 2019 Eleventh International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), pp. 1–3 (2019)
Lin, W., Kuo, C.C.J.: Perceptual visual quality metrics: a survey. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 22(4), 297–312 (2011)
Lin, Z., Gu, Z., Liu, X., Li, H., Lu, J.: Training quality-aware filters for no-reference image quality assessment. IEEE Multimed. 21(4), 67–75 (2014)
Lin, Z., Ying, S., Hongyu, L.: Vsi: a visual saliency-induced index for perceptual image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(10), 4270–4281 (2014)
Liu, T., Yuan, Z., Sun, J., Wang, J., Zheng, N., Tang, X., Shum, H.Y.: Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(2), 353–367 (2010)
Liu, X., van de Weijer, J., Bagdanov, A.D.: Rankiqa: Learning from rankings for no-reference image quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1040–1049 (2017)
Ma, K., Liu, W., Liu, T., Wang, Z., Tao, D.: dipiq: blind image quality assessment by learning-to-rank discriminable image pairs. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(8), 3951–3964 (2017)
Mittal, A., Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(12), 4695–4708 (2012)
Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: A two-step framework for constructing blind image quality indices. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(5), 513–516 (2010)
Ponomarenko, N., Jin, L., Ieremeiev, O., Lukin, V., Egiazarian, K., Astola, J., Vozel, B., Chehdi, K., Carli, M., Battisti, F.: Image database tid2013: peculiarities, results and perspectives. Signal Process. Image Commun. 30, 57–77 (2015)
Rezaie, F., Helfroush, M.S., Danyali, H.: No-reference image quality assessment using local binary pattern in the wavelet domain. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77(2), 1–13 (2017)
Saad, M.A., Bovik, A.C., Christophe, C.: Blind image quality assessment: a natural scene statistics approach in the dct domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(8), 3339 (2012)
Sheikh, H.R., Sabir, M.F., Bovik, A.C.: A statistical evaluation of recent full reference image quality assessment algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(11), 3440–3451 (2006)
Singh, V.K., Kumar, N.: Saliency bagging: a novel framework for robust salient object detection. Vis. Comput. 36(7), 1423–1441 (2020)
Su, S., Yan, Q., Zhu, Y., Zhang, C., Ge, X., Sun, J., Zhang, Y.: Blindly assess image quality in the wild guided by a self-adaptive hyper network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3667–3676 (2020)
Tang, H., Joshi, N., Kapoor, A.: Blind image quality assessment using semi-supervised rectifier networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2877–2884 (2014)
Xu, J.: Blind image quality assessment based on high order statistics aggregation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(9), 4444–4457 (2016)
Yang, S., Jiang, Q., Lin, W., Wang, Y.: Sgdnet: an end-to-end saliency-guided deep neural network for no-reference image quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1383–1391 (2019)
Ye, P., Doermann, D.: No-reference image quality assessment using visual codebooks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(7), 3129–3138 (2012)
Ye, P., Kumar, J., Kang, L., Doermann, D.: Unsupervised feature learning framework for no-reference image quality assessment. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1098–1105. IEEE (2012)
Ye, P., Kumar, J., Kang, L., Doermann, D.: Real-time no-reference image quality assessment based on filter learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 987–994 (2013)
Yildiz, Z.C., Oztireli, A.C., Capin, T.: A machine learning framework for full-reference 3d shape quality assessment. Vis. Comput. 36(1), 127–139 (2020)
Zhang, L., Gu, Z., Li, H.: Sdsp: a novel saliency detection method by combining simple priors. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 171–175. IEEE (2013)
Zhang, L., Zhang, L., Mou, X., Zhang, D.: Fsim: a feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(8), 2378–2386 (2011)
Zhang, W., Ma, K., Yan, J., Deng, D., Wang, Z.: Blind image quality assessment using a deep bilinear convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 1 (2019)
Zhou, T., Fan, D.P., Cheng, M.M., Shen, J., Shao, L.: Rgb-d salient object detection: a survey. In: Computational Visual Media, pp. 1–33 (2021)
Zhou, W., Alan Conrad, B., Hamid Rahim, S., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Zhu, H., Li, L., Wu, J., Dong, W., Shi, G.: Metaiqa: Deep meta-learning for no-reference image quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14143–14152 (2020)
Zhu, H., Li, L., Wu, J., Dong, W., Shi, G.: Generalizable no-reference image quality assessment via deep meta-learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. (2021)
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52075483).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Average PLCC,KROCC and RMSE results on KADID10k
Average PLCC,KROCC and RMSE results on KADID10k
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, J., Xiang, K. & Wang, X. SCVS: blind image quality assessment based on spatial correlation and visual saliency. Vis Comput 39, 443–458 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02340-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02340-x