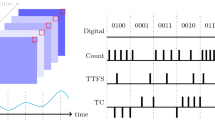
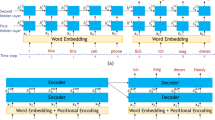
Abstract
The generation of informational sequences and their reorganization or reshaping is one of the most intriguing subjects for both neuroscience and the theory of autonomous intelligent systems. In spite of the diversity of sequential activities of sensory, motor, and cognitive neural systems, they have many similarities from the dynamical point of view. In this review we discus the ideas, models, and mathematical image of sequence generation and reshaping on different levels of the neural hierarchy, i.e., the role of a sensory network dynamics in the generation of a motor program (hunting swimming of marine mollusk Clione), olfactory dynamical coding, and sequential learning and decision making. Analysis of these phenomena is based on the winnerless competition principle. The considered models can be a basis for the design of biologically inspired autonomous intelligent systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott A, Tsay A (2000) Sequence analysis and optimal matching methods in sociology: review and prospect. Sociol Methods Res 29:3–33
Afraimovich V, Hsu S-B (2003) Lectures on Chaotic Dynamical Systems. AMS/IP Studies in Advanced Mathematics. American Mathematical Society, Somerville, MA
Afraimovich V, Zhigulin V, Rabinovich M (2004a) On the origin of reproducible sequential activity in neural circuits. Chaos 14:1123–1129
Afraimovich VS, Rabinovich MI, Varona P (2004b) Heteroclinic contours in neural ensembles and the winnerless competition principle. Int J Bifurcat Chaos 14:1195–1208
Anderson J (1995) An introduction to neural networks. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Ashby WR (1960) Design for a Brain, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Ashwin P, Borresen J (2005) Discrete computation using a perturbed heteroclinic network. Phys Lett A 347:208–214
Bapi R, Pammi VC, Miyapuram K, Ahmed (2005) Investigation of sequence processing: a cognitive and computational neuroscience perspective. Curr Sci 89:1690–1698
Barto AG, Flagg AH, Sitkoff N (1999) A cerebellar model of timing and prediction in the control of reaching. Neural Comput 11:565–594
Bazhenov M, Stopfer M, Rabinovich M, Huerta R, Abarbanel H, Sejnowski T, Laurent G (2001) Model of transient oscillatory synchronization in the locust antennal lobe. Neuron 30:307–309
Bischoff-Grethe A, Goedert KM, Willingham DT, Grafton ST (2004) Neural substrates of response-based sequence learning using fmri. J Cogn Neurosci 16(1):127–138
Busse F, Heikes K (1980) Convenction in a rotating layer: a simple cased of turbulence. Science 208:173–175
Clark D, Fairburn C (eds) (1997) Science and Practice of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Collins D, Wyeth G (1999) Cerebellar control of a line following robot. In: Proceedings of the Australian conference on robotics and automation (ACRA -9) pp 74-9
de Zeeuw CI, Simpson JI, Hoogenaraad CC, Galjart N, Koekkoek SKE, Ruigrok TJH (1998) Microcircuitry and function of the inferior olive. Trends Neurosci 21:391–400
Doboli S, Minai AA, Best P (2000) Latent attractors: a model for context-dependent place representations in the hippocampus. Neural Comput 12:1009–1043
Dominey PF (2005) From sensorimotor sequence to grammatical construction: evidence from simulation and neurophysiology. Adapt Behav 13(4):347–361
Doyon J, Song A, Karni A, Lalonde F, Adams M, Ungerleider L (2002) Experience-dependent changes in cerebellar contributions to motor sequence learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1017–1022
Fox M, Snyder A, Vincent J, Corbetta M, Essen DCV, Raichle M (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(27):9673–9678
Friedrich R, Laurent G (2002) Dynamic optimization of odor representations by slow temporal patterning of mitral cell activity. Science 291:889–894
Galan RF, Sachse S, Galizia CG, Herz AVM (2004) Odor-driven attractor dynamics in the antennal lobe allow for simple and rapid olfactory pattern classification. Neural Comput 16:999–1012
Giambra L (1995) A laboratory method for investigating influences on switching attention to task-unrelated imagery and thought. Conscious Cogn 4:1–21
Gigerenzer G, Todd PM (2000) Simple Heuristics That Make Us Smart. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Glickstein M (1993) Motor skills but not cognitive tasks. Trends Neurosci 16:450–451
Hazeltine E, Ivry R (2002) Can we teach the cerebellum new tricks?. Science 296:1979–1980
Hertz J, Palmer R, Krogh A (1991) Introduction to the theory of neural computation. Addison-Wesley, Redwood City, CA
Hikosaka Nakahara H, Rand MK, Sakai K, Lu X, Nakamura K, Miyachi S, Doya K (1999) Parallel neural networks for learning sequential procedures. Trends Neurosci 22:464–471
Hopfield JJ (1982) Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:2554–2558
Huerta R, Rabinovich MI (2004) Reproducible sequence generation in random neural ensembles. Phys Rev Lett 93:238104
Ito M (1982) Cerebellar control of the vestibulo-ocular reflex-around the flocculus hypothesis. Annu Rev Neurosci 5:275–296
Jefferys J, Traub R, Whittington M (1996) Neuronal networks for induced “0 hz”rhythms. Trends Neurosci 19:202-208
Kistler WM, de Zeeuw CI (2002) Dynamical working memory and timed responses: the role of reverberating loops in the olivo-cerebellar system. Neural Comput 14:2597-2626
Krupa M (1997) Robust heteroclinic cycles. J Nonlin Sci 7:129–176
Lashley K (1960) The problem of serial order in behavior. In: Beach FA, Hebb DO, Morgan CT, Nissen HW (eds) The Neuropsychology of Lashley. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 506–521
Laurent G, Stopfer M, Friedrich RW, Rabinovich MI, Abarbanel HDI (2001) Odor encoding as an active, dynamical process: experiments, computation, and theory. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:263–297
Lawrence M, Trappenberg TP, Fine A (2005) A multi-modular associator network for simple temporal sequence learning and generation. In: Proceedings of ESANN-5, Bruges, Belgium, April 2005, pp 423-28
Leibold C, Kempter R (2006) Memory capacity for sequences in a recurrent network with biological constrain. Neural Comput 18:904–941
Levi R, Varona P, Arshavsky YI, Rabinovich MI, Selverston AI (2004) Dual sensory-motor function for a molluskan statocyst network. J Neurophysiol 91:336–345
Levi R, Varona P, Arshavsky YI, Rabinovich MI, Selverston AI (2005) The role of sensory network dynamics in generating a motor program. J Neuroscience 25:9807–9815
Llinás R, Welsh JP (1993) On the cerebellum and motor learning. Curr Opin Neurobiol 3:958
Mazor O, Laurent G (2005) Transient dynamics versus fixed points in odor representations by locust antennal lobe projection neurons. Neuron 48:661–673
Mccoy AN, Platt ML (2005) Risk-sensitive neurons in macaque posterior cingulate cortex. Nat Neurosci 8:1220–1227
Melamed O, Gerstner W, Maas W, Tsodyks M, Markram H (2004) Coding and learning of behavioral sequences. Trends Neurosci 27:11–14
Miguel MS, Toral R (2001) In: Tirapegui E, Martinez J, Tiemann R (eds) Instabilities and Nonequilibrium Structures VI. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Nusbaum MP, Beenhakken MP (2002) A small-system approach to motor pattern generation. Nature 417:343–350
Oscarsson O (1980) Functional organization of olivary projection to cerebellar anterior lobe. In: Courville J, de Montigny C, Lamarre Y (eds) The inferior olivary nucleus. Raven, New York, pp 279–289
Panchin Y, Arshavsky Y, Deliagina T, Popova L, Orlovsky G (1995) Control of locomotion in marine mollusk clione limacina. IX. Neuronal mechanisms of spatial orientation. J Neurophysiol 73:1924–1937
Poldrack A, Packard MG (2003) Competition among multiple memory systems: converging evidence from animal and human brain studies. Neuropsychologia 41:245–251
Rabinovich M, Ezersky A, Weidman P (2000) The dynamics of patterns. World Scientific, Singapore
Rabinovich M, Huerta R, Varona P (2006a) Heteroclinic synchronization: ultra-subharmonic locking. Phys Rev Lett 96:0141001
Rabinovich M, Varona P, Selverston A, Abarbanel H (2006b) Dynamical principles in neuroscience. Rev Modern Phys 78(4):1213
Rabinovich M, Volkovskii A, Lecanda P, Huerta R, Abarbanel HDI, Laurent G (2001) Dynamical encoding by networks of competing neuron groups: winnerless competition. Phys Rev Lett 8706:U149–U151
Ramnani N (2006) The primate cortico-cerebellar system: anatomy and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:511–522
Rodriguez F, Huerta R (2004) Analysis of perfect mappings of the stimuli through neural temporal sequences. Neural Netw 17:963–973
Seliger P, Tsimring LS, Rabinovich MI (2003) Dynamics-based sequential memory: Winnerless competition of patterns. Phys Rev E 67:011905
Selverston A, Rabinovich M, Abarbanel H, Elson R, Szncs A, Pinto R, Huerta R, Varona P (2000) Reliable circuits from irregular neurons: a dynamical approach to unterstanding central pattern generators. J Physiol (Paris) 94:357–374
Shiv B, Loewenstein G, Bechara A, Damasio H, Damasio A (2005) Investment behavior and the negative side of emotion. Psychol Sci 16:435–439
Stone E, Holmes P (1990) Random perturbations of heteroclinic attractors. SIAM J Appl Math 50:726–743
Sun R, Giles CL (2001) Sequence learning: from recognition and prediction to sequential decision making. IEEE Intell Syst 16:67–70
Tanji J (2001) Sequential organization of multiple movements: involvement of cortical motor areas. Annu Rev Neurosci 24(1):631–651
Teasdale J, Dritschel B, Taylor M, Proctor L, Lloyd C, Nimmo-Smith I, Baddeley A (1995) Stimulus-independent thought depends on central executive resources. Mem Cognit 23(5):551–559
van der Smagt P (2000) Benchmarking cerebellar control. Robot Auton Syst 32:237–251
Varona P, Aguirre C, Torres JJ, Rabinovich MI, Abarbanel HDI (2002a) Spatiotemporal patterns of network activity in the inferior olive. Neurocomputing 44-6:685–690
Varona P, Rabinovich MI, Selverston AI, Arshavsky YI (2002b) Winnerless competition between sensory neurons generates chaos: a possible mechanism for molluscan hunting behavior. Chaos 12:672–677
Venaille A, Varona P, Rabinovich MI (2005) Synchronization and coordination of sequences in two neural ensembles. Phys Rev E 71:061909
Vida I, Bartos M, Jonas P (2006) Shunting inhibition improves robustness of gamma oscillations in hippocampal interneuron networks by homogenizing firing rates. Neuron 49:8–9
Voogd J, Glickstein M (1998) The anatomy of the cerebellum. Trends Neurosci 21(9):370–375
Wang L (2000) Heteroassociations of spatio temporal sequences with the bidirectional associative memory. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 11:1503–1505
Waugh F, Marcus C, Westervelt R (1990) Fixed-point attractors in analog neural computation. Phys Rev Lett 64:1986–1989
Willingham DB, Salidis J, Gabrieli JD (2002) Direct comparison of neural systems mediating conscious and unconscious skill learning. J Neurophysiol 88:2451–1460
Wilson HR, Cowan JD (1973) A mathematical theory of the functional dynamics of cortical and thalamic nervous tissue. Kybernetik 13:55–80
Wilson R, Turner G, Laurent G (2004) Transformation of olfactory representations in the drosophila antennal lobe. Science 303:366–370
Worgotter F, Porr B (2005) Temporal sequence learning, prediction, and control: a review of different models and their relation to biological mechanisms. Neural Comput 17(2):245–319
Yamauchi BM, Beer RD (1994) Sequential behavior and learning in evolved dynamical neural networks. Adapt Behav 2(3): 219–246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabinovich, M.I., Huerta, R., Varona, P. et al. Generation and reshaping of sequences in neural systems. Biol Cybern 95, 519–536 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-006-0121-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-006-0121-5