Abstract
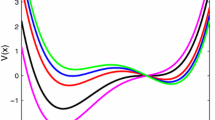
Spike-rate adaptation is investigated within a mean-field model of brain activity. Two different mechanisms of negative feedback are considered; one involving modulation of the mean firing threshold, and the other, modulation of the mean synaptic strength. Adaptation to a constant stimulus is shown to take place for both mechanisms, and limit-cycle oscillations in the firing rate corresponding to bursts of neuronal activity are investigated. These oscillations are found to result from a Hopf bifurcation when the equilibrium lies between the local maximum and local minimum of a given nullcline. Oscillations with amplitudes significantly below the maximum firing rate are found over a narrow range of possible equilibriums.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowitz M, Stegun IA (1970) Handbook of mathematical functions. Dover
Alligood KT, Sauer TD, Yorke JA (1996) Chaos: an introduction to dynamical systems. Springer, Heidelberg
Benda J, Herz AVM (2003) A universal model for spike-frequency adaptation. Neural Comp 15:2523
Benda J, Longtin A, Maler L (2005) Spike-frequency adaptation separates transient communication signals from background oscillations. J Neurosci 25:2312
Bressloff PC (2002) Bloch waves, periodic feature maps, and cortical pattern formation. Phys Rev Lett 89:088101
Freeman WJ (1975) Mass action in the nervous system. Academic, New York
Gollisch T, Herz AVM (2004) Input-driven components of spike- frequency adaptation can be unmasked in vivo. J Neurosci 24:7435
Jirsa VK, Haken H (1996) Field theory of electromagnetic brain activity. Phys Rev Lett 77:960
Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM (2000) Principals of neural science. McGraw-Hill, New York
Koch C (1999) Biophyics of computation. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Lehky SR (1988) An astable multivibrator model of binocular rivalry. Perception 17:215
Lorenzon NM, Foehring RC (1992) Relationship between repetitive firing and afterhyperpolarizations in human neocortical neurons. J Neurophys 67:350
Murray JD (1989) Mathematical biology. Springer, Heidelberg
Nunez PL (1974) The brain wave equation: a model for EEG. Math Biosci 21:279
Rennie CJ, Robinson PA, Wright JJ (1999) Effects of local feedback on dispersion of electrical waves in the cerebral cortex. Phys Rev E 59:3320
Rennie CJ, Robinson PA, Wright JJ (2002) Unified neurophysical model of EEG spectra and evoked potentials. Biol Cybern 86:457
Robinson PA (2006) Patchy propagators, brain dynamics, and the generation of spatially structured gamma oscillations. Phys Rev E 73:041904
Robinson PA, Rennie CJ, Rowe DL (2002) Dynamics of large-scale brain activity in normal arousal states and epileptic seizures. Phys Rev E 65:041924
Robinson PA, Rennie CJ, Rowe DL, O’Connor SC, Wright JJ, Gordon E, Whitehouse RW (2003) Neurophysical modeling of brain dynamics. Neuropsycopharm 28:S74
Robinson PA, Rennie CJ, Rowe DL, O’Connor SC (2004) Estimation of multiscale neurophysiological parameters by electroencephalographic means. Hum Brain Map 23:53
Robinson PA, Rennie CJ, Rowe DL, O’Connor SC, Gordon E (2005) Multiscale brain modelling. Phil Trans B 360:1043
Robinson PA, Rennie CJ, Wright JJ (1997) Propagation and stability of waves of electrical activity in the cerebral cortex. Phys Rev E 56:826
Sanchez-Vives MV, Nowak LG, McCormick DA (2000a) Membrane mechanisms underlying contrast adaptation in cat area 17 in vivo. J Neurosci 20:4267
Sanchez-Vives MV, Nowak LG, McCormick DA (2000b) Cellular mechanisms of long-lasting adaptation in visual cortical neurons in vitro. J Neurosci 20:4286
Stevens CF (1994) Large scale neuronal theories of the brain. In: Koch C, Davies JL (eds). MIT Press
van Rotterdam A, Lopes Da Silva FH, van den Ende J, Viergever MA, Hermans AJ (1982) A model of the spatial-temporal characteristics of the alpha rhythm. Bull Meth Biol 44:283
Wilson HR (1999) Spikes, decisions, and actions. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Wilson HR, Blake R, Lee S-H (2001) Dynamics of travelling waves in visual perception. Nature 412:907
Wilson HR, Cowan JD (1973) A mathematical theory for the functional dynamics of cortical and thalamic nervous tissue. Kybernetik 13:55
Wilson HR, Krupa B, Wilkinson F (2000) Dynamics of perceptual oscillations in form vision. Nature Neuro Sci 3:170
Wright JJ, Liley DTJ (1996) Dynamics of the brain at global and microscopic scales: neural networks and the EEG. Behav Brain Sci 19:285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loxley, P.N., Robinson, P.A. Spike-rate adaptation and neuronal bursting in a mean-field model of brain activity. Biol Cybern 97, 113–122 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-007-0157-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-007-0157-1