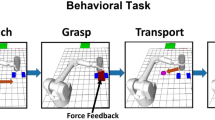
Abstract
Typical patterns of hand-joint covariation arising in the context of grasping actions enable one to provide simplified descriptions of these actions in terms of small sets of hand-joint parameters. The computational model of mirror mechanisms introduced here hypothesizes that mirror neurons are crucially involved in coding and making this simplified motor information available for both action recognition and control processes. In particular, grasping action recognition processes are modeled in terms of a visuo-motor loop enabling one to make iterated use of mirror-coded motor information. In simulation experiments concerning the classification of reach-to-grasp actions, mirror-coded information was found to simplify the processing of visual inputs and to improve action recognition results with respect to recognition procedures that are solely based on visual processing. The visuo-motor loop involved in action recognition is a distinctive feature of this model which is coherent with the direct matching hypothesis. Moreover, the visuo-motor loop sets the model introduced here apart from those computational models that identify mirror neuron activity in action observation with the final outcome of computational processes unidirectionally flowing from sensory (and usually visual) to motor systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbib MA (2005) From monkey-like action recognition to human language: An evolutionary framework for neurolinguistics. Behav Brain Sci 28(2): 105–124
Bishop CM (1995) Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Carr L, Iacoboni M, Dubeau MC, Mazziotta JC, Lenzi GL (2003) Neural mechanisms of empathy in humans: a relay from neural systems for imitation to limbic areas. PNAS 100(9): 5497–5502
Cattaneo L, Rizzolatti G (2009) The mirror neuron system. Arch Neurol 66(5): 557–560
Craighero L, Bello A, Fadiga L, Rizzolatti G (2002) Hand action preparation influences the responses to hand pictures. Neuropsychologia 40(5): 492–502
Fleischer F, Casile A, Giese MA (2009) View-independent recognition of grasping actions with a cortex-inspired model. In: 9th IEEE-RAS international conference on humanoid robots, pp 514–519
Fogassi L, Gallese V, Buccino G, Craighero L, Fadiga L, Rizzolatti G (2001) Cortical mechanism for the visual guidance of hand grasping movements in the monkey. a reversible inactivation study. Brain 124: 571–586
Friston K (2005) A theory of cortical responses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 360(1456): 815–836
Fritsch C (2007) Predictive coding: an account of the mirror neuron system. Cognitive Processing 8: 159–166
Gallese V, Goldman A (1998) Mirror neurons and the simulation theory of mind-reading. Trends Cognitive Sci 2(12): 493–501
Gallese V, Fadiga L, Fogassi L, Rizzolatti G (1996) Action recognition in the premotor cortex. Brain 119: 593–609
Gibson JJ (1979) The ecological approach to visual perception. Houghton Mifflin, Boston
Haruno M, Wolpert DM, Kawato M (2001) Mosaic model for sensorimotor learning and control. Neural Comput 13(10): 2201–2220
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman JH (2003) The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction, corrected edn. Springer
Iberall T, Fagg AH (1996) Neural network models for selecting hand shapes. In: Wing AM, Haggard P, Flanagan JR (eds) Hand and brain: neurophysiology and psychology of hand movements. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 243–264
Iberall T, Bingham G, Arbib MA (1986) Opposition space as a structuring concept for the analysis of skilled hand movements, vol 15. In: Heuer H, Fromm C (eds) Generation and modulation of action patterns. Springer, Berlin, pp 158–173
Ito M, Tani J (2004) Generalization in learning multiple temporal patterns using RNNPB. In: ICONIP: International conference on neural information processing, pp 592–598
Keysers C, Perrett DI (2004) Demystifying social cognition: a hebbian perspective. Trends Cogn Sci 8(11): 501–507
Krzanowski WJ (1979) Between-groups comparison of principal components. J Am Stat Assoc 74(367): 703–707
Mason CR, Gomez JE, Ebner TJ (2001) Hand synergies during reach-to-grasp. J Neurophysiol 86(6): 2896–2910
Matelli M, Luppino G (2001) Parietofrontal circuits for action and space perception in the macaque monkey. NeuroImage 14: S27–S32
Miall RC (2003) Connecting mirror neurons and forward models. Neuroreport 14(17): 2135–2137
Napier JR (1956) The prehensile movements of the human hand. J Bone Joint Surg 38B: 902–913
Oztop E, Arbib MA (2002) Schema design and implementation of the grasp-related mirror neuron system. Biol Cybernet 87: 116–140
Oztop E, Wolpert DM, Kawato M (2005) Mental state inference using visual control parameters. Cogn Brain Res 22(2): 129–151
Oztop E, Kawato M, Arbib MA (2006) Mirror neurons and imitation: a computationally guided review. Neural Netw 19: 254–271
Perrett DI, Harries MH, Bevan R, Thomas S, Benson PJ, Mistlin AJ, Chitty AJ, Hietanen JK, Ortega JE (1989) Frameworks of analysis for the neural representation of animate objects and actions. J exp Biol 146: 87–113
Prevete R, Tessitore G, Santoro M, Catanzariti E (2008) A connectionist architecture for view-independent grip-aperture computation. Brain Res 1225: 133–145
Prevete R, Tessitore G, Catanzariti E, Tamburrini G (2010) Perceiving affordances: a computational investigation of grasping affordances. Cogn Syst Res. doi:10.1016/j.cogsys.2010.07.005
Rizzolatti G, Craighero L (2004) The mirror-neuron system. Ann Rev Neurosci 27: 169–192
Rizzolatti G, Sinigaglia C (2010) The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit: interpretations and misinterpretations. Nat Rev Neurosci 11: 264–274
Rizzolatti G, Fadiga L, Gallese V, Fogassi L (1996) Premotor cortex and the recognition of motor actions. Cogn Brain Res 3(2): 131–141
Rizzolatti G, Fogassi L, Gallese V (2001) Neurophysiological mechanisms underlying the understanding and imitation of action. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(9): 661–670
Santello M, Flanders M, Soechting JF (2002) Patterns of hand motion during grasping and the influence of sensory guidance. J Neurosci 22(4): 1426–1435
Tessitore G, Borriello M, Prevete R, Tamburrini G (2009) How direct is perception of affordances? A computational investigation of grasping affordances. In: Howes RC, Peebles D (eds) 9th international conference on cognitive modeling—ICCM2009, Manchester, UK
Umilta’ M, Kohler E, Gallese V, Fogassi L, Keysers C, Rizzolatti G (2001) I know what you are doing: a neurophysiological study. Neuron 31(19): 155–165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tessitore, G., Prevete, R., Catanzariti, E. et al. From motor to sensory processing in mirror neuron computational modelling. Biol Cybern 103, 471–485 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-010-0415-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-010-0415-5