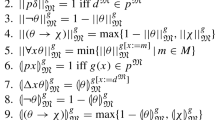Abstract
We survey complexity results concerning a family of propositional many-valued logics. In particular, we shall address satisfiability and tautologousness problems for Hájek's Basic Logic BL and for several of its schematic extensions. We shall review complexity bounds obtained from functional representation results, as well as techniques for dealing with non-trivial ordinal sums of continuous t-norms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglianò P, Montagna F (2003) Varieties of BL-algebras I: general properties. J Pure Appl Algebra 181:105–129
Aguzzoli S (1998) Geometric and proof–theoretic issues in Łukasiewicz propositional logics. PhD Thesis, University of Siena, Italy
Aguzzoli S, Ciabattoni A (2000) Finiteness in infinite-valued Łukasiewicz logic. J Logic Lang Inf 9:5–29
Aguzzoli S, Gerla B (2002) Finite-valued reductions of infinite-valued logics. Arch Math Logic 41:361–399
Aguzzoli S, Gerla B (2002) On countermodels in basic logic. Neural Netw World 12:407–420
Baaz M, Hájek P, Krajíček J, švejda D (1998) Embedding logics into product logic. Studia Logica 61:35–42
Baaz M, Hájek P, Montagna F, Veith H (2002) Complexity of t-tautologies. Ann Pure Appl Logic 113:3–11
Burris S, Sankappanavar HP (1981) A course in universal algebra, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Cignoli R, D'Ottaviano IML, Mundici D (2000) Algebraic foundations of many-valued reasoning, trends in logic, vol 7. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Cignoli R, Esteva F, Godo L, Torrens A (2000) Basic logic is the logic of continuous t-norms and their residua. Soft Comput 4:106–112
Cintula P, Gerla B Semi-normal forms and functional representation of product fuzzy logic. Fuzzy Sets Syst (to appear)
Esteva F, Godo L, Hájek P, Navara M (2000) Residuated fuzzy logics with an involutive negation. Arch Math Logic 39:106–112
Esteva F, Godo L, Montagna F (2003) Equational characterization of the subvarieties of BL generated by t-norm algebras, (preprint)
Ewald G (1996) Combinatorial convexity and algebraic geometry, graduate texts in mathematics. vol 168 Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Gerla B (2000) A note on functions associated with Gödel formulas. Soft Comput 4:206–209
Gerla B (2000) Functional representation of many-valued logics based on continuous t-norms. PhD Thesis, University of Milano, Italy
Gödel K (1933) Zum intuitionistischen Aussagenkalkül, Anzeiger Akademie der Wissenschaften Wien, Math.-naturwissensch. Klasse 69, (1932), 65–66. Also in Ergebnisse eines matematischen Kolloquiums 4:40
Hähnle R (1993) Automated deduction in multiple-valued logics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hähnle R (1994) Many-valued logic and mixed integer programming. Ann Math Artif Intell 12:231–264
Hähnle R (1997) Proof theory of many-valued logic – linear optimization – logic design: connections and interactions. Soft Comput 1:107–119
Hájek P (1998) Metamathematics of fuzzy logic. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Hájek P (1998) Basic fuzzy logic and BL-algebras. Soft Comput 2:124–128
Haniková Z (2001) Standard algebras for fuzzy propositional calculi. Fuzzy Sets Syst 124:309–320
Haniková Z (2002) A note on the complexity of propositional tautologies of individual t-algebras. Neural Netw World 12:453–460
Haniková Z (2003) Mathematical and metamathematical properties of fuzzy logic. PhD Thesis, Charles University in Prague
McNaughton R (1951) A theorem about infinite-valued sentential logic. J Symbolic Logic 16:1–13
Montagna F (2000) The free BL-algebra on one generator. Neural Netw World 5:837–844
Montagna F (2001) Free BLΔ Algebras. In: Antonio Di Nola, Giangiacomo Gerla (eds) Lectures on soft computing and fuzzy logic, pp 159–171
Mostert PS, Shields AL (1957) On the structure of semigroups on a compact manifold with boundary. Ann Math 65:117–143
Mundici D (1987) Satisfiability in many-valued sentential logic is NP-complete. Theor Comput Sci 52:145–153
Mundici D (1994) A constructive proof of McNaughton's theorem in infinite-valued logics. J Symbolic Logic 59:596–602
Novák V, Perfilieva I, Močkoř J (1999) Mathematical principles of fuzzy logic. Kluwer, Boston/Dordrecht/London
Rose A, Rosser JB (1958) Fragments of many-valued statement calculi. Trans Am Math Soc 87:1–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguzzoli, S., Gerla, B. & Haniková, Z. Complexity issues in basic logic. Soft Comput 9, 919–934 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-004-0443-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-004-0443-y