Abstract
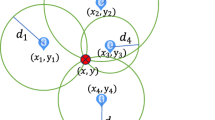
Location awareness is the key capability of mobile computing applications. Despite high demand, indoor location technologies have not become truly ubiquitous mainly due to their requirements of costly infrastructure and dedicated hardware components. Received signal strength (RSS) based location systems are poised to realize economical ubiquity as well as sufficient accuracy for variety of applications. Nevertheless high resolution RSS based location awareness requires tedious sensor data collection and training of classifier which lengthens location system development life cycle. We present a rapid development approach based on online and incremental learning method which significantly reduces development time while providing competitive accuracy in comparison with other methods. ConSelFAM (Context-aware, Self-scaling Fuzzy ArtMap) extends the Fuzzy ArtMap neural network system. It enables on the fly expansion and reconstruction of location systems which is not possible in previous systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad U (2007) CompoNet: programmatically embedding neural networks into AI applications as software components. 19th IEEE international conference on tools with artificial intelligence, October 29–31, Patras, Greec
Ahmad U et al (2006) Modular multilayer perceptron for WLAN based localization. IEEE international joint conference on neural networks. Vancouver, Canada
Andrew et al. (2002) Using wireless ethernet for localization, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems
Bahl P et al (2000) RADAR: an in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. In: IEEE INFOCOM 2000, pp 775–784
Battiti R et al (2002) Neural network model for intelligent networks: deriving the location from signal patterns, the first annual symposium on autonomous intelligent networks and systems
Carpenter GA, Grossberg S and Rosen DB (1991). Fuzzy ART: fast stable learning and categorization of analog patterns by an adaptive resonance system. Neural Netw 4: 759–771
Carpenter GA and Grossberg S (1992). Fuzzy ARTMAP: a neural network architecture for incremental supervised learning of analog multidimensional maps. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 3: 698–713
CompoNet, Componentization of Neural Networks, http://sourceforge.net/projects/componet/
Hagan MT and Menhaj M (1994). Training feedforward networks with the Marquardt algorithm. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5(6): 989–993
Iqbal M et al (2005) Reflective middleware for location-aware application adaptation. Computational science and its applications (LNCS), pp 1045–1054
John K et al (2003) Minimizing calibration effort for an indoor 802.11 device location measurement system. Technical Report, MSR-TR-2003-82 Microsoft Research, November 13
Kohonen T (1995). Learning vector quantization, The handbook of brain theory and neural networks. MIT Press, Cambridge, 537–540
LaMarca A (2005). Place Lab: device positioning using radio beacons in the wild. Pervasive 3468: 116–133
Li B (2005). Method for yielding a database of location fingerprints in WLAN. IEE Proc Commun 152(5): 580–586
Moore B (1988) ART and pattern clustering. In: Proceedings of the 1988 connectionist models summer school, pp 174–183
Nasir U et al (2005) On building a reflective middleware service for location-awareness. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE international conference on embedded and real-time computing systems and applications, pp 439–442
Ogawa T, Yoshino S, Shimizu M (2003) Location determination method for wireless systems based on learning vector quantization. NTT Network Innovation Laboratories, vol 1, no. 9, Japan
Pehlavan K et al (2002) Indoor geolocation science and technology. IEEE Commun Mag 40(2):112–118
Serrano-Gotarredona MT, Linares-Berranco B and Andreaou AG (2005). Adaptive resonance theory microchips-circuit design techniques. Springer, Heidelberg
Smailagic A et al (2001) Location sensing and privacy in a context aware computing environment. Pervasive Comput. IEEE Wireless Communications, October 2002, vol 9(5). pp 10–17
Xuanlong N et al (2005) A kernel-based learning approach to AdHoc sensor network localization. ACM Trans Sensor Netw (TOSN) 1(1):134–152. ISSN:1550-4859
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, U., Gavrilov, A.V., Lee, YK. et al. Context-aware, self-scaling Fuzzy ArtMap for received signal strength based location systems. Soft Comput 12, 699–713 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-007-0243-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-007-0243-2