Abstract
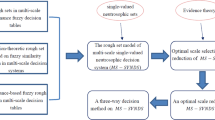
Emergency decision making is still an important issue in unconventional emergency management research. Although many studies have been written on this topic, they remain political and qualitative, and it is difficult to make them operational in practice. Therefore, this article proposes a decision-theoretic rough set over two universes as an approach for solving this difficulty. The proposed approach integrates rough set theory over two universes using a Bayesian decision-making technique. In this study, emergency decision making is considered as a multiple-criteria ranking or multiple-criteria selection problem with multi-granularity linguistic assessment information. A Bayesian decision process based on linguistic description with qualitative data over two universes is first presented to construct the decision model and approach, and then the decision-theoretic rough set theory over two universes is taken to induce a set of decision rules that satisfy minimum risk of loss conditions. These rules can easily give the optimal decision results with minimum risk of loss by considering online information, realistic scenarios, and the dynamic characteristic of unconventional emergency events as they develop. Finally, the steps and the basic principle of the proposed method are illustrated by a numerical example with the background of emergency decision making.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbarosoglu G, Arda Y (2004) A two-stage stochastic programming framework for transportation planning in diaster response. J Op Res Soc 55(1):43–53
Cosgrave J (1996) Decision making in emergencies. Disaster Prev Manag 5:28–35
Chen X, Wang Y, Wu LY, Yan GY, Zhu W (2010) The model of emergency decision-making with multi-stage multi-object and multi-agent. Syst Eng Theory Pract 30(11):1977–1985
Chen CH, Hwang CH (1992) Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making. Springer, Berlin
Fan WC (2007) Advisement and suggestion to scientific problems of emergency management for public incidents. Bull Natl Nat Sci Found China 2:71–76
Forster MR (2000) Key concepts in model selection: performance and generalizability. J Math Psychol 44:205–231
Good IJ (1965) The estimation of probabilities: an essay on modern Bayesian methods. MIT Press, Cambridge
Greco S, Slowinski R, Yao YY (2007) Bayesian decision theory for dominance-based rough set approach. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on rough sets and knowledge technology, RSKT’07
Goudey R (2007) Do statistical inferences allowing three alternative decision give better feedback for environmentally precautionary decision-making. J Environ Manag 85:338–344
Hector TD, Maria EM, Sunarin C, Laura AM (2013) Joint location and dispatching decisions for emergency medical services. Comput Ind Eng 64:917–928
Herbert JP, Yao JT (2011) Game-theoretic rough set. Fundamenta Informaticae 108:267–286
Ju YB, Wang AH (2012) Emergency alternative evaluation under group decision makers: a method of incorporating DS/AHP with extended TOPSIS. Expert Syst Appl 39:1315–1323
Jiang YP, Fan ZP, Su MM (2011) Study on the dynamic adjusting method for emergency decision. Chin J Manag Sci 19(5):104–108
Jia XY, Tang ZM, Liao WH, Shang L (2014) On an optimization representation of decision-theoretic rough set model. Int J Approx Reason 55(1):156–166
Keeneyr L, Raiffa H (1993) Decision with multiple objectives: preferences and value tradeoffs. Cambridge University Press, New York
Levy JK, Taji K (2007) Group decision support for hazards planning and emergency management: a group analytic network process (GANP) approach. Math Comput Model 46:906–917
Liu D, Yao YY, Li TR (2011) Three-way investment decisions with decision-theoretic rough sets. Int J Comput Intell Syst 4(1):66–74
Li HX, Zhou XZ (2011) Risk decision making based on decision-theoretic rough set: a multi-view decision model. Int J Comput Intell Syst 4(1):1–11
Li TJ (2008) Rough approximation operators on two universes of discourse and their fuzzy extensions. Fuzzy Sets Syst 159:3033–3050
Li YF, Zhang CQ, Swanb JR (2000) An information filtering model on the web and its application in job agent. Knowl Based Syst 13:285–296
Liang DC, Liu D, Pedrycz W, Hu P (2013) Triangular fuzzy decision-theoretic rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 54:1087–1106
Lingras P, Chen M, Miao DQ (2009) Rough cluster quality index based on decision theory. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 21(7):1014–1026
Liu GL (2010) Rough set theory based on two universal sets and its applications. Knowl Based Syst 23(2):110–115
Ma WM, Sun BZ (2012a) Probabilistic rough set over two universes and rough entropy. Int J Approx Reason 53:608–619
Ma WM, Sun BZ (2012b) On relationship between probabilistic rough set and Bayesian risk decision over two universes. Int J Gen Syst 41(3):225–245
Mendonca D, Beroggi G, Van GD, Wallace WA (2006) Designing gaming simulations for the assessment of group decision support systems in emergency response. Safety Sci 44:523–535
Marinoff L (2007) The middle way, finding happiness in a world of extremes. Sterling, New York
Ngueveu SU, Prins C, Calvo RW (2010) An effective mimetic algorithm for the cumulative capacitated vehicle routing problem. Comput Op Res 37(11):1877–1885
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Pawlak Z (1991) Rough sets: theoretical aspects of reasoning about data. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Pawlak Z, Grzymala-Busse JW, Slowinski R, Ziarko W (1995) Rough sets. Commun ACM 38(11):88–95
Pauker SG, Kassirer JP (1980) The threshold approach to clinical decision making. N Engl J Med 302:1109–1117
Pawlak Z, Skowron A (2007) Rough sets: some extensions. Inf Sci 177:28–40
Pauwels N, Van DE, Walle B, Hardeman F, Soudan K (2000) The implications of irreversibility in emergency response. Theory Decis 49(1):25–51
Shafer G (1987) Belief functions and possibility measures. In: Proceedings of analysis of fuzzy information, vol 1. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 51–84
Sun BZ, Ma WM (2011) Fuzzy rough set model on two different universes and its application. Appl Math Model 35(4):1798–1809
Sun BZ, Ma WM, Liu Q (2013a) An approach to decision making based on intuitionistic fuzzy rough set over two universes. J Op Res Soc 64(7):1079–1089
Sun BZ, Ma WM, Zhao HY (2013b) A fuzzy rough set approach to emergency material demand prediction over two universes. Appl Math Model 37:7062–7070
Sun BZ, Ma WM, Zhao HY (2012) Decision-theoretic rough set model over two universes for emergency decision-making. In: Proceeding of the 10th conference on uncertainty system and the 14th conference on information and management of China, Yinchuan, July, pp 35–43
Schechter CB (1988) Sequential analysis in a Bayesian model of diastolic blood pressure measurement. Med Decis Mak 8:191–196
Wong SKM, Wang LS, Yao YY (1993a) On modeling uncertainty with interval structures. Comput Intell 11:406–426
Wong SKM, Wang LS, Yao YY (1993b) Interval structures: a framework for representing uncertain information. In: Proceedings of 8th conference on uncertainty artificial intelligent, pp 336–343
Xu ZS (2004) Methodology of uncertainty decision-making and its application. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing
Yu LA, Lai KK (2011) A distance-based group decision-making methodology for multi-person multi-criteria emergency decision support. Decis Support Syst 51:307–315
Yao YY, Wong SKM, Lingras PJ (1990a) A decision-theoretic rough set model. In: Proceedings of the 5th international symposium on methodologies for intelligent systems
Yao YY, Wong SKM, Lingras PJ (1990b) A decision-theoretic rough set model. Methodol Intell Syst 5:17–24
Yao YY, Wong SKM (1992) A decision theoretic framework for approximating concepts. Int J Man-Mach Stud 37:793–809
Yao YY, Wong SKM, Wang LS (1995) A non-numeric approach to uncertain reasoning. Int J Gen Syst 23:343–359
Yao YY (2003) Probabilistic approaches to rough sets. Expert Syst 20:287–297
Yao YY (2008) Probabilistic rough set approximation. Int J Approx Reason 49:255–271
Yao YY (2012) An outline of a theory of three-way decisions. In: Proceedings of RSCTC2012, vol 7413. LNCS (LNAI) pp 1–17
Yuan H (1996) Research on unconventional emergency crisis and its emergency decision-making. Res Explor 2:1–4
Yang WG, Huang J, Chi H, Qi ML (2007) The study on the choosing emergency plan problem with incomplete information. Chin J Manag Sci 15(z1):729–732
Yan RX, Zheng JG, Liu JF, Zhai YM (2010) Research on the model of rough set over dual-universes. Knowl Based Syst 23:817–822
Yang HL, Li SG, Wang SY, Wang J (2012) Bipolar fuzzy rough set model on two different universes and its application. Knowl Based Syst 35:94–101
Zografos KG, Vasilakis GM, Giannouli IM (2000) Methodological framework for developing decision support systems (DSS) for hazardous materials emergency response operations. J Hazard Mater 71:503–521
Ziarko W (1993) Variable precision rough sets model. J Comput Syst Sci 46(1):39–59
Zhang WX, Wu WZ (2000) Rough set models based on random sets (I). J Xi’an Jiaotong Univ 12:75–79
Zhang HY, Zhang WX, Wu WZ (2009) On characterization of generalized interval-valued fuzzy rough sets on two universes of discourse. Int J Approx Reason 51(1):56–70
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the Editor Prof. Marek Reformat, and the two anonymous referees for their thoughtful comments and valuable suggestions. The work was partly supported by the National Science Foundation of China (71161016, 71071113), the National Science Foundation of Gansu Province of China (1308RJYA020), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Xidian University (JB150605).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, B., Ma, W. & Zhao, H. An approach to emergency decision making based on decision-theoretic rough set over two universes. Soft Comput 20, 3617–3628 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1721-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1721-6