Abstract
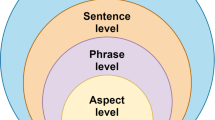
Sentiment analysis in text mining is a challenging task. Sentiment is subtly reflected by the tone and affective content of a writer’s words. Conventional text mining techniques, which are based on keyword frequencies, usually run short of accurately detecting such subjective information implied in the text. In this paper, we evaluate several popular classification algorithms, along with three filtering schemes. The filtering schemes progressively shrink the original dataset with respect to the contextual polarity and frequent terms of a document. We call this approach “hierarchical classification”. The effects of the approach in different combination of classification algorithms and filtering schemes are discussed over three sets of controversial online news articles where binary and multi-class classifications are applied. Meanwhile we use two methods to test this hierarchical classification model, and also have a comparison of the two methods.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal R, Rajagopalan S, Srikant R, Xu Y (2003) Mining newsgroups using networks arising from social behavior. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on World Wide Web. ACM, pp 529–535
Argamon S, Bloom K, Esuli A, Sebastiani F (2009) Automatically determining attitude type and force for sentiment analysis. Human Language Technology. Challenges of the Information Society. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 218–231
Cerini S, Compagnoni V, Demontis A, Formentelli M, Gandini G (2007) Language resources and linguistic theory: typology, second language acquisition, English linguistics (Forthcoming), chapter Micro-WNOp: A gold standard for the evaluation of automatically compiled lexical resources for opinion mining. Franco Angeli Editore, Milan
Chaovalit P, Zhou L (2005) Movie review mining: a comparison between supervised and unsupervised classification approaches. In: System Sciences, 2005. HICSS’05. Proceedings of the 38th Annual Hawaii International Conference on. IEEE
Dave K, Lawrence S, Pennock DM (2003) Mining the peanut gallery: opinion extraction and semantic classification of product reviews. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on World Wide Web. ACM, pp 519–528
Devitt A, Ahmad K (2007) Sentiment polarity identification in financial news: a cohesion-based approach
Esuli A, Sebastiani F (2005) Determining the semantic orientation of terms through gloss classification. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. ACM, pp 617–624
Fong S, Zhuang Y, Li J, Khoury R (2013) (2013) Sentiment analysis of online news using MALLET. In: Computational and Business Intelligence (ISCBI), 2013 International Symposium on. IEEE, pp 301–304
Forman G (2003) An extensive empirical study of feature selection metrics for text classification. J Mach Learn Res 3:1289–1305
Hatzivassiloglou V, McKeown KR (1997) Predicting the semantic orientation of adjectives. In: Proceedings of the 35th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics and eighth conference of the european chapter of the association for computational linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 174–181
Hernández L, López-Lopez A, Medina JE (2009) Recognizing polarity and attitude of words in text. In: New trends in artificial intelligence, Procs. 14th Portuguese Conference on Artificial Intelligence. EPIA, pp 12–15
Kamps J, Marx M, Mokken RJ, De Rijke M (2004) Using WordNet to measure semantic orientations of adjectives. LREC 4:1115–1118
Kim SM, Hovy E (2004) Determining the sentiment of opinions. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics
Kim SM, Hovy EH (2007) Crystal: analyzing predictive opinions on the Web. In: EMNLP-CoNLL. pp 1056–1064
Pang B, Lee L (2005) Seeing stars: exploiting class relationships for sentiment categorization with respect to rating scales. In: Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 115–124
Pang B, Lee L, Vaithyanathan S (2002) Thumbs up? Sentiment classification using machine learning techniques. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP). pp 79–86
Rajaraman A, Ullman JD (2012) Mining of massive datasets, vol 77. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Snyder B, Barzilay R (2007) Multiple aspect ranking using the good grief algorithm. In: Proceedings of the Joint Human Language Technology/North American Chapter of the ACL Conference (HLT-NAACL). pp 300–307
Takamura H, Inui T, Okumura M (2005) Extracting semantic orientations of words using spin model. In: Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 133–140
Turney P (2002) Thumbs up or thumbs down’s semantic orientation applied to unsupervised classification of reviews. In: Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics. pp. 417–424. arXiv:cs.LG/0212032
Turney PD, Littman M (2003) Measuring praise and criticism: Inference of semantic orientation from association. ACM Trans Inf Syst 21(4):315–346
Whitelaw C, Garg N, Argamon S (2005) Using appraisal groups for sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM international conference on Information and knowledge management. ACM, pp 625–631
Wiebe J (1994) Tracking point of view in narrative. Computational Linguistics, 20. R. Nicole, Title of paper with only first word capitalized. J Name Stand Abbrev (in press)
Wilson TA (2008) Fine-grained subjectivity and sentiment analysis: recognizing the intensity, polarity, and attitudes of private states. ProQuest
Yang Y, Pedersen JO (1997) A comparative study on feature selection in text categorization. ICML 97:412–420
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful for the financial support from the research Grants of Grant No. MYRG152 (Y3-L2)-FST11-ZY, and FDCT 019/2011/A1, offered by the University of Macau and Macau SAR government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Deb, T. Hanne and S. Fong.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Fong, S., Zhuang, Y. et al. Hierarchical classification in text mining for sentiment analysis of online news. Soft Comput 20, 3411–3420 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1812-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1812-4