Abstract
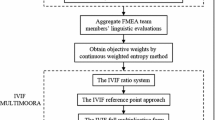
As a powerful pre-accident risk evaluation method, the traditional failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) is extensively used to identify and eliminate the potential failure modes of products or processes, and presents several limitations simultaneously. To improve the accuracy of risk evaluation, this paper proposes a novel FMEA approach considering consensus level between decision makers. First, linguistic variables are applied to express the decision makers’ evaluation information of failure modes, which can be transformed into the corresponding interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy (IVIF) numbers. Second, an IVIF consensus model is constructed to confirm whether the consensus is achieved, and subsequently, the collective evaluation matrix is aggregated by the interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy prioritized weighted averaging operator. Third, a deviation maximization model is used to calculate the weights of risk factors. Finally, the improved IVIF-MULTIMOORA method is implemented to determine the risk ranking of failure modes. This paper also provides a numerical example to illustrate the validity and rationality of the proposed method.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Atanassov KT (1994) Operators over interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 64(2):159–174
Atanassov K, Gargov G (1989) Interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 31(3):343–349
Bai ZY (2013) An interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS method based on an improved score function. Sci World J Article ID 879089
Baležentis T, Baležentis A (2014) A survey on development and applications of the multi-criteria decision making method MULTIMOORA. J Multi-Criteria Decis Anal 21(3–4):209–222
Bowles JB, Peláez CE (1995) Fuzzy logic prioritization of failures in a system failure mode, effects and criticality analysis. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 50(2):203–213
Bozdag E, Asan U, Soyer A, Serdarasan S (2015) Risk prioritization in failure mode and effects analysis using interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Expert Syst Appl 42(8):4000–4015
Brauers WKM (2012) Project management for a country with multiple objectives. Czech Econ Rev 6(1):80–102
Brauers WKM, Zavadskas EK (2010) Project management by MULTIMOORA as an instrument for transition economies. Technol Econ Dev Econ 16(1):5–24
Cabrerizo FJ, Heradio R, Pérez IJ, Herrera-Viedma E (2010) A selection process based on additive consistency to deal with incomplete fuzzy linguistic information. J Univ Comput Sci 16(1):62–81
Chang KH (2014) A more general risk assessment methodology using a soft set-based ranking technique. Soft Comput 18(1):169–183
Chang KH, Cheng CH (2010) A risk assessment methodology using intuitionistic fuzzy set in FMEA. Int J Syst Sci 41(12):1457–1471
Chang KH, Cheng CH (2011) Evaluating the risk of failure using the fuzzy OWA and DEMATEL method. J Intell Manuf 22(2):113–129
Chang CL, Wei CC, Lee YH (1999) Failure mode and effects analysis using fuzzy method and grey theory. Kybernetes 28(9):1072–1080
Chin KS, Wang Y-M, Poon GKK, Yang JB (2009) Failure mode and effects analysis using a group-based evidential reasoning approach. Comput Oper Res 36(6):1768–1779
Deshpande V, Modak J (2002) Application of RCM to a medium scale industry. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 77(1):31–43
Du YX, Lu X, Su XY, Hu Y, Deng Y (2016) New failure mode and effects analysis: an evidential downscaling method. Qual Reliab Eng Int 32(2):737–746
Emovon I, Norman RA, Alan JM, Pazouki K (2015) An integrated multicriteria decision making methodology using compromise solution methods for prioritising risk of marine machinery systems. Ocean Eng 105:92–103
Franceschini F, Galetto M (2001) A new approach for evaluation of risk priorities of failure modes in FMEA. Int J Prod Res 39(13):2991–3002
Herrera-Viedma E, Martinez L, Mata F, Chiclana F (2005) A consensus support system model for group decision-making problems with multigranular linguistic preference relations. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 13(5):644–658
Herrera-Viedma E, Cabrerizo FJ, Kacprzyk J, Pedrycz W (2014) A review of soft consensus models in a fuzzy environment. Inf Fus 17:4–13
Hu AH, Hsu CW, Kuo TC, Wu WC (2009) Risk evaluation of green components to hazardous substance using FMEA and FAHP. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):7142–7147
Ilangkumaran M, Shanmugam P, Sakthivel G, Visagavel K (2014) Failure mode and effect analysis using fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Int J Prod Qual Manag 14(3):296–313
Kutlu AC, Ekmekçioğlu M (2012) Fuzzy failure modes and effects analysis by using fuzzy TOPSIS-based fuzzy AHP. Expert Syst Appl 39(1):61–67
Liu HC, Liu L, Bian QH, Lin QL, Dong N, Xu PC (2011) Failure mode and effects analysis using fuzzy evidential reasoning approach and grey theory. Expert Syst Appl 38(4):4403–4415
Liu HC, Liu L, Liu N (2013) Risk evaluation approaches in failure mode and effects analysis: a literature review. Expert Syst Appl 40(2):828–838
Liu HC, Liu L, Li P (2014a) Failure mode and effects analysis using intuitionistic fuzzy hybrid weighted Euclidean distance operator. Int J Syst Sci 45(10):2012–2030
Liu HC, You JX, You XY (2014b) Evaluating the risk of healthcare failure modes using interval 2-tuple hybrid weighted distance measure. Comput Ind Eng 78:249–258
Liu HC, Fan XJ, Li P, Chen YZ (2014c) Evaluating the risk of failure modes with extended MULTIMOORA method under fuzzy environment. Eng Appl Artif Intell 34:168–177
Liu HC, Li P, You JX, Chen YZ (2015a) A novel approach for FMEA: combination of interval 2-tuple linguistic variables and gray relational analysis. Qual Reliab Eng Int 31(5):761–772
Liu HC, You JX, You XY, Shan MM (2015b) A novel approach for failure mode and effects analysis using combination weighting and fuzzy VIKOR method. Appl Soft Comput 28:579–588
Liu HC, You JX, Chen S, Chen YZ (2016) An integrated failure mode and effect analysis approach for accurate risk assessment under uncertainty. IIE Trans 48(11):1027–1042
Liu HC, You JX, Duan CY (2017) An integrated approach for failure mode and effect analysis under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. International Journal of Production Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2017.03.008
Mohsen O, Fereshteh N (2017) An extended VIKOR method based on entropy measure for the failure modes risk assessment—a case study of the geothermal power plant (GPP). Saf Sci 92:160–172
Pillay A, Wang J (2003) Modified failure mode and effects analysis using approximate reasoning. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 79(1):69–85
Safari H, Faraji Z, Majidian S (2016) Identifying and evaluating enterprise architecture risks using FMEA and fuzzy VIKOR. J Intell Manuf 27(2):475–486
Sharma RK, Kumar D, Kumar P (2005) Systematic failure mode effect analysis (FMEA) using fuzzy linguistic modelling. Int J Qual Reliab Manag 22(9):986–1004
Song WY, Ming XG, Wu ZY, Zhu BT (2013) Failure modes and effects analysis using integrated weight-based fuzzy TOPSIS. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 26(12):1172–1186
Song WY, Ming XG, Wu ZY, Zhu BT (2014) A rough TOPSIS approach for failure mode and effects analysis in uncertain environments. Qual Reliab Eng Int 30(4):473–486
Stamatis DH (2003) Failure mode and effect analysis: FMEA from theory to execution. ASQ Quality Press, Milwaukee
Tooranloo HS, Ayatollah AS (2016) A model for failure mode and effects analysis based on intuitionistic fuzzy approach. Appl Soft Comput 49:238–247
Vahdani B, Salimi M, Charkhchian M (2015) A new FMEA method by integrating fuzzy belief structure and TOPSIS to improve risk evaluation process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 77(1–4):357–368
Wang XF, Zhang YZ, Shen GX (2016) An improved FMECA for feed system of CNC machining center based on ICR and DEMATEL method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83(1–4):43–54
Wu ZB, Xu JP (2012) A consistency and consensus based decision support model for group decision making with multiplicative preference relations. Decis Support Syst 52(3):757–767
Wu ZB, Xu JP (2016) Possibility distribution-based approach for MAGDM with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(3):694–705
Xu ZS (2007a) Methods for aggregating interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information and their application to decision making. Control Decis 22(2):215–219
Xu ZS (2007b) On similarity measures of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their application to pattern recognitions. J Southeast Univ (English Ed) 23(1):139–143
Xu ZS (2010) A deviation-based approach to intuitionistic fuzzy multiple attribute group decision making. Group Decis Negot 19(1):57–76
Xu JP, Wu ZB (2013) A maximizing consensus approach for alternative selection based on uncertain linguistic preference relations. Comput Ind Eng 64(4):999–1008
Yager RR (2008) Prioritized aggregation operators. Int J Approx Reason 48(1):263–274
Yu DJ, Wu YY, Lu T (2012) Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy prioritized operators and their application in group decision making. Knowl Based Syst 30:57–66
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zhang X, Jin F, Liu PD (2013) A grey relational projection method for multi-attribute decision making based on intuitionistic trapezoidal fuzzy number. Appl Math Model 37(5):3467–3477
Zhao H, You JX, Liu HC (2017) Failure mode and effect analysis using MULTIMOORA method with continuous weighted entropy under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Soft Comput 21(18):5355–5367
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71371156, 70971017) and Doctoral Innovation Fund Program of Southwest Jiaotong University (No. D-CX201727).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YL., Wang, R. & Chin, KS. New failure mode and effect analysis approach considering consensus under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Soft Comput 23, 11611–11626 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-03706-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-03706-5