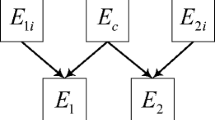
Abstract
Dempster’s rule of combination can only be applied to independent bodies of evidence. This paper proposes a new rule to combine dependent bodies of evidence. The rule is based on the concept of joint belief distribution, and can be seen as a generalization of Dempster’s rule. When the bodies of evidence are independent, the new combination rule will be reduced into Dempster’s rule. Two examples are illustrated to show the use and effectiveness of the proposed method.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoine V, Quost B, Masson MH, Denoeux T (2014) Cevclus: evidential clustering with instance-level constraints for relational data. Soft Comput 18(7):1321–1335
Cattaneo ME (2003) Combining belief functions issued from dependent sources. Seminar für Statistik, Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule (ETH), Zürich
Cattaneo ME (2011) Belief functions combination without the assumption of independence of the information sources. Int J Approx Reason 52(3):299–315
Chen S, Deng Y, Wu J (2013) Fuzzy sensor fusion based on evidence theory and its application. Appl Artif Intell 27(3):235–248
Choenni S, Blok HE, Leertouwer E (2006) Handling uncertainty and ignorance in databases: a rule to combine dependent data. In: Proceedings of the 11th international conference on database systems for advanced applications (DASFAA’06). Springer, Singapore, pp 310–324
Coletti G, Scozzafava R (2006) Toward a general theory of conditional beliefs. Int J Intell Syst 21(3):229–259
Cuzzolin F, Gong W (2013) Belief modeling regression for pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the 16th conference on information fusion (FUSION). Istanbul, pp 1398–1405
Dempster AP (1967) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann Stat 38(2):325–339
Deng X, Deng Y (2018) D-AHP method with different credibility of information. Soft Comput https://doi.org/10.1007/s00,500-017-2993-9
Deng Y, Su X, Wang D, Li Q (2010) Target recognition based on fuzzy dempster data fusion method. Def Sci J 60:525–530
Denœux T (2008) Conjunctive and disjunctive combination of belief functions induced by nondistinct bodies of evidence. Artif Intell 172(2):234–264
Destercke S, Dubois D (2011) Idempotent conjunctive combination of belief functions: extending the minimum rule of possibility theory. Inf Sci 181(18):3925–3945
Destercke S, Dubois D, Chojnacki E (2007) Cautious conjunctive merging of belief functions. In: Symbolic and quantitative approaches to reasoning with uncertainty. Springer, Berlin, pp 332–343
Fung R, Chong C (1985) Metaprobability and Dempster–Shafer in evidential reasoning. In: Proceedings of the 1st conference annual conference on uncertainty in artificial intelligence (UAI-85). AUAI Press, Corvallis, Oregon, pp 76–83
Guralnik V, Mylaraswamy D, Voges H (2006) On handling dependent evidence and multiple faults in knowledge fusion for engine health management. In: Aerospace conference. IEEE, pp 9–17
Hua Z, Gong B, Xu X (2008) A DS-AHP approach for multi-attribute decision making problem with incomplete information. Expert Syst Appl 34(3):2221–2227
Huang S, Su X, Hu Y, Mahadevan S, Deng Y (2014) A new decision-making method by incomplete preferences based on evidence distance. Knowl Based Syst 56:264–272
Jiang W, Zhuang M, Xie C (2017) A reliability-based method to sensor data fusion. Sensors 17(7):1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071,575
Kulasekere E, Premaratne K, Dewasurendra DA (2004) Conditioning and updating evidence. Int J Approx Reason 36(1):75–108
Liu Z, Pan Q, Dezert J (2014) Credal classification rule for uncertain data based on belief functions. Pattern Recognit 47(7):2532–2541
Masson MH, Destercke S, Denoeux T (2016) Modelling and predicting partial orders from pairwise belief functions. Soft Comput 20(3):939–950
Monney PA, Chan M (2007) Modelling dependence in Dempster–Shafer theory. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 15(1):93–114
Mouna C, Arnaud M, Boutheina Y (2015) Combining partially independent belief functions. Decis Support Syst 73:37–46
Nakama T, Ruspini E (2014) Combining dependent evidential bodies that share common knowledge. Int J Approx Reason 55(9):2109–2125
Reformat M, Yager RR (2008) Building ensemble classifiers using belief functions and OWA operators. Soft Comput 12(6):543–558
Shafer G (1976) A mathematical theory of evidence. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Shafer G (2016) The problem of dependent evidence. Int J Approx Reason 79(C):41–44
Shi F, Su X, Qian H, Yang N, Han W (2017) Research on the fusion of dependent evidence based on rank correlation coefficient. Sensors 17:2362–2377
Smets P (1992) The concept of distinct evidence. In: Proceedings of the 4th conference on information processing and management of uncertainty in knowledge-based systems (IPMU). Palma de Mayorca, pp 789–794
Smets P (2002) The application of the matrix calculus to belief functions. Int J Approx Reason 31(1):1–30
Smets P, Kennes R (1994) The transferable belief model. Artif intell 66(2):191–234
Su X, Deng Y, Mahadevan S, Bao Q (2012) An improved method for risk evaluation in failure modes and effects analysis of aircraft engine rotor blades. Eng Fail Anal 26:164–174
Su X, Mahadevan S, Xu P, Deng Y (2015a) Dependence assessment in human reliability analysis using evidence theory and AHP. Risk Anal 35(7):1296–1316
Su X, Mahadevan S, Xu P, Deng Y (2015b) Handling of dependence in Dempster–Shafer theory. Int J Intell Syst 30(4):441–467
Su X, Mahadevan S, Han W, Deng Y (2016) Combining dependent bodies of evidence. Appl Intell 44:634–644
Su X, Li L, Shi F, Qian H (2018) Research on the fusion of dependent evidence based on mutual information. IEEE Access 6:71839
Voorbraak F (1991) On the justification of dempster’s rule of combination. Artif Intell 48(2):171–197
Wu Y, Yang J, Liu L et al (1996) On the evidence inference theory. Inf Sci 89(3):245–260
Xiao W, Wang Z, Wang Y (2011) Combination rule for dependent evidences. Control Decis 26(5):773–776
Xu H, Deng Y (2018) Dependent evidence combination based on shearman coefficient and pearson coefficient. IEEE Access 6(1):11,634–11,640
Xu H, Smets P (1994) Evidential reasoning with conditional belief functions. In: Proceedings of the 10th international conference on uncertainty in artificial intelligence, Washington, USA, pp 598–605
Yager RR (2009) On the fusion of non-independent belief structures. Int J Gen Syst 38(5):505–531
Yager RR, Alajlan N (2015) Dempster-shafer belief structures for decision making under uncertainty. Knowl Based Syst 80:58–66
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the reviewers’ suggestions and the editor’s encouragement. This work was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, (Grant Nos. 61503237, 61573290), “Chenguang Program” supported by Shanghai Education Development Foundation and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, Shanghai Science and Technology Committee Key Program (Grant Nos. 18020500900, 15160500800), Shanghai Key Laboratory of Power Station Automation Technology (No. 13DZ2273800), Shanghai Education Commission Excellent Youth Project (No. ZZsdl15144).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by A. Di Nola.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, X., Li, L., Qian, H. et al. A new rule to combine dependent bodies of evidence. Soft Comput 23, 9793–9799 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03804-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03804-y