Abstract
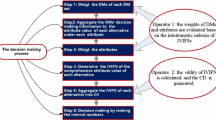
In 2015, Li and Chen proposed a multi-criteria group decision-making (MCGDM) method, as similar as technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution (TOPSIS), with trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy information to derive preference values (i.e., alternative ratings) based on individual differentiation of decision-makers. The individual differentiation consideration of decision-makers was useful because alternative ratings and criteria weights in group were generally derived by mean computation in the past. Additionally, MCGDM with trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy information is regarded to be the extension of multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) with group decision-making under fuzzy environment. Practically, fuzzy extension of MCDM is commonly complicated based on the characteristics of fuzzy numbers, especially for intuitionistic fuzzy numbers that may be the most complex one for all kinds of fuzzy numbers. Obviously, Li and Chen’s contribution was extending MCGDM based on individual differentiation of decision-makers under trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Unfortunately, Li and Chen’s method merely expressed the importance difference of decision-makers for yielding preference values, but they derived criteria weights by mean computation. Therefore, the computations of preference values and criteria weights are inconsistent on considering the importance of decision-makers. Besides, their fuzzy extension was complicated and hard for MCGDM with trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy information. To resolve the importance inconsistent of yielding ratings and weights as well as fuzzy operation complicated ties, we utilize trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and extended fuzzy preference relation for MCGDM based on individual differentiation of decision-makers in this paper. By utilization of extended fuzzy preference relation, both alternative ratings and criteria weights of MCGDM under intuitionistic fuzzy environment are yielded based on individual differentiation of decision-makers, and decision-making problems are easily and reasonably solved. Furthermore, we also use the simplified version of the MCGDM with trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy numbers to evaluate alternatives in the illustrating example of Li and Chen, and compare their evaluating result with the result of proposed method based on individual differentiation of decision-makers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin F, Fahmi A, Abdullah S, Ali A, Ahmed R, Ghani F (2017) Triangular cubic linguistic hesitant fuzzy aggregation operators and their application in group decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 34:2401–2416
Atanassov K (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20:87–96
Churchman CW, Ackoff RJ, Amoff EL (1957) Introduction to operation research. Wiley, New York
Delgado M, Verdegay JL, Vila MA (1992) Linguistic decision-making models. Int J Intell Syst 7:479–492
Epp SS (1990) Discrete mathematics with applications. Wadsworth, California
Fahmi A, Abdullah S, Amin F, Siddque N, Ali A (2017a) Aggregation operators on triangular cubic fuzzy numbers and its application to multi-criteria decision making problems. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 33:3323–3337
Fahmi A, Abdullah S, Amin F, Ali A (2017b) Precursor selection for sol–gel synthesis of titanium carbide nanopowders by a new cubic fuzzy multi-attribute group decision-making model. J Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1515/jisys-2017-0083
Fahmi A, Abdullah S, Amin F, Ali A (2018a) Weighted average rating (WAR) method for solving group decision making problem using triangular cubic fuzzy hybrid aggregation (Tcfha). Punjab Univ J Math 50:23–34
Fahmi A, Abdullah S, Amin F, Ali A, Khan WA (2018b) Some geometric operators with triangular cubic linguistic hesitant fuzzy number and their application in group decision-making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 35:2485–2499
Fahmi A, Abdullah S, Amin F, Khan MSA (2018c) Trapezoidal cubic fuzzy number Einstein hybrid weighted averaging operators and its application to decision making. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3242-6
Fahmi A, Amin F, Abdullah S, Ali A (2018d) Cubic fuzzy Einstein aggregation operators and its application to decision making. Int J Syst Sci 49:2385–2397
Fan ZP, Ma J, Zhang Q (2002) An approach to multiple attribute decision making based on fuzzy preference information on alternatives. Fuzzy Sets Syst 131:101–106
Grzegrorzewski P (2003) The hamming distance between intuitionistic fuzzy sets. In: Proceedings of the 10th IFSA World Congress, Istanbul, Turkey
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Verdegay JL (1996) A model of consensus in group decision making under linguistic assessments. Fuzzy Sets Syst 78:73–87
Hwang CL, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attribute decision making: methods and application. Springer, New York
Keeney R, Raiffa H (1976) Decision with multiple objective: preference and value tradeoffs. Wiley, New Work
Lee HS (2005) On fuzzy preference relation in group decision making. Int J Comput Math 82:133–140
Li X, Chen X (2014) Extension of the TOPSIS method based on prospect theory and trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy numbers for group decision making. J Syst Sci Syst Eng 23:231–247
Li X, Chen X (2015) Multi-criteria group decision making based on trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy information. Appl Soft Comput 30:454–461
Liang GS (1999) Fuzzy MCDM based on ideal and anti-ideal concepts. Eur J Oper Res 112:682–691
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hill, New York
Vahdani B, Mousavi SM, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2011) Group decision making based on novel fuzzy modified TOPSIS method. Appl Math Model 35:4257–4269
Wang YJ (2015) A fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making model based on simple additive weighting method and relative preference relation. Appl Soft Comput 30:412–420
Wang CY, Chen SM (2017) Multiple attribute decision making based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets, linear programming methodology, and the extended TOPSIS method. Inf Sci 397–398:155–167
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8:338–353
Acknowledgements
This research work was partially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China under Grant No. MOST 106-2410-H-346-002-.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China under Grant No. MOST 106-2410-H-346-002-.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The corresponding author (also the sole author) declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YJ. Utilization of trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and extended fuzzy preference relation for multi-criteria group decision-making based on individual differentiation of decision-makers. Soft Comput 24, 397–407 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03921-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03921-8