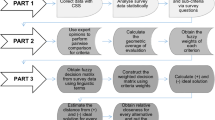
Abstract
Public transport plays an essential role in helping people escape from the congested traffic in large and crowded cities. Evaluating customer satisfaction is the key to the continuous quality improvement of public transport services. This work proposes a new public transport customer satisfaction evaluation approach based on an extended thermodynamic method with q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets. First, we use the q-ROFSs to handle the ambiguity and uncertainty of customer satisfaction evaluation information for public transport. Then, we extend the thermodynamic method to determine the customer satisfaction levels of public transport lines. Moreover, the stepwise weight assessment ratio analysis method is utilized to specify the weights of evaluation criteria as it is simple and time-saving. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is illustrated with a customer satisfaction evaluation of the rail transit network in Shanghai, China. Results showed that Line 7 has the highest customer satisfaction and Line 2 has the lowest customer satisfaction among the considered rail transit lines. Besides, nine evaluation criteria need to be optimized to improve the customer satisfaction level of Line 2 and the most critical one is train crowding.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen J, Eboli L, Forciniti C, Mazzulla G, Ortúzar JDD (2019) The role of critical incidents and involvement in transit satisfaction and loyalty. Transp Policy 75:57–69
Allen J, Eboli L, Mazzulla G, Ortúzar JD (2020) Effect of critical incidents on public transport satisfaction and loyalty: An ordinal probit SEM-MIMIC approach. Transportation 47(2):827–863
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Aydin N, Celik E, Gumus AT (2015) A hierarchical customer satisfaction framework for evaluating rail transit systems of Istanbul. Transp Res Part A: Policy Pract 77:61–81
Balali A, Hakimelahi A, Valipour A (2020) Identification and prioritization of passive energy consumption optimization measures in the building industry: An Iranian case study. J Build Eng 30:101239
Balki MK, Erdoğan S, Aydın S, Sayin C (2020) The optimization of engine operating parameters via SWARA and ARAS hybrid method in a small SI engine using alternative fuels. J Clean Prod 258:120685
Bilişik ÖN, Şeker Ş, Aydın N, Güngör N, Baraçlı H (2018) Passenger satisfaction evaluation of public transportation in Istanbul by using fuzzy quality function deployment methodology. Arab J Sci Eng 44(3):2811–2824
Çelebi D, İmre Ş (2020) Measuring crowding-related comfort in public transport. Transp Plan Technol 43(7):735–750
Darko AP, Liang D (2020) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators and their application to multiple attribute group decision making with modified EDAS method. Eng Appl Artif Intell 87:103259
de Oña J (2020) The role of involvement with public transport in the relationship between service quality, satisfaction and behavioral intentions. Transp Res Part A: Policy Pract 142:296–318
de Oña J (2021) Understanding the mediator role of satisfaction in public transport: a cross-country analysis. Transp Policy 100:129–149
de Aquino JT, de Melo FJC, Jerônimo TB, de Medeiros DD (2019) Evaluation of quality in public transport services: the use of quality dimensions as an input for fuzzy TOPSIS. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(1):176–193
de Oña R, de Abreu e Silva J, Muñoz-Monge C, de Oña J (2018) Users’ satisfaction evolution of a metropolitan transit system in a context of economic downturn. Int J Sustain Transp 12(1):66–74
Du WS (2018) Minkowski-type distance measures for generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 33(4):802–817
Duan CY, Liu HC, Zhang LJ, Shi H (2019) An extended alternative queuing method with linguistic Z-numbers and its application for green supplier selection and order allocation. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(8):2510–2523
Gascon M, Marquet O, Gràcia-Lavedan E, Ambròs A, Götschi T, Nazelle AD, Panis LI, Gerike R, Brand C, Dons E, Eriksson U, Iacorossi F, Ávila-Palència I, Cole-Hunter T, Nieuwenhuisjen MJ (2020) What explains public transport use? Evidence from seven European cities. Transp Policy 99:362–374
Gong JW, Li Q, Yin L, Liu HC (2020) Undergraduate teaching audit and evaluation using an extended MABAC method under q-rung orthopair fuzzy environment. Int J Intell Syst 35(12):1912–1933
Güner S (2018) Measuring the quality of public transportation systems and ranking the bus transit routes using multi-criteria decision making techniques. Case Stud Transp Policy 6(2):214–224
Holmgren J (2020) The effect of public transport quality on car ownership—A source of wider benefits? Res Transp Econ 83:100957
Hrelja R, Khan J, Pettersson F (2020) How to create efficient public transport systems? A systematic review of critical problems and approaches for addressing the problems. Transp Policy 98:186–196
Keršulienė V, Zavadskas E, Turskis Z (2010) Selection of rational dispute resolution method by applying new step-wise weight assessment ratio analysis (SWARA). J Bus Econ Manag 11(2):243–258
Khan MJ, Ali MI, Kumam P (2021) A new ranking technique for q-rung orthopair fuzzy values. Int J Intell Syst 36(1):558–592
Kiani Mavi R, Zarbakhshnia N, Khazraei A (2018) Bus rapid transit (BRT): a simulation and multi criteria decision making (MCDM) approach. Transp Policy 72:187–197
Krishankumar R, Gowtham Y, Ahmed I, Ravichandran KS, Kar S (2020) Solving green supplier selection problem using q-rung orthopair fuzzy-based decision framework with unknown weight information. Appl Soft Comput 94:106431
Kutlu Gündoğdu F, Duleba S, Moslem S, Aydın S (2021) Evaluating public transport service quality using picture fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and linear assignment model. Appl Soft Comput 100:106920
Li X-H, Huang L, Li Q, Liu H-C (2020) Passenger satisfaction evaluation of public transportation using Pythagorean fuzzy MULTIMOORA method under large group environment. Sustainability 12(12):4996
Liao H, Wu D, Huang Y, Ren P, Xu Z, Verma M (2018) Green logistic provider selection with a hesitant fuzzy linguistic thermodynamic method integrating cumulative prospect theory and PROMETHEE. Sustainability 10(4):1291
Liao H, Zhang H, Zhang C, Wu X, Mardani A, Al-Barakati A (2020) A q-rung orthopair fuzzy GLDS method for investment evaluation of be angel capital in China. Technol Econ Dev Econ 26(1):103–134
Liou JJH, Hsu CC, Chen YS (2014) Improving transportation service quality based on information fusion. Transp Res Part A: Policy Pract 67:225–239
Liu P, Wang P (2018) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy aggregation operators and their applications to multiple-attribute decision making. Int J Intell Syst 33(2):259–280
Liu P, Wang Y (2020) Multiple attribute decision making based on q-rung orthopair fuzzy generalized Maclaurin symmetic mean operators. Inf Sci 518:181–210
Liu Y, Wang Y, Xu M, Xu G (2019) Emergency alternative evaluation using extended trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy thermodynamic approach with prospect theory. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(6):1801–1817
Liu P, Chen SM, Wang P (2020) Multiple-attribute group decision-making based on q-rung orthopair fuzzy power Maclaurin symmetric mean operators. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern: Syst 50(10):3741–3756
Naeini MA, Zandieh M, Najafi SE, Sajadi SM (2020) Analyzing the development of the third-generation biodiesel production from microalgae by a novel hybrid decision-making method: the case of Iran. Energy 195:116895
Nassereddine M, Eskandari H (2017) An integrated MCDM approach to evaluate public transportation systems in Tehran. Transp Res Part A: Policy Pract 106:427–439
Ni A, Zhang C, Hu Y, Lu W, Li H (2020) Influence mechanism of the corporate image on passenger satisfaction with public transport in China. Transp Policy 94:54–65
Peng X, Huang H (2020) Fuzzy decision making method based on CoCoSo with CRITIC for financial risk evaluation. Technol Econ Dev Econ 26:695–724
Quddus M, Rahman F, Monsuur F, de Ona J, Enoch M (2019) Analyzing bus passengers’ satisfaction in Dhaka using discrete choice models. Transp Res Rec 2673:758–768
Rani P, Mishra AR (2020) Multi-criteria weighted aggregated sum product assessment framework for fuel technology selection using q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets. Sustain Prod Consum 24:90–104
Ren P, Xu Z, Hao Z (2017a) Hesitant fuzzy thermodynamic method for emergency decision making based on prospect theory. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(9):2531–2543
Ren P, Xu Z, Liao H, Zeng XJ (2017b) A thermodynamic method of intuitionistic fuzzy MCDM to assist the hierarchical medical system in China. Inf Sci 420:490–504
Soltanpour A, Mesbah M, Habibian M (2020) Customer satisfaction in urban rail: A study on transferability of structural equation models. Public Trans 12(1):123–146
Soza-Parra J, Raveau S, Muñoz JC, Cats O (2019) The underlying effect of public transport reliability on users’ satisfaction. Transp Res Part A: Policy Pract 126:83–93
Tahanisaz S, shokuhyar S (2020) Evaluation of passenger satisfaction with service quality: A consecutive method applied to the airline industry. Journal of Air Transport Management 83
Verma M, Rajasankar J (2017) A thermodynamical approach towards group multi-criteria decision making (GMCDM) and its application to human resource selection. Appl Soft Comput 52:323–332
Vicente P, Suleman A, Reis E (2020) Index of satisfaction with public transport: A fuzzy clustering approach. Sustainability 12(22):9759
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Sun H (2018) Assessing customer satisfaction of urban rail transit network in Tianjin based on intuitionistic fuzzy group decision model. Discret Dyn Nat Soc 2018:4205136
Wang J, Wei G, Lu J, Alsaadi FE, Hayat T, Wei C, Zhang Y (2019) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy Hamy mean operators in multiple attribute decision-making and their application to enterprise resource planning systems selection. Int J Intell Syst 34(10):2429–2458
Wang M, Liang D, Xu Z, Ye D (2020) The evaluation of mobile health apps: A psychological perception-based probabilistic linguistic belief thermodynamic multiple attribute decision making method. J Oper Res Soc. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2020.1801361
Wei G, Gao H, Wei Y (2018) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy Heronian mean operators in multiple attribute decision making. Int J Intell Syst 33(7):1426–1458
Yager RR (2014) Pythagorean membership grades in multicriteria decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(4):958–965
Yager RR (2017) Generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 25(5):1222–1230
Yücenur GN, Çaylak GG, Postalcıoğlu M (2020) An integrated solution with SWARA& COPRAS methods in renewable energy production: City selection for biogas facility. Renew Energy 145:2587–2597
Zhang C, Liu Y, Lu W, Xiao G (2019) Evaluating passenger satisfaction index based on PLS-SEM model: Evidence from Chinese public transport service. Transp Res Part A: Policy Pract 120:149–164
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the respected editor and the anonymous referees for their insightful and constructive comments, which helped to improve the overall quality of this paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61773250), the major project of the National Social Science Foundation of China, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Chen, QY., Liu, Z. et al. Public transport customer satisfaction evaluation using an extended thermodynamic method: a case study of Shanghai, China. Soft Comput 25, 10901–10914 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05790-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05790-6