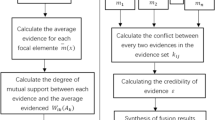
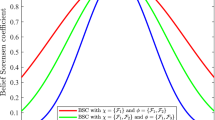
Abstract
Dempster–Shafer evidence theory plays an important role in multi-sensor information fusion and is widely used in the real world. However, fusing the highly conflicting evidences may emerge counter-intuitive results. Recently, researchers found that weighting evidences based on its corresponding credibility and information volume are effective in dealing with the above problem. So it is still an open issue about how to obtain reasonable weights. In this paper, a new divergence measure method is proposed to measure divergence degree of basic probability assignment based on harmonic mean of Deng relative entropy. In determining information volume, Zhou et al.’s entropy is also introduced with considering the cardinality of the discernment frame. Then the weight for each evidence will be generated by the proposed divergence measure method and the modified information volume. Some numerical examples are illustrated to show the outstanding performance of the proposed divergence measure method, and the optimal weighted evidence combination algorithm also gives the relatively highest belief in multi-sensor target recognition.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell DE (1982) Regret in decision making under uncertainty. Oper Res 30:961
Broemeling LD (2011) An account of early statistical inference in Arab cryptology. Am Stat 65(4):255–257
Brose MS, Rebbeck TR, Calzone KA, Stopfer JE, Nathanson KL, Weber BL (2002) Cancer risk estimates for BRCA1 mutation carriers identified in a risk evaluation program. J Natl Cancer Inst 94(18):1365–1372
Charnes A, Cooper WW et al (1979) Measuring the efficiency of decision-making units. Eur J Oper Res 2:429
Chen L, Deng Y (2018) A new failure mode and effects analysis model using Dempster-Shafer evidence theory and grey relational projection method. Eng Appl Artif Intell 76:13–20
Cheng G, Chen XH, Shan XL, Liu HG, Zhou CF (2016) A new method of gear fault diagnosis in strong noise based on multi-sensor information fusion. J Vib Control 22(6):1504–1515
Dempster AP (2008) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. In: Classic works of the Dempster-Shafer theory of belief functions (pp. 57-72). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Dubois D, Prade H (2001) Possibility theory, probability theory and multiple-valued logics: a clarification. Ann Math Artif Intell 32(1–4):35–66
Edwards W (1954) The theory of decision making. Psychol Bull 51(4):3
Fei L, Deng Y (2016) Meausre divergence degree of basic probability assignment based on Deng relative entropy. In: 2016 Chinese control and decision conference (CCDC) (pp. 3857-3859). IEEE
Geng H, Liang Y, Yang F, Xu L, Pan Q (2017) Model-reduced fault detection for multi-rate sensor fusion with unknown inputs. Inf Fusion 33:1–14
Hang J, Zhang J, Cheng M (2014) Fault diagnosis of wind turbine based on multi-sensors information fusion technology. IET Renew Power Gener 8(3):289–298
Hu MK (1962) Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants. IRE Trans Inf Theory 8(2):179–187
Jiang W, Xie C, Zhuang M, Shou Y, Tang Y (2016) Sensor data fusion with z-numbers and its application in fault diagnosis. Sensors 16(9):1509
Klinke A, Renn O (2002) A new approach to risk evaluation and management: risk-based, precaution-based, and discourse-based strategies 1. Risk Anal Int J 22(6):1071–1094
Kullback S (1997) Information theory and statistics. Courier Corporation
Kullback S, Leibler RA (1951) On information and sufficiency. Ann Math Stat 22(1):79–86
Li Z, Chen L (2019) A novel evidential FMEA method by integrating fuzzy belief structure and grey relational projection method. Eng Appl Artif Intell 77:136–147
Lin J (1991) Divergence measures based on the Shannon entropy. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 37(1):145–151
Liu Z, Pan Q, Dezert J, Han JW, He Y (2017) Classifier fusion with contextual reliability evaluation. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(5):1605–1618
Murphy CK (2000) Combining belief functions when evidence conflicts. Decis Support Syst 29(1):1–9
Nashef SA, Roques F, Michel P, Gauducheau E, Lemeshow S, Salamon R, EuroSCORE Study Group (1999) European system for cardiac operative risk evaluation (Euro SCORE). Eur J Cardio-thoracic Sur 16(1):9–13
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Polikar R (2006) Essemble based systems in decision making. IEEE Circuits Syst Mag 6(3):21–45
Shafer G (1976) A mathematical theory of evidence. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Xiao F (2019) Multi-sensor data fusion based on the belief divergence measure of evidences and the belief entropy. Inf Fusion 46:23–32
Yong D, WenKang S, ZhenFu Z, Qi L (2004) Combining belief functions based on distance of evidence. Decis Support Syst 38(3):489–493
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zhang Z, Liu T, Chen D, Zhang W (2014) Novel algorithm for identifying and fusing conflicting data in wireless sensor networks. Sensors 14(6):9562–9581
Zhou D, Tang Y, Jiang W (2017) A modified belief entropy in Dempster-Shafer framework. PLoS ONE 12(5):e0176832
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by National Key Research and Development Program of China, Grant Number 2016YFB0501805.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, K., Sun, R., Li, L. et al. An optimal evidential data fusion algorithm based on the new divergence measure of basic probability assignment. Soft Comput 25, 11449–11457 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06040-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06040-5