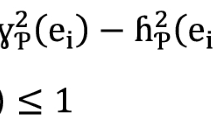Abstract
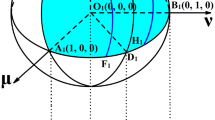
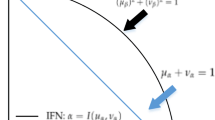
Pythagorean fuzzy set (PFS) is an effective approach for handling uncertainty in practical applications, whereas how to measure the uncertainty degree of PFS is still an open issue. In this paper, we propose a novel entropy measure of PFS by taking into account both Pythagorean fuzziness entropy in terms of the membership and non-membership degrees, and Pythagorean hesitation entropy in terms of hesitation degree. To be specific, we firstly propose a new cross-entropy measure of PFS to assess the difference of uncertainty between PFSs. By measuring the cross-entropy with the crisp set, we then propose a new entropy measure of PFS, which mathematically proves the satisfaction requirements of the axioms defined for the entropy of PFS. Based on that, we propose weighted cross-entropy and entropy measures which can be used for different applications. Furthermore, we illustrate the superiority of the proposed entropy measures of PFS by the comparisons with existing entropy measures of PFS. In addition, we propose an entropy-based multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) method, which intends to minimize the total uncertainty amount of decision matrix to make the deciding result more convincing. As a result, we conduct a sensitivity analysis of the proposed weighted entropy measure in the MCDM method, and a company investment case study is attached to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed MCDM method. The experimental result shows that the MCDM method based on the newly defined weighted entropy measure is stable, even in the setting of the variation of parameter.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Alcantud JC, Feng F, Yager R (2019) An N-soft set approach to rough sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2946526
Atanassov K (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 31:343–349
Babajanyan S, Allahverdyan A, Cheong KH (2020) Energy and entropy: path from game theory to statistical mechanics. Phys Rev Res 2(4):043055
Cao Z, Lin C-T (2018) Inherent fuzzy entropy for the improvement of EEG complexity evaluation. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 26(2):1032–1035
Cao Z, Ding W, Wang Y-K, Hussain FK, Al-Jumaily A, Lin C-T (2019) Effects of repetitive SSVEPs on EEG complexity using multiscale inherent fuzzy entropy. Neurocomputing. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.08.091
Cao Z, Chuang C-H, King J-K, Lin C-T (2019) Multi-channel EEG recordings during a sustained-attention driving task. Sci Data 6:2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0027-4
Cao Z, Lin C-T, Lai K-L, Ko L-W, King J-T, Liao K-K, Fuh J-L, Wang S-J (2019) Extraction of SSVEPs-based Inherent fuzzy entropy using a wearable headband EEG in migraine patients. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2905823
Chang L, Zhang L, Fu C, Chen Y-W (2021) Transparent digital twin for output control using belief rule base. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3063285
Cheng C, Xiao F (2021) A distance for belief functions of orderable set. Pattern Recogn Lett 145(2021):165–170
Cui H, Zhou L, Li Y, Kang B (2022) Belief entropy-of-entropy and its application in the cardiac interbeat interval time series analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals 155(2022):111736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111736
Deng Y (2020) Uncertainty measure in evidence theory. Sci China Inf Sci 63(11):210201
Deng Y (2020) Information volume of mass function. Int J Comput Commun Control 15(6):3983. https://doi.org/10.15837/ijccc.2020.6.3983
Deng Y (2022) Random permutation set. Int J Comput Commun Control 17(1):4542. https://doi.org/10.15837/ijccc.2022.1.4542
Deng J, Deng Y (2021) Information volume of fuzzy membership function. Int J Comput Commun Control 16(1):4106. https://doi.org/10.15837/ijccc.2021.1.4106
Deng X, Jiang W (2020) On the negation of a Dempster-Shafer belief structure based on maximum uncertainty allocation. Inform Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.12.080
Fei L (2019) On interval-valued fuzzy decision-making using soft likelihood functions. Int J Intell Syst 34(7):1631–1652
Fei L, Deng Y (2020) Multi-criteria decision making in Pythagorean fuzzy environment. Appl Intell 50(2):537–561
Fei L, Feng Y, Wang H (2021) Modeling heterogeneous multi-attribute emergency decision-making with Dempster-Shafer theory. Comput Ind Eng 161(2021):107633
Fu C, Xue M, Chang W, Xu D, Yang S (2020) An evidential reasoning approach based on risk attitude and criterion reliability. Knowl-Based Syst 199(2020):105947
Gao X, Su X, Qian H, Pan X (2021) Dependence assessment in human reliability analysis under uncertain and dynamic situations. Nucl Eng Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2021.09.045
Garg H (2020) Linguistic interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy sets and their application to multiple attribute group decision-making process. Cogn Comput 12(6):1313–1337
Garg H (2021) Sine trigonometric operational laws and its based Pythagorean fuzzy aggregation operators for group decision-making process. Artif Intell Rev 54(6):4421–4447
Garg H (2021) New exponential operation laws and operators for interval-valued q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets in group decision making process. Neural Comput Appl 2021:1–27
Garg H (2021) CN-q-ROFS: Connection number-based q-rung orthopair fuzzy set and their application to decision-making process. Int J Intell Syst 36(7):3106–3143
Garg H, Kumar K (2019) Linguistic interval-valued atanassov intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications to group decision making problems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(12):2302–2311
Gou X, Xu Z, Herrera F (2018) Consensus reaching process for large-scale group decision making with double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Knowl-Based Syst 157(2018):20–33
Guo XZ, Xin XL (2005) Partial entropy and relative entropy of fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Syst Math 2:97–102
Jiang W, Cao Y, Deng X (2019) A novel Z-network model based on Bayesian network and Z-number. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2918999
Lai JW, Chang J, Ang L, Cheong KH (2020) Multi-level information fusion to alleviate network congestion. Inform Fus 63(2020):248–255
Liao H, Mi X, Xu Z (2019) A survey of decision-making methods with probabilistic linguistic information: bibliometrics, preliminaries, methodologies, applications and future directions. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-019-09309-5
Liu Z, Pan Q, Dezert J, Han J-W, He Y (2018) Classifier fusion with contextual reliability evaluation. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(5):1605–1618
Liu Z, Zhang X, Niu J, Dezert J (2020) Combination of classifiers with different frames of discernment based on belief functions. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2985332
Mao J, Yao D, Wang C (2013) A novel cross-entropy and entropy measures of ifss and their applications. Knowl-Based Syst 48(2013):37–45
Meng D, Li Y, He C, Guo J, Lv Z, Wu P (2021) Multidisciplinary design for structural integrity using a collaborative optimization method based on adaptive surrogate modelling. Mater Des 206(2021):109789
Pan L, Deng Y (2022) A new complex evidence theory. Inform Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.06.063
Peng X, Yuan H, Yang Y (2017) Pythagorean fuzzy information measures and their applications. Int J Intell Syst 32(10):991–1029
Qiang C, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2022) Information fractal dimension of mass function. Fractals. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X22501109
Rani P, Mishra AR, Pardasani KR, Mardani A, Liao H, Streimikiene D (2019) A novel VIKOR approach based on entropy and divergence measures of Pythagorean fuzzy sets to evaluate renewable energy technologies in India. J Clean Prod 238(2019):117936
Song Y, Deng Y (2021) Entropic explanation of power set. Int J Comput Commun Control 16(4):4413. https://doi.org/10.15837/ijccc.2021.4.4413
Song X, Xiao F (2022) Combining time-series evidence: a complex network model based on a visibility graph and belief entropy. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02956-5
Song Y, Fu Q, Wang Y-F, Wang X (2019) Divergence-based cross entropy and uncertainty measures of atanassov’s intuitionistic fuzzy sets with their application in decision making. Appl Soft Comput 84(2019):105703
Wan S-P, Li S-Q, Dong J-Y (2018) A three-phase method for Pythagorean fuzzy multi-attribute group decision making and application to haze management. Comput Ind Eng 123(2018):348–363
Wang L, Garg H (2021) Algorithm for multiple attribute decision-making with interactive Archimedean norm operations under Pythagorean fuzzy uncertainty. Int J Comput Intell Syst 14(1):503–527
Wang Z, Wang C, Li X, Gao C, Li X, Zhu J (2020) Evolutionary markov dynamics for network community detection. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2020.2997043
Wang Z, Li Z, Wang R, Nie F, Li X (2021) Large graph clustering with simultaneous spectral embedding and discretization. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(12):4426–4440. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3002587
Wang Z, Xiao F, Ding W (2022) Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy Jenson-Shannon divergence and its application in multi-attribute decision making. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03347-0
Wen T, Cheong KH (2021) The fractal dimension of complex networks: a review. Inform Fus 73(2021):87–102
Xiao F (2020) Generalized belief function in complex evidence theory. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 38(4):3665–3673
Xiao F, Pedrycz W (2022) Negation of the quantum mass function for multisource quantum information fusion with its application to pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3167045
Xiao F, Wen J, Pedrycz W (2022) Generalized divergence-based decision making method with an application to pattern classification. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2022.3177896
Xie D, Xiao F, Pedrycz W (2021) Information quality for intuitionistic fuzzy values with its application in decision making. Eng Appl Artif Intell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104568
Xiong L, Su X, Qian H (2021) Conflicting evidence combination from the perspective of networks. Inf Sci 580(2021):408–418
Xu X, Zheng J, Yang J-B, Xu D-L, Chen Y-W (2017) Data classification using evidence reasoning rule. Knowl-Based Syst 116(2017):144–151
Xue W, Xu Z, Zhang X, Tian X (2018) Pythagorean fuzzy LINMAP method based on the entropy theory for railway project investment decision making. Int J Intell Syst 33(1):93–125
Yager RR (2014) Pythagorean Membership Grades in Multicriteria Decision Making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(4):958–965
Zadeh L (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zhang L, Xiao F (2022) A novel belief \(\chi \)2 divergence for multisource information fusion and its application in pattern classification. Int J Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22912
Zhang X, Xu Z (2014) Extension of TOPSIS to multiple criteria decision making with Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 29(12):1061–1078
Zhi P, Xu Y, Chen B (2020) Time-dependent reliability analysis of the motor hanger for EMU based on stochastic process. Int J Struct Integr 11(3):453–469
Zhou M, Liu X-B, Chen Y-W, Qian X-F, Yang J-B, Wu J (2020) Assignment of attribute weights with belief distributions for MADM under uncertainties. Knowl-Based Syst 189(2020):105110
Zhou Q, Mo H, Deng Y (2020) A new divergence measure of Pythagorean fuzzy sets based on belief function and its application in medical diagnosis. Mathematics 8(1):2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8010142
Zhu C, Xiao F, Cao Z (2022) A generalized Rényi divergence for multi-source information fusion with its application in EEG data analysis. Inform Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.05.012
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the reviewers’ suggestions and the editor’s encouragement. This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62003280), Chongqing Talents: Exceptional Young Talents Project (cstc2022ycjhbgzxm0070), and Chongqing Overseas Scholars Innovation Program (No. cx2022024). In addition, this study is partially supported by Dr. Cao’s ARC DECRA Fellowship DE220100265.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Xiao, F. & Cao, Z. Uncertainty measurements for Pythagorean fuzzy set and their applications in multiple-criteria decision making. Soft Comput 26, 9937–9952 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07361-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07361-9