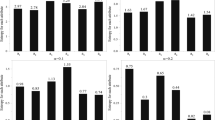
Abstract
In the real world, there may exist manifold data (e.g., Boolean, categorical, real-valued, set-valued, interval-valued, image, decision and missing data or attributes) in an information system which is referred to as a hybrid information system with images (HISI). Handling an HISI is conducive to generalize applications of rough set theory. This paper studies entropy measurement for a hybrid information system with images and considers an application for attribute reduction. We first give the distance between information values on each attribute in an HISI. Then, we present tolerance relations on the object set of an HISI based on this distance. Next, we define the rough approximations in an HISI by means of the presented tolerance relations. Furthermore, we study entropy measurement for an HISI by using \(\theta \)-information entropy, \(\theta \)-conditional information entropy and \(\theta \)-joint information entropy. Based on Kryszkiewicz’s ideal, we introduce the concepts of \(\theta \)-generalized decision and \(\theta \)-consistent in an HISI. Finally, we apply entropy measurement to perform attribute reduction in a \(\theta \)-consistent HISI. It is worth mentioning that attribute reduction based on generalized decision and common attribute reduction in a \(\theta \)-consistent HISI are the same.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Beaubouef T, Petry FE, Arora G (1998) Information-theoretic measures of uncertainty for rough sets and rough relational databases. Inf Sci 109:185–195
Cament LA, Castillo LE, Perez JP, Galdames FJ, Perez CA (2014) Fusion of local normalization and Gabor entropy weighted features for face identification. Pattern Recognit 47(2):568–577
Chen JZ, Hu JJ, (2022) Zhang GQ Feature selection based on gain ratio in hybrid incomplete information systems. In: 2021 IEEE international conference on intelligent systems and knowledge engineering, vol 4, pp 728–735
Cornelis C, Jensen R, Martin GH, Slezak D (2010) Attribute selection with fuzzy decision reducts. Inf Sci 180:209–224
Dai JH, Xu Q (2013) Attribute selection based on information gain ratio in fuzzy rough set theory with application to tumor classification. Appl Soft Comput 13(1):211–221
Dai JH, Wang WT, Xu Q, Tian HW (2012) Uncertainty measurement for interval-valued decision systems based on extended conditional entropy. Knowl Based Syst 27:443–450
Dai JH, Xu Q, Wang WT, Tian HW (2012) Conditional entropy for incomplete decision systems and its application in data mining. Int J Gen Syst 41(7):713–728
Dai JH, Wang WT, Mi JS (2013) Uncertainty measurement for interval-valued information systems. Inf Sci 251:63–78
Dai JH, Hu H, Zheng GJ, Hu QH, Han HF, Shi H (2016) Attribute reduction in interval-valued information systems based on information entropies. Front Inf Technol Electron Eng 17(9):919–928
De Luca A, Termini S (1972) A definition of nonprobilistic entropy in the setting of fuzzy sets theory. Inf Control 20:301–312
Delgado A, Romero I (2016) Environmental conflict analysis using an integrated grey clustering and entropy-weight method: a case study of a mining project in Peru. Environ Model Softw 77:108–121
Dntsch I, Gediga G (1998) Uncertainty measures of rough set prediction. Artif Intel 106:283–297
Greco S, Inuiguchi M, Slowinski R (2006) Fuzzy rough sets and multiple premise gradual decision rules. Int J Approx Reason 41:179–211
Hempelmann CF, Sakoglu U, Gurupur VP, Jampana S (2016) An entropy-based evaluation method for knowledge bases of medical information systems. Expert Syst Appl 46:262–273
Hu Q, Yu D, Liu J, Wu C (2008) Neighborhood rough set based heterogeneous feature subset selection. Inf Sci 178(18):3577–3594
Kadkhodaei HR, Moghadam AME, Dehghan M (2020) HBoost: a heterogeneous ensemble classifier based on the Boosting method and entropy measurement. Expert Syst Appl 157:113482
Kryszkiewicz M (1998) Rough set approach to incomplete information Systems. Inf Sci 112:39–49
Kryszkiewicz M (1999) Rules in incomplete information systems. Inf Sci 113:271–292
Li CR, Duan GD, Zhong FJ (2015) Rotation invariant texture retrieval considering the scale dependence of Gabor wavelet. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(8):2344–2354
Li ZW, Liu XF, Zhang GQ, Xie NX, Wang SC (2017) A multi-granulation decision theoretic rough set method for distributed fc-decision information systems: an application in medical diagnosis. Appl Soft Comput 56:233–244
Li ZW, Qu LD, Zhang GQ, Xie NX (2021) Attribute selection for heterogeneous data based on information entropy. Int J Gen Syst 50:548–566
Liang JY, Li DY (2005) Uncertainty and knowledge acquisition in information systems. Science Press, Beijing
Liang BH, Wang L, Liu Y (2018) Attribute reduction based on improved information entropy. Intel Fuzzy Syst 36:1–10
Maji P (2012) Rough hypercuboid approach for feature selection in approximation spaces. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 99:1–14
Navarrete J, Viejo D, Cazorla M (2016) Color smoothing for RGB-D data using entropy information. Appl Soft Comput 46:361–380
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11:341–356
Pawlak Z (1991) Rough sets: theoretical aspects of reasoning about data. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Pawlak Z, Skowron A (2007) Rough sets and Boolean reasoning. Inf Sci 177:41–73
Qian YH, Liang JY (2006) Combination entropy and combination granulation in incomplete information system. Lecture Notes Artif Intel 4062:184–190
Qu LD, He JL, Zhang GQ, Xie XN (2022) Entropy measure for a fuzzy relation and its application in attribute reduction for heterogeneous data. Appl Soft Comput 118:1–12
Sakai H, Nakata M, Slezak D (2011) A prototype system for rule generation in Lipskis incomplete information databases. In: Proceedings of 13th rough sets, fuzzy sets, data mining and granular computing, pp 175–182
Sang BB, Chen HM, Yang L, Li TR, Xu WH (2021) Incremental feature selection using a conditional information entropy based on fuzzy dominance neighborhood rough sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2021.3064686
Shannon C (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27:379–423
Singh S, Shreevastava S, Som T, Somani G (2020) A fuzzy similarity-based rough set approach for attribute selection in set-valued information systems. Soft Comput 24:4675–4691
Slowinski R, Vanderpooten D (2000) A generalized definition of rough approximations based on similarity. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 12:331–336
Sun BZ, Gong ZT, Chen DG (2008) Fuzzy rough set theory for the interval-valued fuzzy information systems. Inf Sci 178:2794–2815
Swiniarski RW, Skowron A (2003) Rough set methods in feature selection and recognition. Pattern Recognit Lett 24:833–849
Wang H, Yue HB (2016) Entropy measures and granularity measures for interval and set-valued information systems. Soft Comput 20:3489–3495
Wang YB, Chen XJ, Dong K (2019) Attribute reduction via local conditional entropy. Mach Learn Cybern 10(12):3619–3634
Wang P, Zhang PF, Li ZW (2019) A three-way decision method based on Gaussian kernel in a hybrid information system with images: an application in medical diagnosis. Appl Soft Comput 77:734–749
Xie SD, Wang YX (2014) Construction of tree network with limited delivery latency in homogeneous wireless sensor networks. Wirel Pers Commun 78(1):231–246
Xie XL, Li ZW, Zhang PF, Zhang GQ (2019) Information structures and uncertainty measures in an incomplete probabilistic set-valued information system. IEEE Access 7:27501–27514
Yang T, Li QG (2010) Reduction about approximation spaces of covering generalized rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 51(3):335–345
Yang XB, Yu DJ, Yang JY, Wei L (2009) Dominance-based rough set approach to incomplete interval-valued information system. Data Knowl Eng 68(11):1331–1347
Yao YY (1998) Relational interpretations of neighborhood operators and rough set approximation operators. Inf Sci 111:239–259
Yao YY (2001) Information granulation and rough set approximation. Int J Intel Syst 16:87–104
Yu GJ (2019) Information structures and uncertainty measures in a hybrid information system with images. Soft Comput 23:12961–12979
Zeng AP, Li TR, Liu D, Zhang JB, Chen HM (2015) A fuzzy rough set approach for incremental feature selection on hybrid information systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst 258:39–60
Zeng AP, Li TR, Hu J, Chen HM, Luo C (2017) Dynamical updating fuzzy rough approximations for hybrid data under the variation of attribute values. Inf Sci 378:363–388
Zhang X, Mei CL, Chen DG, Li JH (2016) Feature selection in mixed data: a method using a novel fuzzy rough set-based information entropy. Pattern Recognit 56:1–16
Zhang GQ, Song Y, Liao SM, Qu LD, Li ZW (2022) Uncertainty measurement for a three heterogeneous information system and its application in feature selection. Soft Comput 26:1711–1725
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions which have helped immensely in improving the quality of this paper.
Funding
Funding was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (2022GXNSFAA035552, 2021GXNSFAA220114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, G. et al. Entropy measurement for a hybrid information system with images: an application in attribute reduction. Soft Comput 26, 11243–11263 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07502-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07502-0