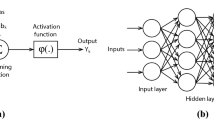
Abstract
Art, like language, is a method for expressing a person's thoughts and opinions to others. Art design is a way of conveying human sentiments and emotions, particularly via the use of visual structures such as paintings or drawings. Every element of our lives, including arts and crafts, has been favorably influenced by the introduction of innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning (DL). In today's modern era, the technologies have revolutionized the way art is created, consumed, and distributed. Machine learning and human emotions are the two most important aspects of interactive and high-quality art design. In the teaching and learning of art-related courses, AI and machine learning are used to develop students' creative talents more successfully than traditional learning methods. With the use of information technology, designers build and design more productive artwork in very little time and with much less effort. In the evolution and creation of interactive and intelligent digital art, artificial intelligence and machine learning are playing a highly positive role. Art developed with the use of these approaches is capable of conveying human emotions and sentiments precisely and correctly. The proposed study presents a comprehensive overview of various AI-grounded smart and intelligent applications employed for the betterment and development of art design. The study provided a summary of the existing approaches used in the area of art design for the designing of high-quality and precise artwork. Then, based on the proposed overview, various features are extracted from the existing literature. From these extracted features, important features were selected for the decision-making procedure and ranking. To perform the decision-making process for the ranking of the accessible alternatives, the Graph Theory Matrix Approach was applied. The results of the study show effectiveness of the AI-based systems for art design.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Bonnardel N, Zenasni F (2010) The impact of technology on creativity in design: an enhancement? Creat Innov Manag 19(2):180–191
Castellano G, Vessio G (2021) Deep learning approaches to pattern extraction and recognition in paintings and drawings: an overview. Neural Comput Appl 33(19):12263–12282
Chen L, Chen P (2020) Interactive art design aided by artificial intelligence. In Education and Awareness of Sustainability: Proceedings of the 3rd Eurasian Conference on Educational Innovation 2020 (ECEI 2020), pp 491–495, World Scientific.
Chen W, Shidujaman M, Tang X (2020) AiArt: towards artificial intelligence art. In: The 12th International Conference on Advances in Multimedia
Deng Y (2021) Application of artificial intelligence in art design, In: 2021 International Conference on Computer Technology and Media Convergence Design (CTMCD), pp 200–203, IEEE.
Deng J, Chen X (2021) Research on artificial intelligence interaction in computer-aided arts and crafts. Mob Inf Syst, 2021.
Hong J-W, Curran NM (2019) Artificial intelligence, artists, and art: attitudes toward artwork produced by humans vs. artificial intelligence. ACM Trans Multimedia Comput Commun Appl 15(2s):1–16
Hou Y, Xu XF (2021) Research on art design and application of indoor environment based on Artificial Intelligence. E3S Web Conf 275:03036
Hu J, Fu L (2022) Innovation and Development of environmental art design thinking based on artificial intelligence in culture, form and function. In: International Conference on Cognitive based Information Processing and Applications (CIPA 2021), pp 635–642, Springer.
Kong F (2020) Application of artificial intelligence in modern art teaching. Int J Emerg Technol Learn 15(13):238–251
Li Y (2021) "Intelligent Environmental art design combining big data and artificial intelligence. Complexity, 2021
Li J, Zhang B (2022) The application of artificial intelligence technology in art teaching taking architectural painting as an example. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022.
Lin Y (2020) Research on application and breakthrough of artificial intelligence in art design in the new era. J Phys Conf Ser 1648(3):032187
Lin C (2021) Application of traditional cultural symbols in art design under the background of artificial intelligence. Math Probl Eng, 2021.
Liu X (2020) Artistic reflection on artificial intelligence digital painting. J Phys Conf Ser 1648(3):032125
Mazzone M, Elgammal A (2019) Art, creativity, and the potential of artificial intelligence. Arts 8(1):26
Nemade R, Nitsure A, Hirve P, Mane SB (2017) “Detection of forgery in art paintings using machine learning,” Int. J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol 6(5):8681–8692
Niu Z, Xiang S, Zhang M (2022) Application of artificial intelligence combined with three-dimensional digital technology in the design of complex works of art, Wirel Commun Mob Comput, 2022
Rao RV, Padmanabhan K (2007) Rapid prototyping process selection using graph theory and matrix approach. J Mater Process Technol 194(1–3):81–88
Shen Y, Yu F (2021) The influence of artificial intelligence on art design in the digital age. Sci Program. 2021.
Yang R (2020) Artificial intelligence-based strategies for improving the teaching effect of art major courses in colleges. Int J Emerg Technol Learn 15(22):146–160
Zhang W, Tsai SB (2021) An empirical study on the artificial intelligence-aided quantitative design of art images. Wirel Commun Mob Comput. 2021
Zhai Q (2022) Application of artificial intelligence in art design. In: 2021 International Conference on Big Data Analytics for Cyber-Physical System in Smart City, pp 981–986, Springer.
Zujovic J, Gandy L, Friedman S, Pardo B, Pappas TN (2009) Classifying paintings by artistic genre: an analysis of features & classifiers. In: 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, pp 1–5, IEEE.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The paper does not deal with any ethical problems.
Informed consent
We declare that all the authors have informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wenjing, X., Cai, Z. Assessing the best art design based on artificial intelligence and machine learning using GTMA. Soft Comput 27, 149–156 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07555-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07555-1