Abstract
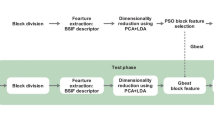
This paper proposes a novel binary particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm using artificial immune system (AIS) for face recognition. Inspired by face recognition ability in human visual system (HVS), this algorithm fuses the information of the holistic and partial facial features. The holistic facial features are extracted by using principal component analysis (PCA), while the partial facial features are extracted by non-negative matrix factorization with sparseness constraints (NMFs). Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) is then applied to enhance adaptability to illumination and expression. The proposed algorithm is used to select the fusion rules by minimizing the Bayesian error cost. The fusion rules are finally applied for face recognition. Experimental results using UMIST and ORL face databases show that the proposed fusion algorithm outperforms individual algorithm based on PCA or NMFs.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The ORL database is available from http://www.cam-orl.co.uk/facedatabase.html
References
Jain AK, Ross A, Prabhakar S (2004) An introduction to biometric recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I 14(1):4–20
Lee DD, Seung HS (1999) Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 401:788–791
Patrik OH (2004) Non-negative matrix factorization with sparseness constraints. J Mach Learn Res 5:1457–1469
Pu XR, Yi Z et al (2005) Face recognition using fisher non-negative matrix factorization with sparseness constraints. Lect Notes Comput Sci LNCS 3497, pp. 112–117
Turk MA, Pentland (1991) A face recognition using eigenfaces. Computer vision and pattern recognition, 1991. Proc. CVPR ’91., IEEE Computer Society Conference, pp. 586–591 3–6 June 1991
Turk MA, Pentland A (1991) Eigenfaces for recognition. J Cogn Neurosci 3:71–86
Zhao W, Chellappa R, Rosenfeld A, Phillips P (2000) Face recognition: a literature survey. Technical Report CAR-TR-948, University of Maryland
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on neural networks. IV, 1942–1948, IEEE Service Center, Piscataway, NJ
Eberhart RC, Shi Y (1998) Evolving artificial neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on neural networks and brain, Beijing, China.
Fang Y, Tan T, Wang Y (2002) Fusion of global and local features for face verification. Pattern recognition, 2002. In: Proceedings of the 16th international conference, vol. 2, pp. 11–15, Aug 2002, see also vol. l2, pp. 382–385
Belhumeur PN, Hespanha JP, Kriegman DJ (1997) Eigenfaces vs. fisherfaces: recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19(7):711–720
Martinez AM, Kak AC (2001) PCA versus LDA. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(2):228–233
Brunelli R, Falavigna D (1995) Person identification using multiple cues. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 17(10):955–966
Ross A, Jain AK (2003) Information Fusion in Biometrics. Pattern Recognition Letters 24(13):2115–2125
Veeramachaneni K, Osadciw L, Varshney P (2005) An adaptive multimodal biometric management algorithm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern C Appl Rev, 35(3):344–356
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1997) A discrete binary version of the particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of the 1997 Conference System, Man, Cybernetics. Piscataway, NJ
Afshinmanesh F, Marandi A, Rahimi-Kian A (2007) A novel binary particle swarm optimization method using artificial immune system. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer as a tool (EUROCON 2005) (in press)
Abraham A, He Guo, and Hongbo Liu (2006) Swarm intelligence: foundations, perspectives and applications in swarm intelligence in data mining. In: Abraham A, Grosan C, Ramos V (eds) Studies in computational intelligence, p. 300, Springer, Germany, 2006
Liu H, Abraham A (2005) Fuzzy turbulent particle swarm optimization. In: Proceeding of the 5th international conference on hybrid intelligent systems, Brazil. IEEE CS Press, USA
Pohlheim H (2005) Genetic algorithm toolbox test functions. Department of Automatic Control and Systems Engineering, University of Sheffield
William Spears, C function code [Online]. Available: http://www.aic.nrl.navy.mil/spears/functs.dejong.html
Graham D, Allinson N (1998) [Online]. The UMIST database is available from: http://images. ee.umist.ac.uk/danny/database.html
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Miss Sheekha for proof reading this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by National Science Foundation of China under Grant 60471055, and UESTC Youth Fund under Grant L08010601JX04030.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, X., Yi, Z. & Fang, Z. Holistic and partial facial features fusion by binary particle swarm optimization. Neural Comput & Applic 17, 481–488 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-007-0148-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-007-0148-0