Abstract
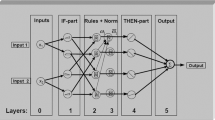
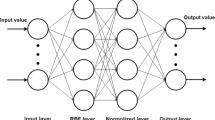
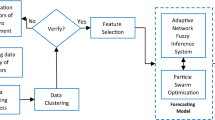
Reliable business performance forecasting of convenience store (CVS) can not only help in making the correct local selection decision but also in decreasing the store cost and thereby enlarging the profit significantly. Therefore, the main aim of this paper is to design an enhanced fuzzy neural network (EFNN)-based predictor to forecast the business performance of CVS. Without considering relevant domain knowledge, traditional fuzzy neural networks suffer from the problem of low accuracy of forecasting unseen examples. Moreover, traditional fuzzy neural networks have to turn weights with a kind of time-consuming gradient steepest descent training algorithm. Considering the relationship between the evaluation factors globally, we devise the EFNN which assigns connection weights based on the expert domain knowledge without painstakingly and repeatedly turning them. Furthermore, by generating and refining the activation function based on genetic algorithm, our EFNN can provide comprehensive and accurate activation functions and fit a wider range of nonlinear models. By experimenting our methods with several benchmark methods, the proposed methods are found to have an optimal accuracy in forecasting the business performance of CVS with a permanent good performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Applebaum W (1996) Method for determining store trade areas, marketing penetration and potential sales. J Mark Res 3:124–141
Berman B, Evans JR (2003) Retail management: a strategic approach, 9th edn. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Chang PC, Lai CY (2005) A hybrid system combining self organizing maps with case-based reasoning in wholesaler’s new-release book forecasting. Expert Syst Appl 29:183–192
Chang PC, Wang YW, Tsai CY (2005) Evolving neural network for printed circuit board sales. Expert Syst Appl 29:83–92
Chang PC, Wang YW (2006) Fuzzy Delphi and back-propagation model for sales forecasting in PCB industry. Expert Syst Appl 30:715–726
Charytoniuk W, Box ED, Lee WJ, Chen MS (2000) Neural-network-based demand forecasting in a deregulated environment. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 36:93–898
Chen D, Yuan XJ (2004) A Markov model for seasonal forecast of Antarctic sea ice. J Clim 17:3156–3168
Chu CW, Zhang GQ (2003) A comparative study of linear and nonlinear models for aggregate retail sales forecasting. Int J Prod Econ 86:217–231
Coelho CAS, Pezzulli S, Balmaseda M (2004) Forecast calibration and combination: a simple Bayesian approach for ENSO. J Clim 17:1504–1516
Craig CS, Ghosh A, Me LS (1984) Model of the retail location process: a review. J Retail 60:5–36
Goldberg DE (1989) Algorithm in search optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Gorucu FB, Geris PU, Gumrah F (2004) Artificial neural network modeling for forecasting gas consumption. Energy Sources 26:299–307
Haykin S (1999) Neural networks, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Holland JH (1992) Genetic algorithms. Science 267:44–150
Ishibuchi H,Yamamoto T (2004) Fuzzy rule selection by multi-objective genetic local search algorithms and rule evaluation measures in data mining. Fuzzy Sets Syst 141:59–88
Jiang CW (2005) Chain store administration. Science Press, Beijing
Jones C, Carvalho LMV, Higgins RW (2004) A statistical forecast model of tropical intraseasonal convective anomalies. J Clim 17:2078–2095
Kuo RJ (2001) A sales forecasting system based on fuzzy neural network with initial weights generated by genetic algorithm. Eur J Oper Res 129:496–517
Kuo RJ, Chi SC, Kao SS (2002) A decision support system for selection convenience store location through integration of fuzzy AHP and artificial network. Comput Ind 47:199–214
Lam M (2004) Neural network techniques for financial performance prediction: integrating fundamental and technical analysis. Decis Support Syst 37:567–581
Li SG,Wu ZM, Pang XH (2005) Job shop in real time case. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26:870–875
McCauley-Bell P, Badiru A (1996) Fuzzy modeling and analytic hierarchy processing—means to quantify risk levels associated with occupational injuries—part II: the development of a fuzzy rule-based model for the prediction of injury. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 4:132–138
Pantelidaki S, Bunn DW (2005) Development of a multifunctional sales response model with the diagnostic aid of artificial neural networks. J Forecast 24:505–521
Zhang B, Zhang Y, Chen D (2004) A quantitative evaluation system of soil productivity for intensive agriculture in China. Geoderma 123:319–331
Zhao FY (2003) Theory of supermarket management. Enterprise Management Publishing House, Beijing
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (No. 70501021, 70418013 and 60574049) and the National High Tech Committee. The authors express their sincere thanks to the anonymous referees, with whose valuable help the quality of the paper has been very much improved.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S.G., Wu, Z.M. Business performance forecasting of convenience store based on enhanced fuzzy neural network. Neural Comput & Applic 17, 569–578 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-007-0158-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-007-0158-y