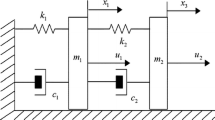
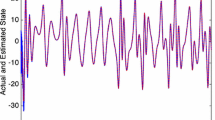
Abstract
Compared to normal learning algorithms, for example backpropagation, the optimal bounded ellipsoid (OBE) algorithm has some better properties, such as faster convergence, since it has a similar structure as Kalman filter. OBE has some advantages over Kalman filter training, the noise is not required to be Guassian. In this paper OBE algorithm is applied in training the weights of the feedforward neural network for nonlinear system identification. Both hidden layers and output layers can be updated. From a dynamic system point of view, such training can be useful for all neural network applications requiring real-time updating of the weights. Two simulations give the effectiveness of the suggested algorithm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bland RG, Goldfarb D, Todd MJ (1981) The ellipsoid method: a survey. Oper Res 29:1039–1091
Chowdhury FN (2003) A new approach to real-time training of dynamic neural networks. Int J Adapt Control Signal Process 31:509–521
Correa MV, Aguirre LA, Saldanha RR (2002) Using steady-state prior knowledge to constrain parameter estimates in nonlinear system identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Part I 49(9):1376–1381
Dickerson JA, Kosko B (1996) Fuzzy function approximation with ellipsoidal rules. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 26:542–560
Fogel E, Huang YF (1982) On the value of information in system identification: bounded noise case. Automatica 18(2):229–238
Gazor S, Shahtalebi K (2002) A new NLMS algorithm for slow noise magnitude variation. IEEE Signal Process Lett 9(11):348–351
El Ghaoui (2001) Robust filtering for discrete-time systems with bounded noise and parametric uncertainty. IEEE Trans Autom Control 46(7):1084–1089
Gollamudi S, Nagaraj S, Kapoor S, Huang YF (1996) Set membership state estimation with optimal bounding ellipsoids. In: Proceedings of international symposium on information theory and its applications, Victoria, BC, Canada, pp 262–265
Goodwin GC, Sang Sin K (1984) Adaptive filtering prediction and control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffis
Haykin S (1994) Neural networks—a comprehensive foundation. Macmillan, New York
Jiang ZP, Wang Y (2001) Input-to-state stability for discrete-time nonlinear systems. Automatica 37(2):857–869
Jin L, Nikiforunk PN, Gupta MM (1999) Adaptive model reference control of discrete-time nonlinear systems using neural networks. Control Theory Adv Technol Part 3 10(4):1373–1399
Joachim D, Deller JR (2006) Multiweight optimization in optimal bounding ellipsoid algorithms. IEEE Trans Signal Process 54(2):679–690
Kapoor S, Gollamudi S, Nagaraj S, Huang YF (1996) Tracking of time-varing parameters using optimal bounding ellipsoid algorithms. In: Proceedings of 34th Allerton conference on communication, control and computing Monticello
Kayuri NS, Vienkatasubramanian V (1993) Representing bounded fault classes using neural networks with ellipsoidal activation functions. Comput Chem Eng 17(2):139–163
Kosmatopoulos EB, Polycarpou MM, Christodoulou MA, Ioannou PA (1995) High-order neural network structures for identification of dynamical systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 6(2):422–431
Liguni Y, Sakai H, Higekatsu Tokumaru (1992) A real-time learning algorithm for a multilayered neural network based on the extended Kalman filter. IEEE Trans Signal Process 40(4):959–966
Lorenz RG, Boyd SP (2005) Robust minimum variance beamforming. IEEE Trans Signal Process 53(5):1684–1696
Narendra KS, Parthasarathy K (1990) Identification and control of dynamical systems using neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 1(1):4–27
Nazin SA, Polyak BT (2001) Limiting behavior of bounding ellipsoids for state estimation. In: Proceedings of the 5th IFAC symposium on nonlinear control systems, St Petersburg, Russia, vol 4–6, pp 585–589
Parlos AG, Menon SK, Atiya AF (2001) An algorithm approach to adaptive state filtering using recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(6):1411–1432
Puskorius GV, Feldkamp LA (1994) Neurocontrol of nonlinear dynamical systems with Kalman filter trained recurrent networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5(2):279–297
Ros L, Sabater A, Thomas F (2002) An ellipsoidal alculus based on propagation and fusion. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 32(4):430-442
Rubio JJ, Yu W (2005) Dead-zone Kalman filter algorithm for recurrent neural networks. In: 44rd IEEE conference on decision and control, CDC’05, Seville, Spain, pp 2562–2567
Ruck DW, Rogers SK, Kabrisky M, Maybeck PS, Oxley ME (1992) Comparative analysis of backpropagation and the extended Kalman filter for training multilayer perceptrons. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 14(6):686–691
Safonov MG, Athans M (1978) Robustness and computational aspects of nonlinear stochastic estimators and regulators. IEEE Trans Autom Control 23(4):717–725
Sastry PS, Santharam G, Unnikrishnan KP (1994) Memory neural networks for identification and control of dynamic systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5:306–319
Schueppe FC (1973) Uncertain dynamic systems. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Singhal S, Wu L (1989) Training multilayer perceptrons with the extended Kalman algorithm. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst I 133–140
Weyer E, Campi MC (2000) Non-asymptotic confidence ellipsoids for the least squares estimate. In: 39rd IEEE conference on decision and control, Sydney, Australia, pp 2688–2693
Wang LX (1997) A course in fuzzy systems and control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Yu W (2002) Nonlinear system identification using discrete-time recurrent neural networks with stable learning algorithms. Inf Sci 158(1):131–147
Yu W, Ferreyra A (2005) On-line clustering for nonlinear system identification using fuzzy neural networks. In: IEEE international conference on fuzzy systems, pp 678–683
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Jesús Rubio, J., Yu, W. & Ferreyra, A. Neural network training with optimal bounded ellipsoid algorithm. Neural Comput & Applic 18, 623–631 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-008-0203-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-008-0203-5