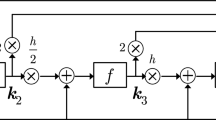
Abstract
In order to conveniently analyze the stability of various discrete-time recurrent neural networks (RNNs), including bidirectional associative memory, Hopfield, cellular neural network, Cohen-Grossberg neural network, and recurrent multiplayer perceptrons, etc., the novel neural network model, named standard neural network model (SNNM) is advanced to describe this class of discrete-time RNNs. The SNNM is the interconnection of a linear dynamic system and a bounded static nonlinear operator. By combining Lyapunov functional with S-Procedure, some useful criteria of global asymptotic stability for the discrete-time SNNMs are derived, whose conditions are formulated as linear matrix inequalities. Most delayed (or non-delayed) RNNs can be transformed into the SNNMs to be stability analyzed in a unified way. Some application examples of the SNNMs to the stability analysis of the discrete-time RNNs shows that the SNNMs make the stability conditions of the RNNs easily verified.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warwich K (1995) Neural networks: an introduction. Neural network applications in control. In: Irwin GW, Warwick K, Hunt KJ (eds) The Institution of Electrical Engineers, London, pp 1–16
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle JPL, De Moor BLR (1996) Artificial neural networks for modeling and control of non-linear systems. Kluwer, Boston
Medsker LR, Jain LC (eds) (2000) Recurrent neural networks: design and applications, CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton
Miyoshi S, Yanai HF, Okada M (2004) Associative memory by recurrent neural networks with delay elements. Neural Netw 17(1):55–63. doi:10.1016/S0893-6080(03)00207-7
Xia Y, Wang J (2004) A recurrent neural network for nonlinear convex optimization subject to nonlinear inequality constraints. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 51(7):1385–1394. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2004.830694
Liao XF, Chen GR, Sanchez EN (2002) LMI-based approach for asymptotically stability analysis of delayed neural networks. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I Fundam Theory Appl 49(7):1033–1039. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2002.800842
Liao XF, Chen GR, Sanchez EN (2002) Delay-dependent exponential stability analysis of delayed neural networks: an LMI approach. Neural Netw 15(7):855–866. doi:10.1016/S0893-6080(02)00041-2
Guo S, Huang L (2004) Exponential stability of discrete-time Hopfield neural networks. Comput Math Appl 47(8–9):1249–1256. doi:10.1016/S0898-1221(04)90119-8
Liang J, Cao J, Ho DWC (2005) Discrete-time bidirectional associative memory neural networks with variable delays. Phys Lett A 335(2–3):226–234. doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2004.12.026
Xiong W, Cao J (2005) Global exponential stability of discrete-time Cohen–Grossberg neural networks. Neurocomputing 64:433–446. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2004.08.004
Liu MQ (2006) Discrete-time delayed standard neural network model and its application. Sci China Ser F Inf Sci 49(2):137–154. doi:10.1007/s11432-006-0137-4
Barabanov NE, Prokhorov DV (2002) Stability analysis of discrete-time recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13(2):292–303. doi:10.1109/72.991416
Zhang SL, Liu MQ (2005) Stability analysis of discrete-time BAM neural networks based on standard neural network models. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 6A(7):689–696. doi:10.1631/jzus.2005.A0689
Wang L, Xu Z (2006) Sufficient and necessary conditions for global exponential stability of discrete-time recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 53(6):1373–1380. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2006.874179
Mak KL, Peng JG, Xu ZB, Yiu KFC (2007) A new stability criterion for discrete-time neural networks: nonlinear spectral radius. Chaos Solitons Fractals 31(2):424–436. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2005.09.075
Hu S, Wang J (2002) Global stability of a class of discrete-time recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Fundam Theory Appl 49(8):1104–1117. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2002.801284
Liu MQ (2007) Delayed standard neural network models for control systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 18(5):1376–1391. doi:10.1109/TNN.2007.894084
Chandrasekharan PC (1996) Robust control of linear dynamical systems. Academic Press, London
Rios-Patron E (2000) A general framework for the control of nonlinear systems, PhD thesis, University of Illinois
Boyd SP, Ghaoui LE, Feron E, Balakrishnan V (1994) Linear matrix inequalities in system and control theory. SIAM, Philadelphia
Li CD, Liao XF, Zhang R (2004) Global asymptotical stability of multi-delayed interval neural networks: an LMI approach. Phys Lett A 328(6):452–462. doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2004.06.053
Xie L, de Souza CE (1992) Robust H∞ control for linear systems with norm-bounded time-varying uncertainty. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 37(8):1188–1191. doi:10.1109/9.151101
Khargonekar PP, Petersen IR, Zhou K (1990) Robust stabilization of uncertain linear systems: quadratic stability and H∞ control theory. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 35(3):356–361. doi:10.1109/9.50357
Bhaya A, Kaszkurewicz E, Kozyakin VS (1996) Existence and stability of a unique equilibrium in continuous-valued discrete-time asynchronous Hopfield neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 7(3):620–628. doi:10.1109/72.501720
Guo S, Huang L (2004) Periodic oscillation for discrete-time Hopfield neural networks. Phys Lett A 329(3):199–206. doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2004.07.007
Hopfield JJ (1984) Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-state neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81(10):3088–3092. doi:10.1073/pnas.81.10.3088
Gahinet P, Nemirovski A, Laub AJ, Chilali M (1995) LMI control toolbox- for use with Matlab. The MATH Works, Inc., Natick
Kosko B (1987) Adaptive bidirectional associative memories. Appl Opt 26(23):4947–4960
Kosko B (1988) Adaptive bi-directional associative memories. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 18(1):49–60. doi:10.1109/21.87054
Arik S, Tavsanoglu V (2005) Global asymptotic stability analysis of bidirectional associative memory neural networks with constant time delays. Neurocomputing 68:161–176. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2004.12.002
Cao J, Liang J, Lam J (2004) Exponential stability of high-order bidirectional associative memory neural networks with time delays. Physica D Nonlinear Phenomena 199(3–4):425–436. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2004.09.012
Wang L, Zou X (2004) Capacity of stable periodic solutions in discrete-time bidirectional associative memory neural networks. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 51(6):315–319. doi:10.1109/TCSII.2004.829571
Cohen MA, Grossberg S (1983) Absolute stability of global pattern formation and parallel memory storage by competitive neural network. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 13(5):815–826
Wang W, Cao J (2006) LMI-based criteria for globally robust stability of delayed Cohen-Grossberg neural networks. IEE Proc Contr Theory Appl 153(4):397–402. doi:10.1049/ip-cta:20050197
Guo S, Huang L (2006) Stability analysis of Cohen-Grossberg neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(1):106–117. doi:10.1109/TNN.2005.860845
Chen Y (2006) Global asymptotic stability of delayed Cohen-Grossberg neural network. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 53(2):351–357. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2005.856047
Cao J, Liang J (2004) Boundedness and stability for Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with time-varying delays. J Math Anal Appl 296(2):665–685. doi:10.1016/j.jmaa.2004.04.039
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 60504024 and 60874050, in part by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Y106010, and in part by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (SRFDP), China under Grant 20060335022. This work was also supported by the “151 Talent Project” of Zhejiang Province (No. 05-3-1013 and No. 06-2-034).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M. Stability analysis of discrete-time recurrent neural networks based on standard neural network models. Neural Comput & Applic 18, 861–874 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-008-0211-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-008-0211-5