Abstract
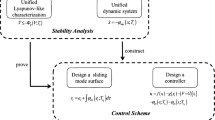
This paper deals with the synchronization of time-varying delay cellular neural networks. Based on the Lyapunov stability analysis and the zoned discussion and maximax synthesis (ZDMS) method, the quadratic matrix inequality (QMI) criterion for the guaranteed cost synchronous controller is designed to synchronize the given chaotic systems. For the convenience to solve, using a generalized result of Schur complement, the criterion in the form of QMI is turned into the linear matrix inequality (LMI) form, which can be used efficiently via existing numerical convex optimization algorithms such as the interior-point algorithms for solving LMIs. The minimization of the guaranteed cost is further studied, and the corresponding LMI criterion for getting the controller is given. Finally, numerical examples are given to show the effectiveness of proposed guaranteed cost synchronous control and its corresponding minimization problem.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Z, Sun J, Oh S (2009) Design, analysis and experimental validation of a robust nonlinear path following controller for marine surface vessels. Automatica 45(7):1649–1658
O’Brien JF (2009) Multi-path nonlinear dynamic compensation for rudder roll stabilization. Control Eng Pract 17(12):1405–1414
Brieger O, Kerr M, Leißling D, Postlethwaite I, Sofrony J, Turner MC (2009) Flight testing of a rate saturation compensation scheme on the ATTAS aircraft. Aerosp Sci Technol 13(2–3):92–104
Indiveri G, Paulus J, Plöger PG (2007) Motion control of Swedish wheeled mobile robots in the presence of actuator saturation. Lect Notes Comput Sci 4434:35–46
Pedra J, Candela I, Barrera A (2009) Saturation model for squirrel-cage induction motors. Electric Power Syst Res 79(7):1054–1061
Loboda V, Lapusta Y, Sheveleva A (2010) Limited permeable crack in an interlayer between piezoelectric materials with different zones of electrical saturation and mechanical yielding. Int J Solids Struct 47(14–15):1795–1806
Faldin N, Morzhov A, Boiko I (2009) Analysis of periodic motions in relay feedback systems with saturation in plant dynamics. Int J Syst Sci 40(6):659–668
Ponce FJM, Gómez FMF (2010) Stability, bifurcations and response analysis of time delay control system with initial conditions and saturation effects. In: 18th Mediterranean conference on control & automation, MED2010, Marrakech, June 2010, pp 987–992
Corsellas AG (2008/2009) Virtual orbits and two-parameter bifurcation analysis in power electronic converters [D]. Enginyeria de Sistemes, Universitat Politècnica de catalunya/Automàtica i Informàtica Industrial
Salarieh H (2007) Nonlinear feedback control of chaotic pendulum in presence of saturation effect. Chaos Solitons Fractals 31(2):292–304
Zeng ZG, Wang J (2007) Analysis and design of associative memories based on recurrent neural networks with linear saturation activation functions and time-varying delays. Neural Comput 19(8):2149–2182
Zeng ZG, Jun W (2009) Associative memories based on continuous-time cellular neural networks designed using space-invariant cloning templates. Neural Netw 22(5–6):651–657
Li N, Lu HX (2008) Single-electron tunneling depressing synapse for cellular neural networks. Neural Comput Appl 17(2):111–118
Su TJ, Huang MY, Hou CL, Lin YJ (2010) Cellular neural networks for gray image noise cancellation based on a hybrid linear matrix inequality and particle swarm optimization approach. Neural Process Lett 32(2):147–165
Leine RI, van Campen DH (2006) Bifurcation phenomena in non-smooth dynamical systems. Eur J Mech A/Solids 25(4):595–616
Leine RI (2006) Bifurcations of equilibria in non-smooth continuous systems. Physica D: Onlinear Phenomena 223(1):121–137
Leine RI, van de Wouw N (2008) Stability and convergence of mechanical systems with unilateral constraints. Springer, Berlin
Hu T, Teel AR (2006) Stability and performance for saturated systems via quadratic and nonquadratic Lyapunov functions. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 51(11):1770–1786
Dai D, Hu T, Teel AR (2007) Analysis of systems with saturation/deadzone via piecewise–quadratic Lyapunov functions. In: American control conference, ACC2007, New York, pp 5822–5827
Zhang LX, Boukas EK, Haidar A (2008) Delay-range-dependent control synthesis for time-delay systems with actuator saturation. Automatica 44(10):2691–2695
Shi T, Su HY, Chu J (2010) On stability and stabilization for uncertain stochastic systems with time-delay and actuator saturation. Int J Syst Sci 41(5):501–509
Kao YG, Gao CC (2008) Global exponential stability analysis for cellular neural networks with variable coefficients and delays. Neural Comput Appl 17(3):291–295
Yakoubi K, Chitour Y (2007) Linear systems subject to input saturation and time delay: global asymptotic stabilization. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 52(5):874–879
Xin H, Gan D, Qiu J (2008) Stability analysis of linear dynamical systems with saturation nonlinearities and a short time delay. Phys Lett A 372(22):3999–4009
Fang HJ, Lin ZL, Shamash Y (2006) Disturbance tolerance and rejection of linear systems with imprecise knowledge of actuator input output characteristics. Automatica 42(9):1523–1530
Kebriaei H, Yazdanpanah MJ (2010) Robust adaptive synchronization of different uncertain chaotic systems subject to input nonlinearity. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 15(2):430–441
Wang K, Teng ZD, Jiang HJ (2010) Global exponential synchronization in delayed reaction-diffusion cellular neural networks with the Dirichlet boundary conditions. Math Comput Model 52(1–2):12–24
Khalil HK (2002) Nonlinear systems, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Fliegner T, Logemann H, Ryan EP (2003) Low-gain integral control of continuous-time linear systems subject to input and output nonlinearities. Automatica 39(3):455–462
Fan Y, Jiang ZP, Zhang H (2006) Network flow control under capacity constraints: a case study. Syst Control Lett 55(8):681–688
Hu TS, Lin ZL, Chen BM (2002) An analysis and design method for linear systems subject to actuator saturation and disturbance. Automatica 38(2):351–359
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 60974136).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, J., He, H. & Xiong, P. Guaranteed cost synchronous control of time-varying delay cellular neural networks. Neural Comput & Applic 22, 103–110 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0667-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0667-6