Abstract
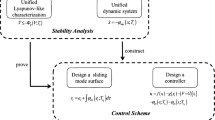
This paper presents the chaos suppression problem in the class of Hopfield neural networks (HNNs) with input nonlinearity using inverse optimality approach. Using the inverse optimality technique and based on Lyapunov stability theory, a stabilizing control law, which is optimal with respect to meaningful cost functional, is determined to achieve global asymptotically stability in the closed-loop system. Numerical simulation is performed on a four-dimensional hyper-chaotic HNN to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yuan Y (2007) Dynamics in a delayed-neural network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 33:443–454
Cheng CJ (2008) Robust control of a class of neural networks with bounded uncertainties and time-varying delays. Comput Math Appl 56:1245–1254
Lu JG, Chen G (2009) Global asymptotical synchronization of chaotic neural networks by output feedback impulsive control: an LMI approach. Chaos Solitons Fractals 41:2293–2300
Wena UP, Lan KM, Shih HS (2009) A review of Hopfield neural networks for solving mathematical programming problems. Eur J Oper Res 198:675–687
Singh V (2010) New LMI-based criteria for global robust stability of delayed neural networks. Appl Math Model 34:2958–2965
Yang XS, Yuan Q (2005) Chaos and transient chaos in simple Hopfield neural networks. Neurocomputing 69:232–241
Yanga D, Hu C (2009) Novel delay-dependent global asymptotic stability condition of Hopfield neural networks with delays. Comput Math Appl 57:1978–1984
Jiang Y, Yang B, Wang J, Shao C (2009) Delay-dependent stability criterion for delayed Hopfield neural networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 39:2133–2137
Ott E, Grebogi C, Yorke JA (1990) Controlling chaos. Phys Rev Lett 64:1196–1199
Carrol TL, Pecora LM (1991) Synchronizing chaotic circuits. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst 38:453–456
Rafikov M, Balthazar JM (2004) On an optimal control design for Rösler system. Phys Lett A 333:241–245
Yan JJ (2004) Design of robust controllers for uncertain chaotic systems with nonlinear inputs. Chaos Solitons Fractals 19:541–547
Chen SH, Lu J (2002) Parameter identification and synchronization of chaotic systems based upon adaptive control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 14:643–647
Mou C, Chang-sheng J, Bin J, Qing-xian W (2009) Sliding mode synchronization controller design with neural network for uncertain chaotic systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 39:1856–1863
Yassen MT (2002) The optimal control of Chen chaotic dynamical system. Appl Math Comput 131:171–180
Glad T (1987) Robustness of nonlinear state feedback: a survey. Automatica 23:425–435
Sepulchre R, Jankovic M, Kokotovic P (1996) Constructive nonlinear control. Springer, Berlin
Curtis JW, Beard RW (2004) Satisficing: a new approach to constructive nonlinear control. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 49:1090–1102
Fuh CC (2009) Optimal control of chaotic systems with input saturation using an input-state linearization scheme. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 14:3424–3431
Hamzi B (2001) Some results on inverse optimality based designs. Syst Control Lett 43:239–246
Magni L, Sepulchre R (1997) Stability margins of nonlinear receding-horizon control via inverse optimality. Syst Control Lett 32:241–245
Krstic M (2008) Lyapunov tools for predictor feedbacks for delay systems: inverse optimality and robustness to delay mismatch. Automatica 44:2930–2935
Li WQ, Xie XJ (2009) Inverse optimal stabilization for stochastic nonlinear systems whose linearizations are not stabilizable. Automatica 45:498–503
Qu Z, Wang J, Hull RA, Martin J (2009) Continuous and inverse optimal control designs for chained systems: a global state-scaling transformation and a time-scaling method. Optim Control Appl Methods 30:1–25
Huang WZ, Huang Y (2008) Chaos of a new class of Hopfield neural networks. Appl Math Comput 206:1–11
Huang Y, Yang XS (2006) Hyperchaos and bifurcation in a new class of four-dimensional Hopfield neural networks. Neurocomputing 69:1787–1795
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farid, Y., Bigdeli, N. Inverse optimality in the class of Hopfield neural networks with input nonlinearity. Neural Comput & Applic 22, 711–717 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0756-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0756-6