Abstract
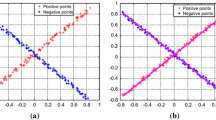
The recently proposed twin support vector machine (TWSVM) obtains much faster training speed and comparable performance than classical support vector machine. However, it only considers the empirical risk minimization principle, which leads to poor generalization for real-world applications. In this paper, we formulate a robust minimum class variance twin support vector machine (RMCV-TWSVM). RMCV-TWSVM effectively overcomes the shortcoming in TWSVM by introducing a pair of uncertain class variance matrices in its objective functions. As a special case, we present a special type of the uncertain class variance matrices by combining the empirical positive and negative class variance matrices. Computational results on several synthetic as well as benchmark datasets indicate the significant advantages of proposed classifier in both computational time and test accuracy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vapnik VN (1995) The natural of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Vapnik VN (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Osuna E, Freund R, Girosi F (1997) Training support vector machines: An application to face detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer vision and pattern recognition, San Juan, Puerto Rico, pp 130–136
Joachims T, Ndellec C, Rouveriol C (1998) Text categorization with support vector machines: learning with many relevant features. In: European conference on machine learning No. 10, Chemnitz, Germany, vol. 1398, pp 137–142
Brown MPS, Grundy WN, Lin D, Cristianini N, Sugnet CW, Furey TS, Ares M Jr, Haussler D (2000) Knowledge-based analysis of microarray gene expression data by using support vector machine. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(1):262–267
Ebrahimi T, Garcia GN, Vesin JM (2003) Joint time-frequency-space classification of EEG in a brain-computer interface application. EURASIP J Appl Signal Process 1(7):713–729
Mukherjee S, Osuna E, Girosi F (1997) Nonlinear prediction of chaotic time series using a support vector machine. In: Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE workshop, Amelia Island, FL, pp 511–520
Saitoh S (1988) Theory of reproducing kernels and its applications. Longman Scientific & Technical, Harlow
Williamson RC, Smola AJ, Schölkopf B (2001) Generalization performance of regularization networks and support vector machines via entropy numbers of compact operators. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 47(6):2516–2532
Cortes C, Vapnik VN (1995) Support vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Osuna E, Freund R, Girosi F (1997) An improved training algorithm for support vector machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE workshop on neural networks for signal processing, Amelia Island, FL, USA, pp 276–285
Platt J (1999) Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization. In: Schölkopf B, Burges CJC, Smola AJ (eds) Advances in Kernel methods–support vector learning. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 185–2008
Keerthi SS, Shevade SK, Bhattacharyya C, Murthy KRK (2000) A fast iterative nearest point algorithm for support vector machine classifier design. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 11(1):124–136
Tao Q, Wu GW, Wang J (2004) A generalized S-K algorithm for learning ν-SVM classifiers. Pattern Recogn Lett 25(10):1165–1171
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9(3):293–300
Suykens JAK, Lukas L, Van Dooren P, Moor BD, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers: a large scale algorithm. In: Processings of European conference circuit theory design, pp 839–842
Zhu J, Rosset S, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2004) 1-norm support vector machines. In: Thrun S, Saul LK, Schölkopf B (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Lin C-F, Wang S-D (2003) Fuzzy support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13(2):464–471
Tsang IW, Kwok JT, Cheung P-M (2005) Core vector machines: fast SVM training on very large data sets. J Mach Learn Res 6:363–392
Tsang IW, Kocsor A, Kwok JT (2007) Simpler core vector machines with enclosing balls. In: Proceedings of the 24th international conference on machine learning. Corvallis, OR
Mangasarian OL, Wild EW (2006) Multisurface proximal support vector classification via generalized eigenvalues. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(1):69–74
Jayadeva, Khemchandani R, Chandra S (2007) Twin support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(5):905–910
Shao Y, Zhang C, Wang X, Deng N (2011) Improvements on twin support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(6):962–968
Kumar MA, Gopal M (2009) Least squares twin support vector machines for pattern classification. Expert Syst Appl 36:7535–7543
Kumar MA, Gopal M (2008) Application of smoothing technique on twin support vector machines. Pattern Recogn Lett 29:1842–1848
Ghorai S, Mukherjee A, Dutta PK (2009) Nonparallel plane proximal classifier. Signal Process 89(4):510–522
Ghorai S, Dutta PK, Mukherjee A (2010) Newton’s method for nonparallel plane proximal classifier with unity norm hyperplanes. Signal Process 90(1):93–104
Peng X (2010) TSVR: an efficient twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Netw 23(3):365–372
Peng X (2010) Primal twin support vector regression and its sparse approximation. Neurocomputing 73(16-18):2846–2858
Fukunaga K (1990) Statistical pattern recognition. Academic, San Diego, CA
Tefas A, Kotropoulos C, Pitas I (2001) Using support vector machines to enhance the performance of elastic graph matching for frontal face authentication. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(7):735–746
Mika S, Ratsch G, Weston J, Schölkopf B, Smola A, Muller K-R (2003) Constructing descriptive and discriminative nonlinear features: Ayleigh coefficients in Kernel feature spaces. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(5):623–628
Muller K-R, Mika S, Ratsch G, Tsuda K, Schölkopf B (2001) An introduction to kernel-based learning algorithms. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(2):181–201
Zafeiriou S, Tefas A, Pitas I (2007) Minimum class variance support vector machines. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(10):2551–2564
Fung G, Mangasarian OL (2001) Proximal support vector machines. In: Proceedings of KDD-2001, San Francisco, pp 77–86
Lanckriet G, El Ghaoui L, Bhattacharyya C, Jordan M (2002) A robust minimax approach to classification. J Mach Learn Res 3:555–582
Blake CI, Merz CJ (1998) UCI repository for machine learning databases. University of California, Department of Information and Computer Sciences, Irvine, CA. On-line at: http://www.ics.uci.edu/mlearn/MLRepository.html
MATLAB, On-line at: http://www.mathworks.com
Acknowledgments
This work has been partly supported by the Innovative Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (11YZ81), the foundation of SHNU (SK201204), and the Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (S30405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, X., Xu, D. Robust minimum class variance twin support vector machine classifier. Neural Comput & Applic 22, 999–1011 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0791-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0791-3