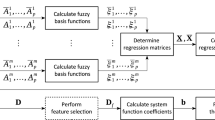
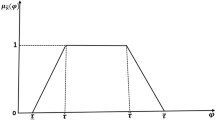
Abstract
An optimized design of a fuzzy logic system can be regarded as setting of different parameters of the system automatically. For a single parameter, there may exist multiple feasible values. Consequently, with the increase in number of parameters, the complexity of a system increases. Type 2 fuzzy logic system has more parameters than the type 1 fuzzy logic system and is therefore much more complex than its counterpart. This paper proposes optimal parameters for an extreme learning machine-based interval type 2 fuzzy logic system to learn its best configuration. Extreme learning machine (ELM) is utilized to tune the consequent parameters of the interval type 2 fuzzy logic system (IT2FLS). A disadvantage of ELM is the random generation of its hidden neuron that causes additional uncertainty, in both approximation and learning. In order to overcome this limitation in an ELM-based IT2FLS, artificial bee colony optimization algorithm is utilized to obtain its antecedent parts parameters. The simulation results verified better performance of the proposed IT2FLS over other models with the benchmark data sets.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABC:
-
Artificial bee colony
- ANFIS:
-
Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system
- ELM:
-
Extreme learning machine
- FLS:
-
Fuzzy logic system
- IT2FLS:
-
Interval type 2 fuzzy logic system
- IT2FELM:
-
IT2FLS trained using extreme learning machine
- IT2FKF:
-
IT2FLS trained using KF method
- KF:
-
Kalman filter
- NN:
-
Neural network
- MF:
-
Membership function
- MSE:
-
Mean square error
- SLFN:
-
Single-hidden layer feedforward neural networks
- T1:
-
Type 1
- T1FLS:
-
Type 1 fuzzy logic system
- T2:
-
Type 2
- T2FLS:
-
Type 2 fuzzy logic system
References
Abraham A (2005) Adaptation of fuzzy inference system using neural learning. In: Nedjah N, Macedo Mourelle LD (eds) Fuzzy systems engineering. Studies in fuzziness and soft computing, vol 181. Springer, Berlin, pp 53–83
Alcala R, Ducange P, Herrera F, Lazzerini B, Marcelloni F (2009) A multiobjective evolutionary approach to concurrently learn rule and data bases of linguistic fuzzy-rule-based systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 17(5):1106–1122
Almaraashi M (2012) Learning of type-2 fuzzy logic systems using simulated annealing. Ph.D. thesis. Department of Informatics DE MONTFORT UNIVERSITY
Cao J, Lin Z, Huang G-B (2012) Self-adaptive evolutionary extreme learning machine. Neural Process Lett 36(3):285–305
Castillo O, Melin P (2012a) Ant colony optimization algorithms for the design of type-2 fuzzy systems. In: Recent advances in interval type-2 fuzzy systems. Springer briefs in applied sciences and technology, vol 1. Springer, Berlin, pp 33–35
Castillo O, Melin P (2012b) Optimization of type-2 fuzzy systems based on bio-inspired methods: a concise review. Inf Sci 205:1–19
Cho JH, Chun MG Lee DJ (2007) Parameter optimization of extreme learning machine using bacterial foraging algorithm. In: SIS 2007 Proceedings of the 8th symposium on advanced intelligent systems, pp 742–747
Cordon O, Herrera F, Sanchez L (1999) Solving electrical distribution problems using hybrid evolutionary data analysis techniques. Appl Intell 10(1):5–24. doi:10.1023/A:1008384630089
Cordon O, Herrera F, Villar P (2001a) Generating the knowledge base of a fuzzy rule-based system by the genetic learning of the data base. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 9(4):667–674
Cordon O, Herrera F, Hoffmann F, Magdalena L (2001b) Genetic fuzzy systems: evolutionary tuning and learning of fuzzy knowledge bases. Advances in fuzzy systems applications and theory, vol 19, 1st edn. World Scientific, Singapore
Cordon O, Herrera F, Magdalena L, Villar P (2001c) A genetic learning process for the scaling factors, granularity and contexts of the fuzzy rule-based system data base. Inf Sci 136(14):85–107. Recent advances in genetic fuzzy systems. doi:10.1016/S0020-0255(01)00143-8. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025501001438
Deng J, Li K, Irwin GW (2011) Fast automatic two-stage nonlinear model identification based on the extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 74(16):2422–2429
Deng Z, Choi K-S, Cao L, Wang S (2014) T2fela: Type-2 fuzzy extreme learning algorithm for fast training of interval type-2 tsk fuzzy logic system. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(4):664–676
Hayashi Y, Buckley JJ (1994) Approximations between fuzzy expert systems and neural networks. Int J Approx Reason 10(1):63–73
He Y-L, Geng Z-Q, Zhu Q-X (2015) Data driven soft sensor development for complex chemical processes using extreme learning machine. Chem Eng Res Des 102:1–11
Herrera F, Casillas J, Cordon O (2002) COR: a methodology to improve ad hoc data-driven linguistic rule learning methods by inducing cooperation among rules. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 32(4):526–537
Hosseini R, Qanadli SD, Barman S, Mazinani M, Ellis T, Dehmeshki J (2012) An automatic approach for learning and tuning gaussian interval type-2 fuzzy membership functions applied to lung CAD classification system. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 20(2):224–234
Huang G-B, Chen L, Siew C-K (2006a) Universal approximation using incremental constructive feedforward networks with random hidden nodes. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(4):879–892
Huang G-B, Zhu Q-Y, Siew C-K (2006b) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1–3):489–501
Huang G-B, Zhou H, Ding X, Zhang R (2012) Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 42(2):513–529
Hyndman RJ, Koehler AB (2006) Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. Int J Forecast 22(4):679–688
Jang J-SR, Sun C-T (1993) Functional equivalence between radial basis function networks and fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 4(1):156–159
Juang C-F, Tsao Y-W (2008) A self-evolving interval type-2 fuzzy neural network with online structure and parameter learning. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 16(6):1411–1424
Karaboga D (2005) An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization. Technical report TR06, Erciyes University, Engineering Faculty, Computer Engineering Department
Karaboga D, Ozturk C (2009) Neural networks training by artificial bee colony algorithm on pattern classification. Neural Netw World 19:279–292
Kayacan E, Kayacan E, Khanesar MA (2015) Identification of nonlinear dynamic systems using type-2 fuzzy neural networks-a novel learning algorithm and a comparative study. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 62(3):1716–1724
Khanesar MA, Kayacan E, Teshnehlab M, Kaynak O (2011) Levenberg marquardt algorithm for the training of type-2 fuzzy neuro systems with a novel type-2 fuzzy membership function. In: 2011 IEEE symposium on advances in type-2 fuzzy logic systems (T2FUZZ), pp 88–93
Khanesar MA, Kayacan E, Teshnehlab M, Kaynak O (2012) Extended Kalman filter based learning algorithm for type-2 fuzzy logic systems and its experimental evaluation. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(11):4443–4455
Liang Q, Mendel JM (2000) Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: theory and design. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8(5):535–550. doi:10.1109/91.873577
Liang N-Y, Huang G-B, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N (2006) A fast and accurate online sequential learning algorithm for feedforward networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(6):1411–1423
Lu C-H (2011) Wavelet fuzzy neural networks for identification and predictive control of dynamic systems. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(7):3046–3058
Luo X, Chang X, Ban X (2015) Extreme learning machine for regression and classification using L 1-morm and L 2-norm. In: Cao J, Mao K, Cambria E, Man Z, Toh K-A (eds) Proceedings of ELM-2014 volume 1. Proceedings in adaptation, learning and optimization, vol 3. Springer, Berlin, pp 293–300
Mendel JM (2001) Uncertain rule-based fuzzy logic systems: introduction and new directions. Prentice-Hall PTR, London
Mendel JM (2004) Computing derivatives in interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 12(1):84–98
Olatunji SO, Selamat A, Abdulraheem A (2014) A hybrid model through the fusion of type-2 fuzzy logic systems and extreme learning machines for modelling permeability prediction. Inf Fusion 16(0):29–45 (Special Issue on Information Fusion in Hybrid Intelligent Fusion Systems)
Olatunji SO, Selamat A, Raheem AAA (2014) Improved sensitivity based linear learning method for permeability prediction of carbonate reservoir using interval type-2 fuzzy logic system. Appl Soft Comput 14 Part B: 144–155. Evolving soft computing techniques and applications. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2013.02.018. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568494613000720
Olatunji SO, Selamat A, Azeez ARA (2015) Modeling permeability and PVT properties of oil and gas reservoir using hybrid model based on type-2 fuzzy logic systems. Neurocomputing 157:125–142. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2015.01.027
Paplinski AP. Neuro-fuzzy computing. http://www.csse.monash.edu.au/courseware/cse5301/2006/04/Lnts/L01.pdf
Petalas YG, Parsopoulos KE, Vrahatis MN (2009) Improving fuzzy cognitive maps learning through memetic particle swarm optimization. Soft Comput 13(1):77–94
Qu Y, Shang C, Wei W, Shen Q (2011) Evolutionary fuzzy extreme learning machine for mammographic risk analysis. Int J Fuzzy Syst 13(4):282–291
Rao CR, Mitra SK (1971) Generalized inverse of matrices and its applications. Wiley, New York
Rong H-J, Sundararajan N, Huang G-B, Saratchandran P (2006) Sequential adaptive fuzzy inference system (safis) for nonlinear system identification and prediction. Fuzzy Sets Syst 157(9):1260–1275
Rong H-J, Huang G-B, Sundararajan N, Saratchandran P (2009) Online sequential fuzzy extreme learning machine for function approximation and classification problems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 39(4):1067–1072
Serre D (2002) Matrices: theory and application. Springer, New York
Soria-Olivas E, Gomez-Sanchis J, Jarman IH, Vila-Frances J, Martinez M, Magdalena JR, Serrano AJ (2011) Belm: Bayesian extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(3):505–509
Sun Z-L, Au K-F, Choi T-M (2007) A neuro-fuzzy inference system through integration of fuzzy logic and extreme learning machines. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 37(5):1321–1331
Tseng T-LB, Jiang F, Kwon YJ (2015) Hybrid type II fuzzy system and data mining approach for surface finish. J Computat Des Eng 2(3):137–147. doi:10.1016/j.jcde.2015.02.002
Wang C, Cheng C, Lee T (2004) Dynamical optimal training for interval type-2 fuzzy neural network (T2FNN). IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 12(4):524–539
Wu D (2013) Approaches for reducing the computational cost of interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: overview and comparisons. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 21(1):80–99
Xiang J, Westerlund M, Sovilj D, Pulkkis G (2014) Using extreme learning machine for intrusion detection in a big data environment. In: Proceedings of the 2014 workshop on artificial intelligent and security workshop. ACM, pp 73–82
Xin J, Wang Z, Qu L, Wang G (2015) Elastic extreme learning machine for big data classification. Neurocomputing 149:464–471
Xu Y, Shu Y (2006) Evolutionary extreme learning machine—based on particle swarm optimization. In: Advances in neural networks—ISNN 2006. In: Wang J, Yi Z, Zurada J, Lu B-L, Yin H (eds) Lecture notes in computer science, vol 3971. Springer, Berlin, pp 644–652. 978-3-540-34439-1
Yin S, Kaynak O (2015) Big data for modern industry: challenges and trends [point of view]. Proc IEEE 103(2):143–146
Yin S, Wang G, Gao H (2015a) Data-driven process monitoring based on modified orthogonal projections to latent structures. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 99:1–8
Yin S, Zhu X, Kaynak O (2015b) Improved pls focused on key-performance-indicator-related fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 62(3):1651–1658
Yong Z, Joo EM, Sundaram S (2014) Meta-cognitive fuzzy extreme learning machine. In: 2014 13th international conference on control automation robotics vision (ICARCV), pp 613–618
Zhang WB, Ji HB (2013) Fuzzy extreme learning machine for classification. Electron Lett 49(7):448–450
Zhang R, Lan Y, Huang G-B, Xu Z-B (2012) Universal approximation of extreme learning machine with adaptive growth of hidden nodes. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(2):365–371
Zhang Y, Cai Z, Gong W, Wang X (2015) Self-adaptive differential evolution extreme learning machine and its application in water quality eva. Comput Inf Syst 11(4):1443–1451
Zhao L (2011) Adaptive interval type-2 fuzzy control based on gradient descent algorithm. In: 2011 2nd international conference on Intelligent control and information processing (ICICIP), vol 2, pp 899–904
Zheng E, Liu J, Lu H, Wang L, Chen L (2013) A new fuzzy extreme learning machine for regression problems with outliers or noises. In: Motoda H, Wu Z, Cao L, Zaiane O, Yao M, Wang W (eds) Advanced data mining and applications. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 8347. Springer, Berlin, pp 524–534
Zhou P, Yuan M, Wang H (2015) ELM based dynamic modeling for online prediction of molten iron silicon content in blast furnace. In: Proceedings of ELM-2014, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 267–277
Zhu Q-Y, Qin AK, Suganthan PN, Huang G-B (2005) Evolutionary extreme learning machine. Pattern Recogn 38(10):1759–1763
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, S., Khanesar, M.A., Jaafar, J. et al. Optimal parameters of an ELM-based interval type 2 fuzzy logic system: a hybrid learning algorithm. Neural Comput & Applic 29, 1001–1014 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2503-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2503-5