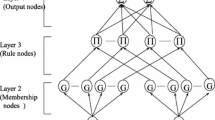
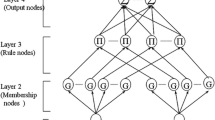
Abstract
For robot trajectory tracking control, it is necessary to model inverse dynamics system sufficiently well to allow high-performance control. However, for complex robots such as wheeled mobile manipulators (WMMs), it is often difficult to model the dynamics system owing to system uncertainties, nonlinearity, and coupling. In this paper, we propose an effective tracking control method based on fuzzy neural network (FNN) and extended Kalman filter (EKF) to achieve WMM followed reference trajectory efficiently. The FNN is trained to generate a feedforward torque. In order to increase the computational efficiency and precision of the training algorithm, the EKF is used to sequentially update both the output weights and centers of the FNN. The effectiveness of the proposed control algorithm is confirmed through system experiments.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atawnih A, Papageorgioua D (2016) Kinematic control of redundant robots with guaranteed joint limit avoidance. Robot Auton Syst 79:122–131
Li L, Gruver WA (2001) Kinematic control of redundant robots and the motion optimizability measure. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 31(1):155–160
Lin H, Chen C (2011) A hybrid control policy of robot arm motion for assistive robots. IEEE Int Proc Inf Autom 33(7):163–168
Masoud S, Masoud A (2000) Constrained motion control using vector potential fields. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern A 30(2):251–272
Falco P, Natale C (2011) On the stability of closed-loop inverse kinematics algorithms for redundant robots. IEEE Trans Robot 27(4):780–784
Bloch AM, Reyhanoglu M (1992) Control and stabilization of nonholonomic dynamic systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 37(11):1746–1757
Samson C (1995) Control of chained systems: application to path following and time-varying point-stabilization of mobile robots. IEEE Trans Autom Control 40(1):64–77
Sordalen OJ, Egeland O (1995) Exponential stabilization of nonholonomic chained systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 40(1):35–49
Wang ZP, Ge SS, Lee TH (2004) Robust adaptive neural network control of uncertain nonholonomic systems with strong nonlinear drifts. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 34(5):2048–2059
Dong WJ, Huo W, Tso SK, Xu WL (2000) Tracking control of uncertain dynamic nonholonomic system and its application to wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 16(6):870–874
Dong WJ, Xu WL (2001) Adaptive tracking control of uncertain nonholonomic dynamic system. IEEE Trans Autom Control 46(3):450–454
Oya M, Su CY, Katoh R (2003) Robust adaptive motion/force tracking control of uncertain nonholonomic mechanical systems. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 19(1):175–181
Shojaei K, Shahri AM (2012) Adaptive robust time varying control of uncertain nonholonomic robotic systems. IET Control Theory Appl 6(1):90–102
Li Z, Ge SS, Adams M, Wijesoma WS (2008) Robust adaptive control of uncertain force/motion constrained nonholonomic mobile manipulators. Automatica 44(3):776–784
Li Z, Yang YP, Li JX (2010) Adaptive motion/force control of mobile under-actuated manipulators with dynamics uncertainties by dynamic coupling and output feedback. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 5(18):1068–1079
Li Z, Ge SS, Adams M, Wijesoma WS (2008) Adaptive robust output-feedback motion/force control of electrically driven nonholonomic mobile manipulators. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 16(6):1308–1315
Hua CC, Yang Y, Guan X (2013) Neural network-based adaptive position tracking control for bilateral teleoperation under constant time delay. Neurocomputing 113:204–212
Lin CM, Hsu CF (2005) Recurrent neural network based adaptive backstepping control for induction servomotors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 52(6):1677–1684
Lin FJ, Wai RJ (2003) Robust recurrent fuzzy neural network control for linear synchronous motor drive system. Neurocomputing 50:365–390
Das T, Kar IN, Chaudhury S (2006) Simple neuron-based adaptive controller for a nonholonomic mobile robot including actuator dynamics. Neurocomputing 69:2140–2151
Fierro R, Lewis FL (1998) Control of a nonholonomic mobile robot using neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 9(4):589–600
Xu D, Zhao D, Yi J, Tan X (2009) Trajectory tracking control of omnidirectional wheeled mobile manipulators: robust neural network-based sliding mode approach. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 39(3):788–799
de Sousa C, Hemerly EM Jr., Galvao RKH (2002) Adaptive control for mobile robot using wavelet networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 32(4):493–504
Park BS, Yoo SJ, Choi YH (2009) Adaptive neural sliding mode control of nonholonomic wheeled mobile robots with model uncertainty. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 17(1):207–214
Broomhead D, Lowe D (1988) Multivariable functional interpolation and adaptive networks. Complex Syst 2:321–355
Bezdek J, Keller J, Krishnapuram R, Kuncheva L, Pal H (1999) Will the real Iris data please stand up? IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 7:368–369
Moody J, Darken C (1989) Fast learning in networks of locally-tuned processing units. Neural Comput 1:289–303
Chen S, Cowan C, Grant P (1991) Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 2:302–309
Chen S, Wu Y, Luk B (1999) Combined genetic algorithm optimization and regularized orthogonal least squares learning for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10:1239–1243
Duro R, Reyes J (1999) Discrete-time backpropagation for training synaptic delay-based artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10:779–789
Shah S, Palmieri F, Datum M (1992) Optimal filtering algorithms for fast learning in feedforward neural networks. Neural Netw 5:779–787
Sum J, Leung C, Young G, Kan W (1999) On the Kalman Filtering method in neural network training and pruning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10:161–166
Zhang Y, Li X (1999) A fast U-D factorization-based learning algorithm with applications to nonlinear system modeling and identification. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10:930–938
Obradovic D (1996) On-line training of recurrent neural networks with continuous topology adaptation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 7:222–228
Puskorius G, Feldkamp L (1994) Neurocontrol of nonlinear dynamical systems with Kalman filter trained recurrent networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5:279–297
Birgmeier M (1995) A fully Kalman-trained radial basis function network for nonlinear speech modeling. IEEE international conference on neural networks, Perth, Western Australia, pp 259–264
Nabney IT (1996) Practical methods of tracking of non-stationary time series applied to real world problems. In: Rogers SK, Ruck DW (eds) AeroSense’96: applications and science of artificial neural networks II, SPIE Proc. No. 2760, pp 152–163
Connor J, Martin R, Atlas L (1994) Recurrent neural networks and robust time series prediction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5(2):240–254
Puskorious G, Feldkamp L (1994) Neural control of nonlinear dynamic systems with Kalman filter trained recurrent networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5(2):279–297
Nelson AT, Wan EA (1997) Neural speech enhancement using dual extended Kalman filtering, ICNN, pp 2171–2175
Ding L, Gao H, Xia K, Liu Z, Tao J, Liu Y (2012) Adaptive sliding mode control of mobile manipulators with Markovian switching joints. J Appl Math 10(3):812–836
Wu SQ, Er MJ, Gao Y (2001) A fast approach for automatic generation of fuzzy rules by generalized dynamic fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 9(4):578–594
Xia K, Ding L, Gao H, Deng Z, Liu G, Wu Y (2016) Switch control for operating constrained mechanisms using a rescuing mobile manipulator with multiple working modes. In: Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), International Conference on IEEE, pp 139–146
Gao H, Xia K, Ding L, Deng Z, Liu Z, Liu G (2015) Optimized control for longitudinal slip ratio with reduced energy consumption. Acta Astronaut (115):1–17
Wu Q, Rete W (2000) Dynamic fuzzy neural networks-a novel approach to function approximation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Part B-Cybern 30(2):358–364
Chen S, Cowan CFN, Grant PM (1991) Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 2(2):302–309
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research Development Plan Project (973) (2013CB035502), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61370033/51275106), Harbin Talent Program for Distinguished Young Scholars (NO. 2014RFYXJ001). Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. HIT.BRETIII.201411), Foundation of Chinese State Key Laboratory of Robotics and Systems (Grant No. SKLRS201401A01), Postdoctoral Youth Talent Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, China (Grant No. LBH-TZ0403), and “111” Project (B07018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, K., Gao, H., Ding, L. et al. Trajectory tracking control of wheeled mobile manipulator based on fuzzy neural network and extended Kalman filtering. Neural Comput & Applic 30, 447–462 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2643-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2643-7