Abstract
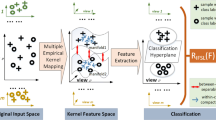
In practice, huge amount of samples is readily available, while labeled samples are often very limited and too expensive to be easily obtained. Multi-view features usually reveal different types of traits of labeled and unlabeled samples. Semi-supervised multi-view learning is a learning paradigm designed to meet the requirement of learning from complementary information of multiple views of labeled and unlabeled samples. In this paper, we propose a semi-supervised multiple kernel intact discriminant space learning (SMKIDSL) method to discover latent intact feature representations for those samples. SMKIDSL employs correlation discriminant analysis and label regression to fully use class label information for enhancing the discriminant power of latent intact feature representations. In SMKIDSL, multi-view collaboration learning mechanism is utilized to efficiently integrate complementary information of multiple views, which enables optimal view being dominant in learning process. Besides, kernel technique is used to tackle nonlinear issue of original multi-view features for exploiting more discriminant information. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on Caltech 101, LFW, MNIST and RGB-D datasets. And the experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed method. The robustness of our method is also confirmed by those results.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun S (2013) A survey of multi-view machine learning. Neural Comput Appl 23(7):2031–2038
Zhang H, Cao X, Ho JK, Chow TW (2017) Object-level video advertising: an optimization framework. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 13(2):520–531
Oyedotun OK, Khashman A (2017) Deep learning in vision-based static hand gesture recognition. Neural Comput Appl 28:3941–3951
Hardoon D, Szedmak S, Shawe-Taylor J (2004) Canonical correlation analysis: an overview with application to learning methods. Neural Comput 16:2639–2664
Sun T, Chen S, Yang J, Shi P (2008) A novel method of combined feature extraction for recognition. In: IEEE international conference on data mining, pp 1043–1048
Xu C, Tao D, Xu C (2015) Multi-view intact space learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(12):2531–2544
Rupnik J, Shawe-Taylor J (2010) Multi-view canonical correlation analysis. In: Conference on data mining and data warehouses, pp 1–4
Kan M, Shan S, Zhang H, Lao S, Chen X (2016) Multi-view discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(1):188–194
Zhao M, Chow TW, Wu Z, Zhang Z, Li B (2015) Learning from normalized local and global discriminative information for semi-supervised regression and dimensionality reduction. Inf Sci 324(10):286–309
Blum A, Mitchell T (1998) Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. In: International conference on computational learning theory, pp 92–100
Hou C, Zhang C, Wu Y, Nie F (2010) Multiple view semi-supervised dimensionality reduction. Pattern Recognit 43(3):720–730
Wang S, Jiang S, Huang Q, Tian Q (2010) S3MKL: scalable semi-supervised multiple kernel learning for image data mining. In: ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 163–172
Nie F, Cai G, Li X (2017) Multi-view clustering and semi-supervised classification with adaptive neighbours. In: AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2408–2414
Shen X, Sun Q (2014) A novel semi-supervised canonical correlation analysis and extensions for multi-view dimensionality reduction. J Vis Commun Image Represent 25(8):1894–1904
Lazebnik S, Schmid C, Ponce J (2006) Beyond bags of features: spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2169–2178
Kimura A, Sugiyama M, Nakano T, Kameoka H, Sakano H, Maeda E, Ishiguro K (2013) SemiCCA: efficient semi-supervised learning of canonical correlations. Inf Media Technol 8(2):311–318
Jiang Y, Liu J, Li Z, Lu H (2014) Semi-supervised unified latent factor learning with multi-view data. Mach Vis Appl 25(7):1635–1645
Wang J, Wang X, Tian F, Liu CH, Yu H, Liu Y (2016) Adaptive multi-view semi-supervised nonnegative matrix factorization. In: International conference on neural information processing, pp 435–444
Xie X, Li B, Chai X (2016) A manifold framework of multiple-kernel learning for hyperspectral image classification. Neural Comput Appl 27(3):1–11
Jing XY, Wu F, Dong X, Shan S, Chen S (2017) Semi-supervised multi-view correlation feature learning with application to webpage classification. In: AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1374–1381
Ma Y, Lao S, Takikawa E, Kawade M (2007) Discriminant analysis in correlation similarity measure space. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 577–584
Zhao M, Zhang Z, Chow TW, Li B (2014) A general soft label based linear discriminant analysis for semi-supervised dimension reduction. Neural Netw 55:83–97
Zhao M, Zhang Z, Chow TW (2012) Trace ratio criterion based generalized discriminative learning for semi-supervised dimensionality reduction. Pattern Recognit 45(4):1482–1499
Luo Y, Tao D, Ramamohanarao K, Xu C, Wen Y (2015) Tensor canonical correlation analysis for multi-view dimension reduction. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(11):3111–3124
Waaijenborg S, de Witt Verselewel, Hamer PC, Zwinderman AH (2008) Quantifying the association between gene expressions and DNA-markers by penalized canonical correlation analysis. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 7(1):1–28
Hardoon DR, Shawe-Taylor J (2011) Sparse canonical correlation analysis. Mach Learn 83(3):331–353
Zu C, Zhang D (2016) Canonical sparse cross-view correlation analysis. Neurocomputing 191:263–272
Sun QS, Liu ZD, Heng PA, Xia DS (2005) A theorem on the generalized canonical projective vectors. Pattern Recognit 38(3):449–452
Kim TK, Kittler J, Cipolla R (2007) Discriminative learning and recognition of image set classes using canonical correlations. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(6):1005–1018
Sun T, Chen S, Yang J, Shi P (2008) A supervised combined feature extraction method for recognition. In: IEEE international conference on data mining, pp 1043–1048
Peng Y, Zhang D, Zhang J (2010) A new canonical correlation analysis algorithm with local discrimination. Neural Process Lett 31(1):1–15
Sakar CO, Kursun O (2017) Discriminative feature extraction by a neural implementation of canonical correlation analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(1):164–176
Balcan MF, Blum A, Yang K (2005) Co-training and expansion: towards bridging theory and practice. In: Saul LK, Weiss Y, Bottou L (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 89–96
Wang W, Zhou ZH (2007) Analyzing co-training style algorithms. In: European conference on machine learning, pp 454–465
Wang W, Zhou ZH (2013) Co-training with insufficient views. In: Asian conference on machine learning, pp 467–482
Blaschko MB, Lampert CH, Gretton A (2008) Semi-supervised Laplacian regularization of kernel canonical correlation analysis. In: Joint European conference on machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases, pp 133–145
Chen X, Chen S, Xue H, Zhou X (2012) A unified dimensionality reduction framework for semi-paired and semi-supervised multi-view data. Pattern Recognit 45(5):2005–2018
Guan Z, Zhang L, Peng J, Fan J (2015) Multi-view concept learning for data representation. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(11):3016–3028
Lanckriet GR, Bie TD, Cristianini N, Jordan MI, Noble WS (2004) A statistical framework for genomic data fusion. Bioinformatics 20(16):2626–2635
Sonnenburg S, Rätsch G, Schäfer C, Schölkopf B (2006) Large scale multiple kernel learning. J Mach Learn Res 7(7):1531–1565
Sonnenburg S, Rätsch G, Schäfer C (2006) A general and efficient multiple kernel learning algorithm. In: Weiss Y, Schölkopf B, Platt J (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 1273–1280
Xu Z, Jin R, King I, Lyu M (2009) An extended level method for efficient multiple kernel learning. In: Koller D, Schuurmans D, Bengio Y, Bottou L (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 1825–1832
Rakotomamonjy A, Bach F, Canu S, Grandvalet Y (2007) More efficiency in multiple kernel learning. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 775–782
Kloft M, Brefeld U, Sonnenburg S, Zien A (2011) Lp-norm multiple kernel learning. J Mach Learn Res 12(3):953–997
Vishwanathan SVN, Sun Z, Ampornpunt N, Varma M (2010) Multiple kernel learning and the SMO algorithm. In: Lafferty JD, Williams CKI, Shawe-Taylor J, Zemel RS, Culotta A (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 2361–2369
Feng J, Jiao L, Sun T, Liu H, Zhang X (2016) Multiple kernel learning based on discriminative kernel clustering for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(11):6516–6530
Bach FR (2008) Consistency of the group lasso and multiple kernel learning. J Mach Learn Res 9(6):1179–1225
Xu Z, Jin R, Yang H, King I, Lyu MR (2010) Simple and efficient multiple kernel learning by group lasso. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 1175–1182
Liu T, Gu Y, Jia X, Benediktsson JA, Chanussot J (2016) Class-specific sparse multiple kernel learning for spectral-spatial hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(12):7351–7365
Shrivastava A, Patel VM, Chellappa R (2014) Multiple kernel learning for sparse representation-based classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(7):3013–3024
Wang Q, Gu Y, Tuia D (2016) Discriminative multiple kernel learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(7):3912–3927
Wu X, Li Q, Xu L, Chen K, Yao L (2017) Multi-feature kernel discriminant dictionary learning for face recognition. Pattern Recognit 66:404–411
Zhu X, Jing XY, Wu F, Wu D, Cheng L, Li S, Hu R (2017) Multi-kernel low-rank dictionary pair learning for multiple features based image classification. In: AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2970–2976
Zhang Z (1997) Parameter estimation techniques: a tutorial with application to conic fitting. Image Vis Comput 15(1):59–76
Li Z, Yang Y, Liu J, Zhou X, Lu H (2012) Unsupervised feature selection using nonnegative spectral analysis. In: AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1026–1032
Ding C, Zhou D, He X, Zha H (2006) R1-PCA: rotational invariant L1-norm principal component analysis for robust subspace factorization. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 281–288
Aronszajn N (1950) Theory of reproducing kernels. Trans Am Math Soc 68(3):337–404
Mika S, Ratsch G, Weston J, Scholkopf B, Mullers KR (1999) Fisher discriminant analysis with kernels. In: IEEE signal processing society workshop, pp 41–48
Roth V, Steinhage V (1999) Nonlinear discriminant analysis using kernel functions. In: Solla SA, Leen TK, Mueller K-R (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 568–574
Lu H, Plataniotis KN, Venetsanopoulos AN (2008) MPCA: multilinear principal component analysis of tensor objects. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 19(1):18–39
Grant M, Boyd S (2013) CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming, version 2.0 beta. http://cvxr.com/cvx
He R, Tan T, Wang L, Zheng WS (2012) L2,1 regularized correntropy for robust feature selection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2504–2511
Li F, Rob F, Pietro P (2007) Learning generative visual models from few training examples: an incremental Bayesian approach tested on 101 object categories. Comput Vis Image Underst 106(1):59–70
Huang G, Mattar M, Lee H, Learned-Miller EG (2012) Learning to align from scratch. In: Bartlett PL, Pereira F, Burges CJC, Bottou L, Weinberger KQ (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems. Curran Associates Inc, Red Hook, pp 764–772
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324
Lai K, Bo L, Ren X, Fox D (2011) A large-scale hierarchical multi-view RGB-D object dataset. In: IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 1817–1824
Jing XY, Hu R, Zhu YP, Wu S, Liang C, Yang JY (2014) Intra-view and inter-view supervised correlation analysis for multi-view feature learning. In: AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1882–1889
Wu F, Jing XY, Yue D (2017) Multi-view discriminant dictionary learning via learning view-specific and shared structured dictionaries for image classification. Neural Process Lett 45(2):649–666
Beveridge JR, She K, Draper B, Givens GH (2001) Parametric and nonparametric methods for the statistical evaluation of human ID algorithms. In: 3rd workshop on the empirical evaluation of computer vision systems, pp 1–14
Acknowledgements
This work is partially funded by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) with Grant numbers of 61272273 and 61702280. It is also supported by Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications under Grant number of XJKY14016, the Scientific Research Staring Foundation for Introduced Talents in NJUPT (NUPTSF, No. NY217009) and Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. KYCX17_0777). In addition, it is also funded by Education Department of Jiangxi Province under the Grant numbers GJJ151066 and GJJ151076. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, X., Wu, F. & Jing, XY. Semi-supervised multiple kernel intact discriminant space learning for image recognition. Neural Comput & Applic 31, 5309–5326 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3367-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3367-7