Abstract
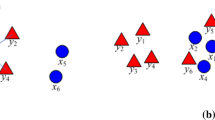
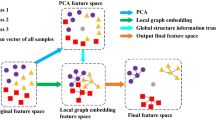
Graph embedding is a popular graph based dimensionality reduction framework, and it consists of two successive steps, i.e., graph construction and embedding. The traditional graph construction methods such as \(k\)-nearest-neighbor (k-NN) and \(\varepsilon\)-ball suffer from the difficulty in parameter selection and are also sensitive to noises. On the other hand, the property of embedding projection is not fully explored by many methods. In this paper, we explicitly investigate these two steps and propose three adaptive graph orthogonal discriminant embedding techniques (termed as AGODE-gs, AGODE-dl and AGODE-tr) for dimensionality reduction, and their differences lie in the way of orthogonalization. In our proposed methods, both the intra-class adjacency graph and the inter-class repulsion graph are constructed by a \(\ell_{2}\)-norm regularized least square, and an orthogonal constraint between the projection vectors is then imposed. The time and space complexity of the proposed methods are also analyzed in detail. We further show that the proposed methods are computationally more efficient than those \(\ell_{1}\)-norm based graph construction methods. Extensive experiments on four face databases (ORL, Yale, CUM-PIE and Extended YaleB) verify the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed methods with encouraging results.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turk M, Pentland A (1991) Eigenfaces for recognition. J Cogn Neurosci 3(1):71–86
Belhumeur PN, Hespanha JP, Kriegman DJ (1997) Eigenfaces vs. fisherfaces: recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 19(7):711–720
Roweis ST, Saul LK (2000) Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 290(5500):2323–2326
He X, Cai D, Yan S, Zhang H-J (2005) Neighborhood preserving embedding. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision. IEEE, pp 1208–1213
Belkin M, Niyogi P (2003) Laplacian eigenmaps for dimensionality reduction and data representation. Neural Comput 15(6):1373–1396
He X, Niyogi P (2003) Locality preserving projections. In: Proceedings of the 16th international conference on neural information processing systems. MIT Press, pp 153–160
Yan S, Xu D, Zhang B, Zhang H-J, Yang Q, Lin S (2007) Graph embedding and extensions: a general framework for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 29(1):40–51
Nie F, Zeng Z, Tsang IW, Xu D, Zhang C (2011) Spectral embedded clustering: a framework for in-sample and out-of-sample spectral clustering. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(11):1796–1808
Von Luxburg U (2007) A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat Comput 17(4):395–416
Ng AY, Jordan MI, Weiss Y (2002) On spectral clustering: analysis and an algorithm. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2:849–856
He X, Cai D, Niyogi P (2005) Laplacian score for feature selection. In: Proceedings of the 18th international conference on neural information processing systems. MIT Press, pp 507–514
Zhao Z, Liu H (2007) Spectral feature selection for supervised and unsupervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 24th international conference on machine learning. ACM, pp 1151–1157
Chen H-T, Chang H-W, Liu T-L (2005) Local discriminant embedding and its variants. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 846–853
Zhu Z, Similä T, Corona F (2013) Supervised distance preserving projections. Neural Process Lett 38(3):445–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-013-9285-x
Corona F, Zhu Z, de Souza Júnior AH, Mulas M, Muru E, Sassu L, Barreto G, Baratti R (2015) Supervised distance preserving projections: applications in the quantitative analysis of diesel fuels and light cycle oils from NIR spectra. J Process Control 30(Supplement C):10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.11.005
Jebara T, Wang J, Chang S-F (2009) Graph construction and b-matching for semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 26th annual international conference on machine learning. ACM, pp 441–448
Yang B, Chen S (2010) Sample-dependent graph construction with application to dimensionality reduction. Neurocomputing 74(1–3):301–314
Raducanu B, Dornaika F (2012) A supervised non-linear dimensionality reduction approach for manifold learning. Pattern Recogn 45(6):2432–2444
Zhang L, Qiao L, Chen S (2010) Graph-optimized locality preserving projections. Pattern Recogn 43(6):1993–2002
Cheng B, Yang J, Yan S, Fu Y, Huang TS (2010) Learning with l1-graph for image analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(4):858–866
Qiao L, Chen S, Tan X (2010) Sparsity preserving projections with applications to face recognition. Pattern Recogn 43(1):331–341
Yan S, Wang H (2009) Semi-supervised learning by sparse representation. In: SDM. SIAM, pp 792–801
Raducanu B, Dornaika F (2014) Embedding new observations via sparse-coding for non-linear manifold learning. Pattern Recogn 47(1):480–492
Wright J, Yang AY, Ganesh A, Sastry SS, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 31(2):210–227
Nie F, Xiang S, Liu Y, Hou C, Zhang C (2012) Orthogonal vs. uncorrelated least squares discriminant analysis for feature extraction. Pattern Recogn Lett 33(5):485–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2011.11.028
Gui J, Sun Z, Jia W, Hu R, Lei Y, Ji S (2012) Discriminant sparse neighborhood preserving embedding for face recognition. Pattern Recogn 45(8):2884–2893
Lu G-F, Jin Z, Zou J (2012) Face recognition using discriminant sparsity neighborhood preserving embedding. Knowl Based Syst 31:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2012.02.014
Gu Z, Yang J (2013) Sparse margin–based discriminant analysis for feature extraction. Neural Comput Appl 23(6):1523–1529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-1124-x
Lou S, Zhao X, Chuang Y, Yu H, Zhang S (2016) Graph regularized sparsity discriminant analysis for face recognition. Neurocomputing 173:290–297
Zang F, Zhang J (2011) Discriminative learning by sparse representation for classification. Neurocomputing 74:2176–2183
Gao Q, Huang Y, Zhang H, Hong X, Li K, Wang Y (2015) Discriminative sparsity preserving projections for image recognition. Pattern Recogn 48(8):2543–2553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2015.02.015
Zhang L, Yang M, Feng X, Ma Y, Zhang D (2012) Collaborative representation based classification for face recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:12042358
Zhang L, Yang M, Feng X (2011) Sparse representation or collaborative representation: Which helps face recognition? In: IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). IEEE, pp 471–478
Shi Q, Eriksson A, Van Den Hengel A, Shen C (2011) Is face recognition really a compressive sensing problem? In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 553–560
Hua J, Wang H, Ren M, Huang H (2016) Collaborative representation analysis methods for feature extraction. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2299-3
Yang W, Wang Z, Sun C (2015) A collaborative representation based projections method for feature extraction. Pattern Recogn 48(1):20–27
Kokiopoulou E, Saad Y (2007) Orthogonal neighborhood preserving projections: a projection-based dimensionality reduction technique. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 29(12):2143–2156
Lei Y-K, Zou J-W, Dong T, You Z-H, Yuan Y, Hu Y (2014) Orthogonal locally discriminant spline embedding for plant leaf recognition. Comput Vis Image Underst 119:116–126
Cai D, He X, Han J, Zhang H-J (2006) Orthogonal laplacianfaces for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(11):3608–3614
Zheng Y, Fang B, Tang YY, Zhang T, Liu R (2013) Learning orthogonal projections for Isomap. Neurocomputing 103:149–154
Gao Q, Ma J, Zhang H, Gao X, Liu Y (2013) Stable orthogonal local discriminant embedding for linear dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(7):2521–2531
Yu X, Wang X (2008) Uncorrelated discriminant locality preserving projections. IEEE Signal Proc Lett 15:361–364
Jin Z, Yang J-Y, Hu Z-S, Lou Z (2001) Face recognition based on the uncorrelated discriminant transformation. Pattern Recogn 34(7):1405–1416
Lu C-Y, Huang D-S (2013) Optimized projections for sparse representation based classification. Neurocomputing 113:213–219
Ye J (2005) Characterization of a family of algorithms for generalized discriminant analysis on undersampled problems. J Mach Learn Res 6:483–502
Peng X, Yi Z, Tang H (2015) Robust subspace clustering via thresholding ridge regression. In: AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (AAAI), Austin, Texas, USA, Jan 25–29, 2015
Yuan M-D, Feng D-Z, Liu W-J, Xiao C-B (2016) Collaborative representation discriminant embedding for image classification. J Vis Commun Image Represent 41:212–224
Golub G, Cv Loan (1989) Matrix computations, 2nd edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, London
Duchene J, Leclercq S (1988) An optimal transformation for discriminant and principal component analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 10(6):978–983
Jia Y, Nie F, Zhang C (2009) Trace ratio problem revisited. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 20(4):729–735. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2009.2015760
Zhao M, Zhang Z, Chow TWS (2012) Trace ratio criterion based generalized discriminative learning for semi-supervised dimensionality reduction. Pattern Recogn 45(4):1482–1499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2011.10.008
Samaria FS, Harter AC (1994) Parameterisation of a stochastic model for human face identification. In: Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE workshop on applications of computer vision. IEEE, pp 138–142
The Yale face database (1997) http://cvc.yale.edu/projects/yalefaces/yalefaces.html
Sim T, Baker S, Bsat M (2003) The CMU pose, illumination, and expression database. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 25(12):1615–1618
Georghiades AS, Belhumeur PN, Kriegman DJ (2001) From few to many: illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 23(6):643–660. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.927464
Han PY, Jin ATB, Abas FS (2009) Neighbourhood preserving discriminant embedding in face recognition. J Vis Commun Image Represent 20(8):532–542
Yang W, Sun C, Zheng W (2016) A regularized least square based discriminative projections for feature extraction. Neurocomputing 175:198–205
Chen X, Yang J, Mao Q, Han F (2013) Regularized least squares fisher linear discriminant with applications to image recognition. Neurocomputing 122(Supplement C):521–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.05.006
Chen X, Yang J, Zhang D, Liang J (2013) Complete large margin linear discriminant analysis using mathematical programming approach. Pattern Recogn 46(6):1579–1594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2012.11.019
Yang M, Zhang L (2010) Gabor feature based sparse representation for face recognition with gabor occlusion dictionary. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 448–461
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y (2013) Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 35(1):171–184. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.88
Lu G-F, Zou J, Wang Y (2016) L1-norm and maximum margin criterion based discriminant locality preserving projections via trace Lasso. Pattern Recogn 55:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.01.029
He R, Hu BG, Zheng WS, Kong XW (2011) Robust principal component analysis based on maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(6):1485–1494. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2103949
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:visi.0000029664.99615.94
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Ttans Pattern Anal 24(7):971–987. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017623
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61271293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, MD., Feng, DZ., Shi, Y. et al. Adaptive graph orthogonal discriminant embedding: an improved graph embedding method. Neural Comput & Applic 31, 5461–5476 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3374-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3374-8