Abstract
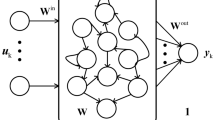
Echo state network (ESN), a novel recurrent neural network, has a randomly and sparsely connected reservoir. Since the reservoir size is very large, the collinearity problem may exist in the ESN. To address this problem and get a sparse architecture, an adaptive lasso echo state network (ALESN) is proposed, in which the adaptive lasso algorithm is used to calculate the output weights. The ALESN combines the advantages of quadratic regularization and adaptively weighted lasso shrinkage; furthermore, it has the oracle properties and can deal with the collinearity problem. Meanwhile, to obtain the optimal model, the selection of tuning regularization parameter based on modified Bayesian information criterion is proposed. Simulation results show that the proposed ALESN has better performance and relatively uniform output weights than some other existing methods.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han HG, Wu XL, Qiao JF (2013) Real-time model predictive control using a self-organizing neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(9):1425–1436
Zhang YW, Chai TY, Li ZM, Yang CY (2012) Modeling and monitoring of dynamic processes. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(2):277–284
Qiao JF, Han HG (2012) Identification and modeling of nonlinear dynamical systems using a novel self-organizing RBF-based approach. Automatica 48(8):1729–1734
Chang WD (2014) Recurrent neural network modeling combined with bilinear model structure. Neural Comput Appl 24(3–4):765–773
Han HG, Wu XL, Qiao JF (2014) Nonlinear system modeling based on self-organizing fuzzy-neural-network with adaptive computation algorithm. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(4):554–564
Li FJ, Qiao JF, Han HG, Yang CL (2016) A self-organizing cascade neural network with random weights for nonlinear system modeling. Appl Soft Comput 42:184–193
Han HG, Zhang S, Qiao JF (2017) An adaptive growing and pruning algorithm for designing recurrent neural network. Neurocomputing 242:51–62
Hwang CL, Jan C (2016) Recurrent neural network based multivariable adaptive control for a class of nonlinear dynamic systems with time-varying delay. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(2):388–401
Geng K, Marmarelis VZ (2017) Methodology of recurrent Laguerre-Volterra network for modeling nonlinear dynamic systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(9):2196–2208
Wang L, Zhang L, Yi Z (2017) Trajectory predictor by using recurrent neural networks in visual tracking. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(10):3172–3183
Jaeger H, Haas H (2004) Harnessing nonlinearity: predicting chaotic systems and saving energy in wireless communication. Science 304(5667):78–80
Bacciu D, Barsocchi P, Chessa S et al (2014) An experimental characterization of reservoir computing in ambient assisted living applications. Neural Comput Appl 24(6):1451–1464
Qiao JF, Li FJ, Han HG, Li WJ (2017) Growing echo state network with multiple subreservoirs. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(2):391–404
Peng Y, Lei M, Li JB et al (2014) A novel hybridization of echo state networks and multiplicative seasonal ARIMA model for mobile communication traffic series forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 24(3–4):883–890
Oubbati M, Palm G (2010) A neural framework for adaptive robot control. Neural Comput Appl 19(1):103–114
Skowronski MD, Harris JG (2007) Automatic speech recognition using a predictive echo state network classifier. Neural Netw 20(3):414–423
Xia Y, Jelfs B, Van Hulle MM (2011) An augmented echo state network for nonlinear adaptive filtering of complex noncircular signals. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(1):74–83
Xu M, Han M (2016) Adaptive elastic echo state network for multivariate time series prediction. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(10):2173–2183
Dutoit X, Schrauwen B, Van Campenhout J, Stroobandt D, Van Brussel H, Nuttin M (2009) Pruning and regularization in reservoir computing. Neurocomputing 72(7–9):1534–1546
Reinhart RF, Steil JJ (2012) Regularization and stability in reservoir networks with output feedback. Neurocomputing 90:96–105
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Stat Soc B 58(1):267–288
Donoho DL, Huo X (2001) Uncertainty principles and ideal atomic decomposition. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 47(7):2845–2862
Meinshausen N, Bühlmann P (2006) High-dimensional graphs and variable selection with the lasso. Ann Statist 34(3):1436–1462
Zou H (2006) The adaptive lasso and its oracle properties. J Am Stat Assoc 101(476):1418–1429
Kwon S, Lee S, Na O (2017) Tuning parameter selection for the adaptive lasso in the autoregressive model. J Kor Stat Soc 46(2):285–297
Shibata R (1976) Selection of the order of an autoregressive model by Akaike’s information criterion. Biometrika 63(1):117–126
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6(2):461–464
Jaeger H (2001) The ‘echo state’ approach to analysing and training recurrent neural networks-with an erratum note. German Nat Res Center Inf Technol, Bonn, Germany, Tech Rep 148
Efron B, Hastie T, Johnstone I, Tibshirani R (2004) Least angle regression. Ann Stat 32(2):407–499
Hom RA, Johnson CR (1991) Topics in matrix analysis. Cambridge University Press, New York
Wang HS, Yan XF (2014) Improved simple deterministically constructed cycle reservoir network with sensitive iterative pruning algorithm. Neurocomputing 145:353–362
Zhang L, Li K (2015) Forward and backward least angle regression for nonlinear system identification. Automatica 53:94–102
Chen H, Gong Y, Hong X (2013) Online modeling with tunable RBF network. IEEE Trans Cybern 43(3):935–947
Han HG, Lu W, Hou Y (2018) An Adaptive-PSO-based self-organizing RBF neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(1):104–117
Lorenz EN (1963) Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J Atm Sci 20:130–141
Jaeger H (2005) Reservoir riddles: suggesting for echo state network research. IEEE Int J Conf Neural Netw Montreal, Canada, pp 1460–1462
Ferreira AA, Ludermir TB, De Aquino RRB (2013) An approach to reservoir computing design and training. Expert Syst Appl 40(10):4172–4182
Malik ZK, Hussain A, Wu QJ (2017) Multilayered echo state machine: a novel architecture and algorithm. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(4):946–959
Hénon M (1976) A two-dimensional mapping with a strange attractor. Commun Math Phy 50(1):69–77
National Geophysical Data Center (2014) Sunspot numbers (Online). http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/stp/space-weather/solar-data/solarsolarindices/sunspot-numbers/international/tables/
Rodan A, Tiňo P (2011) Minimum complexity echo state network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(1):131–144
Han HG, Zhang L, Hou Y, Qiao JF (2016) Nonlinear model predictive control based on a self-organizing recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(2):402–415
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61533002 and Grant 61603012, in part by the Beijing Municipal Education Commission Foundation under Grant KM201710005025, in part by the Beijing Postdoctoral Research Foundation of China under Grant 2017ZZ-028 and in part by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation-funded project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, J., Wang, L. & Yang, C. Adaptive lasso echo state network based on modified Bayesian information criterion for nonlinear system modeling. Neural Comput & Applic 31, 6163–6177 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3420-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3420-6