Abstract
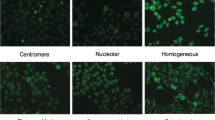
The recognition of staining patterns present in human epithelial type 2 (HEp-2) cells helps to diagnose connective tissue disease. In this context, the paper introduces a robust method, termed as CanSuR, for automatic recognition of antinuclear autoantibodies by HEp-2 cell indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) image analysis. The proposed method combines the advantages of a new sequential supervised canonical correlation analysis (CCA), introduced in this paper, with the theory of rough hypercuboid approach. While the proposed CCA efficiently combines the local textural information of HEp-2 cells, derived from various scales of rotation-invariant local binary patterns, the relevant and significant features of HEp-2 cell for staining pattern recognition are extracted using rough hypercuboid approach. Finally, the support vector machine, with radial basis function kernel, is used to recognize one of the known staining patterns present in IIF images. The effectiveness of the proposed staining pattern recognition method, along with a comparison with related approaches, is demonstrated on MIVIA, SNP and ICPR HEp-2 cell image databases. An important finding is that the proposed method performs significantly better than state-of-the art methods, on three HEp-2 cell image databases with respect to both classification accuracy and F1 score.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agmon-Levin N, Damoiseaux J, Kallenberg C, Sack U, Witte T, Herold M, Bossuyt X, Musset L, Cervera R, Plaza-Lopez A, Dias C, Sousa MJ, Radice A, Eriksson C, Hultgren O, Viander M, Khamashta M, Regenass S, Andrade LEC, Wiik A, Tincani A, Rönnelid J, Bloch DB, Fritzler MJ, Chan EKL, Garcia-De La Torre I, Konstantinov KN, Lahita R, Wilson M, Vainio O, Fabien N, Sinico RA, Meroni P, Shoenfeld Y (2014) International recommendations for the assessment of autoantibodies to cellular antigens referred to as anti-nuclear antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis 73(1):17–23
Agmon-Levin N, Shapira Y, Selmi C, Barzilai O, Ram M, Szyper-Kravitz M, Sella S, Katz BS, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y, Larida B, Invernizzi P, Gershwin ME, Shoenfeld Y (2010) A comprehensive evaluation of serum autoantibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Autoimmun 34(1):55–58
Banerjee A, Maji P (2016) Rough-probabilistic clustering and hidden markov random field model for segmentation of HEp-2 cell and brain MR images. Appl Soft Comput 46:558–576
Banerjee A, Maji P (2017) Stomped-\(t\): a novel probability distribution for rough-probabilistic clustering. Inf Sci 421:104–125
Di Cataldo S, Bottino A, Islam I, Vieira TF, Ficarra E (2014) Subclass discriminant analysis of morphological and textural features for HEp-2 staining pattern classification. Pattern Recognit 47(7):2389–2399
Cordelli E, Soda P (2011) Color to grayscale staining pattern representation in IIF. In Proceedings of the 24th international symposium on computer-based medical systems, pp 1–6
Cruz-Cano R, Lee MT (2014) Fast regularized canonical correlation analysis. Comput Stat Data Anal 70:88–100
Ensafi S, Lu S, Kassim AA, Tan CL (2016) Accurate HEp-2 cell classification based on sparse coding of superpixels. Pattern Recognit Lett 82:64–71
Foggia P, Percannella G, Soda P, Vento M (2010) Early experiences in mitotic cells recognition on HEp-2 slides. In: Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE international symposium on computer-based medical systems, pp 38–43
Foggia P, Percannella G, Soda P, Vento M (2013) Benchmarking HEp-2 cells classification methods. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 32(10):1878–1889
Friou GJ, Finch SC, Detre KD, Santarsiero C (1958) Interaction of nuclei and globulin from lupus erythematosis serum demonstrated with fluorescent antibody. J Immunol 80(4):324–329
Gao Z, Wang L, Zhou L, Zhang J (2017) HEp-2 cell image classification with deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 21(2):416–428
Gladwell GML (1995) On isospectral spring mass systems. Inverse Probl 11(3):591–602
Golugula A, Lee G, Master SR, Feldman MD, Tomaszewski JE, Speicher DW, Madabhushi A (2011) Supervised regularized canonical correlation analysis: integrating histologic and proteomic measurements for predicting biochemical recurrence following prostate surgery. BMC Bioinf 12:483
Guo Z, Zhang L, Zhang D (2010) A completed modeling of local binary pattern operator for texture classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(6):1657–1663
Hiemann R, Buttner T, Krieger T, Roggenbuck D, Sack U, Conrad K (2009) Challenges of automated screening and differentiation of non-organ specific autoantibodies on HEp-2 cells. Autoimmun Rev 9(1):17–22
Hiemann R, Hilger N, Sack U, Weigert M (2006) Objective quality evaluation of fluorescence images to optimize automatic image acquisition. Cytometry A 69(3):182–184
Hotelling H (1936) Relations between two sets of variates. Biometrika 28(3/4):321–377
Hsieh TY, Huang YC, Chung CW, Huang YL (2009) HEp-2 cell classification in indirect immunofluorescence images. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on information, communications and signal processing, pp 1–4
Huang G-B, Zhu Q-Y, Siew C-K (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1):489–501
Humbel RL (1993) Detection of antinuclear antibodies by immunofluorescence. Man Biolog Markers Dis A2:1–16
Li Y, Shen L, Yu S (2017) HEp-2 specimen image segmentation and classification using very deep fully convolutional network. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36(7):1561–1572
Maji P (2014) A rough hypercuboid approach for feature selection in approximation spaces. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(1):16–29
Maji P, Mandal A (2017) Multimodal omics data integration using max relevance-max significance criterion. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(8):1841–1851
Mandal A, Maji P (2018) FaRoC: fast and robust supervised canonical correlation analysis for multimodal omics data. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(4):1229–1241
Mariz HA, Sato EI, Barbosa SH, Rodrigues SH, Dellavance A, Andrade LE (2011) Pattern on the antinuclear antibody-HEp-2 test is a critical parameter for discriminating antinuclear antibody-positive healthy individuals and patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum 63(1):191–200
Nosaka R, Fukui K (2014) HEp-2 cell classification using rotation invariant co-occurrence among local binary patterns. Pattern Recognit 47(7):2428–2436
Nosaka R, Ohkawa Y, Fukui K (2012) Feature extraction based on co-occurrence of adjacent local binary patterns. In: Proceedings of the 5th Pacific Rim conference on advances in image and video technology, pp 82–91. Springer, Berlin
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Harwood D (1994) Performance evaluation of texture measures with classification based on kullback discrimination of distributions. In: Proceedings of the 12th IAPR international conference on pattern recognition, conference a: computer vision & image processing, pp 582–585
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(7):971–987
Ojala T, Valkealahti K, Oja E, Pietikainen M (2001) Texture discrimination with multidimensional distributions of signed gray-level differences. Pattern Recognit 34(3):727–739
Qi X, Zhao G, Li C, Guo J, Pietikainen M (2017) HEp-2 cell classification via combining multiresolution co-occurrence texture and large region shape information. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 21(2):429–440
Roy S, Maji P (2017) Rough-fuzzy segmentation of HEp-2 cell indirect immunofluorescence images. Int J Data Min Bioinf 17(4):311–340
Soda P, Iannello G (2006) A multi-expert system to classify fluorescent intensity in antinuclear autoantibodies testing. In: Proceedings of the 19th IEEE symposium on computer-based medical systems, pp 219–224
Soda P, Rigon A, Afeltra A, Iannello G (2006) Automatic acquisition of immunofluorescence images: algorithms and evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 19th IEEE symposium on computer-based medical systems, pp 386–390
Solomon DH, Kavanaugh AJ, Schur PH (2002) Evidence-based guidelines for the use of immunologic tests: antinuclear antibody testing. Arthritis Rheum 47(4):434–444
Strandmark P, Ulen J, Kahl F (2012) HEp-2 staining pattern classification. In: Proceedings of the 21st international conference on pattern recognition, pp 33–36
Tan EM (1989) Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv Immunol 44:93–151
Theodorakopoulos I, Kastaniotis D, Economou G, Fotopoulos S (2012) HEp-2 cells classification via fusion of morphological and textural features. In: Proceedings of the 12th IEEE international conference on bioinformatics and bioengineering, pp 689–694
Theodorakopoulos I, Kastaniotis D, Economou G, Fotopoulos S (2014) HEp-2 cells classification via sparse representation of textural features fused into dissimilarity space. Pattern Recognit 47(7):2367–2378
Vapnik V (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Vinod HD (1976) Canonical ridge and econometrics of joint production. J Economet 4(2):147–166
White PA (1958) The computation of eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix. J Soc Ind Appl Math 6(4):393–437
Wiik AS (2005) Anti-nuclear autoantibodies: clinical utility for diagnosis, prognosis, monitoring, and planning of treatment strategy in systemic immunoinflammatory diseases. Scand J Rheumatol 34(4):260–268
Wiliem A, Wong Y, Sanderson C, Hobson P, Chen S, Lovell BC (2013) Classification of human epithelial type 2 cell indirect immunofluoresence images via codebook based descriptors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE workshop on applications of computer vision, pp 95–102
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (Grant No. SB/S3/EECE/050/2015). The authors would like to thank Debamita Kumar of Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata, for her valuable experimental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, A., Maji, P. CanSuR: a robust method for staining pattern recognition of HEp-2 cell IIF images. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 16471–16489 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04108-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04108-w