Abstract
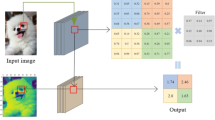
The convolutional neural network architecture has different components like convolution and pooling. The pooling is crucial component placed after the convolution layer. It plays a vital role in visual recognition, detection and segmentation course to overcome the concerns like overfitting, computation time and recognition accuracy. The elementary pooling process involves down sampling of feature map by piercing into subregions. This piercing and down sampling is defined by the pooling hyperparameters, viz. stride and filter size. This down sampling process discards the irrelevant information and picks the defined global feature. The generally used global feature selection methods are average and max pooling. These methods decline, when the main element has higher or lesser intensity than the nonsignificant element. It also suffers with locus and order of nominated global feature, hence not suitable for every situation. The pooling variants are proposed by numerous researchers to overcome concern. This article presents the state of the art on selection of global feature for pooling process mainly based on four categories such as value, probability, rank and transformed domain. The value and probability-based methods use the criteria such as the way of down sampling, size of kernel, input output feature map, location of pooling, number stages and random selection based on probability value. The rank-based methods assign the rank and weight to activation; the feature is selected based on the defined criteria. The transformed domain pooling methods transform the image to other domains such as wavelet, frequency for pooling the feature.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scherer D, Muller A, Behnke S (2010) Evaluation of pooling operations in convolutional architectures for object recognition, In: Proceedings of the international conference on artificial neural networks, pp 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15825-4_10
Zhong Z, Jin L, Feng Z (2015) Multi-font printed Chinese character recognition using multi-pooling convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of 13th international conference on document analysis and recognition, pp 96-100. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDAR.2015.7333733
Springenberg JT, Dosovitskiy A, Brox T (2015) Martin riedmiller, striving for simplicity the all convolutional net. arXiv:1412.6806v3
Chen J, Hua Z, Wang J, Cheng S (2017) A convolutional neural network with dynamic correlation pooling. In: Proceedings of international conference on computational intelligence and security, pp 496-499. https://doi.org/10.1109/CIS.2017.00115
Karpathy A (2017) Stanford University CS231n: convolutional neural networks for visual recognition. http://cs231n.stanford.edu/syllabus.html. Accessed 28 Nov 2018
Li C, Yang SX, Yang Y, Gao H, Zhao J, Qu X, Wang Y, Yao D, Gao J (2018) Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification based on maximum overlap pooling convolutional neural network. Sensors 18:3587. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103587
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Int 37(9):1904–1916. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824
Yu D, Wang H, Chen P, Wei Z (2014) Mixed pooling for convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 9th international conference on rough sets and knowledge technology, pp 364–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11740-9_34
Wu H, Gu X (2015) Max-pooling dropout for regularization of convolutional neural networks. arXiv:1512.01400v1
Shi W, Loy CC, Tang X (2016) Deep specialized network for illuminant estimation. In: European conference on computer vision, pp 371–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_23
Nagi J, Ducatelle F, Di Caro GA, Ciresan D, Meier U, Giusti A, Nagi F, Schmidhuber J, Gambardella LM (2011) Max-pooling convolutional neural networks for vision-based hand gesture recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on signal and image processing applications, pp 342–347. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSIPA.2011.6144164
Graham B (2015) Fractional max-pooling. arXiv:1412.6071v4
Ranzato MA, Huang FJ, Boureau Y, LeCun Y (2007) Unsupervised learning of invariant feature hierarchies with applications to object recognition. In: Proceedings. computer vision and pattern recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2007.383157
Netzer Y, Wang T, Coates A, Bissacco A, Wu B, Ng AY (2011) Reading digits in natural images with unsupervised feature learning. In: Proceedings of the neural information processing systems
LeCun Y, Huang FJ, Bottou L (2004) Learning methods for generic object recognition with invariance to pose and lighting. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2004.1315150
Boureau Y, Ponce J, LeCun Y (2010) A theoretical analysis of feature pooling in visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 27th international conference on machine learning, pp 111–118
Lee H, Grosse R, Ranganath R, Ng AY (2009) Convolutional deep belief networks for scalable unsupervised learning of hierarchical representations. In: Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations, pp 609–616. https://doi.org/10.1145/1553374.1553453
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.726791
Fei-Fei L, Fergus R, Perona P (2006) One-shot learning of object categories. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(4):594–611. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2006.79
Ciresan DC, Meier U, Masci J, Maria Gambardella L, Schmidhuber J (2011) Flexible, high performance convolutional neural networks for image classification. Proc Int Joint Conf Artif Intell 1:1237–1242. https://doi.org/10.5591/978-1-57735-516-8/IJCAI11-210
Zeiler MD, Fergus R (2013) Stochastic pooling for regularization of deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv: 1301.3557v1
Sainath TN, Kingsbury B, Mohamed A, Dahl GE, Saon G, Soltau H, Beran T, Aravkin Aleksandr Y, Ramabhadran B (2013) Improvements to deep convolutional neural networks for LVCSR. In: 2013 IEEE workshop on automatic speech recognition and understanding, pp 315–320. https://doi.org/10.1109/ASRU.2013.6707749
Jarrett K, Kavukcuoglu K, LeCun Y (2009) What is the best multi-stage architecture for object recognition?. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2146–2153. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2009.5459469
Long Y, Zhu F, Shao L, Han J (2018) Face recognition with a small occluded training set using spatial and statistical pooling. Inf Sci 430–431:634–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.042
Wang F, Huang S, Shi L, Fan W (2017) The application of series multi-pooling convolutional neural networks for medical image segmentation. Int J Distrib Sensor Netw 13:12. https://doi.org/10.1177/1550147717748899
Eom H, Choi H (2018) Alpha-pooling for convolutional neural networks. arXiv:1811.03436v1
Lin M, Chen Q, Yan S (2013) Network in network. arXiv: 1312.4400v3
Zhang B, Zhao Q, Feng W, Lyu S (2018) AlphaMEX: a smarter global pooling method for convolutional neural networks. Neurocomputing 321:36–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.07.079
Saeedan F, Weber N, Goesele M, Roth S (2018) Detail-preserving pooling in deep networks. arXiv:1804.04076v1
Sun M, Song Z, Jiang X, Pan J, Pang Y (2017) Learning pooling for convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 24(8):96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.10.049
Grauman K, Darrell T (2005) The pyramid match kernel: discriminative classification with sets of image features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1458–1465. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2005.239
Lazebnik S, Schmid C, Ponce J (2006) Beyond bags of features: spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. Proceeding of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2169–2178. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2006.68
Jose A, Lopez RD, Heisterklaus I, Wien M (2018) Pyramid pooling of convolutional feature maps for image retrieval. Proc Int Conf Image Process 1:480–484. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2018.8451361
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2018) DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Laptev D, Savinov N, Buhmann JM, Pollefeys M (2016) TI-POOLING: transformation-invariant pooling for feature learning in convolutional neural networks. arXiv: 1604.06318
Wu J, Yu Y, Huang C, Yu K (2015) Deep multiple instance learning for image classification and auto-annotation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3460–3469. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298968
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2014) Going deeper with convolutions. arXiv:1409.4842v1
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proc Int Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Cui Y, Zhou F, Wang J, Liu X, Lin Y, Belongie S (2017) Kernel pooling for convolutional neural networks. Int Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 1:3049–3058. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.325
Shahriari A, Porikli F (2017) Multipartite pooling for deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv:1710.07435v1
Krizhevsky A (2009) Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Master’s Dissertation, University of Toronto, Canada
Hang ST, Aono M (2017) Bi-linearly weighted fractional max pooling: an extension to conventional max pooling for deep convolutional neural network. Int J Multimed Too Appl 76(21):22095–22117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4840-5
Han X-H, Lei J, Chen Y-W (2016) HEp-2 cell classification using K-support spatial pooling in deep CNNs. LNCS 10008:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46976-8_1
Zhao Q, Lyu S, Zhang B, Feng W (2018) Multiactivation pooling method in convolutional neural networks for image recognition. Wirel Commun Mob Comput. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8196906
Zhang J, Huang Q, Wu H, Liu Y (2017) A shallow network with combined pooling for fast traffic sign recognition. Information 8:45–58. https://doi.org/10.3390/info8020045
Qi K, Guan Q, Yang C, Peng F, Shen S, Huayi W (2018) Concentric circle pooling in deep convolutional networks for remote sensing scene classification. Remote Sens 10:934. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060934
Dias CA et al (2018) Using the choquet integral in the pooling layer in deep learning networks. In: Barreto G, Coelho R (eds) Fuzzy information processing. NAFIPS 2018. Communications in computer and information science, vol 831. Springer, Cham
Gong Y, Wang L, Guo R, Lazebnik S (2014) Multi-scale orderless pooling of deep convolutional activation features. arXiv:1403.1840v3
Zhi T, Duan L-Y, Wang Y, Huang T (2016) Two-stage pooling of deep convolutional features for image retrieval. Proc Int Conf Image Process 1:2465–2469. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2016.7532802
Gao F, Lou Y, Bai Y, Wang S, Huang T, Duan L-Y (2017) Improving object detection with region similarity learning. arXiv:1703.00234v1
Ouyang W, Wang X, Zeng X, Qiu S, Luo P, Tian Y, Li H, Yang S, Wang Z, Loy C-C, Tang X (2015) DeepID-Net: deformable deep convolutional neural networks for object detection. Proc Comput Vis Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298854
Yang F, Choi W, Lin Y (2016) Exploit all the layers: fast and accurate CNN object detector with scale dependent pooling and cascaded rejection classifiers. Int Conf Comput Vis and Pattern Recognit 1:2129–2137. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.234
Sadigh S, Sen P (2018) Improving the resolution of cnn feature maps efficiently with multisampling. arXiv:1805.10766v1
Takeki A, Ikami D, Irie G, Aizawa K (2018) Parallel grid pooling for data augmentation. arXiv:1803.11370v1
Hyvarinen A, Koster U (2007) Complex cell pooling and the statistics of natural images. Netw Comput Neural Syst 18(2):81–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/09548980701418942
Estrach JB, Szlam A, Lecun Y (204) Signal recovery from pooling representations. In: Proceedings of the international conference on machine learning , pp 307–315. arXiv:1311.4025v3
Sermanet P, Chintala S, LeCun Y (2012) Convolutional neural networks applied to house numbers digit classification. In: Proceedings of the 21st international conference on pattern recognition, pp 3288–3291
Turaga SC, Murray JF, Jain V, Roth F, Helmstaedter M, Briggman K, Briggman W, Denk H Sebastian, Seung HS (2010) Convolutional networks can learn to generate affinity graphs for image segmentation. Neural Comput 22(2):511–538. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.2009.10-08-881
Wan L, Zeiler M, Zhang S, LeCun Y, Fergus R (2013) Regularization of neural networks using dropconnect. In: Proceedings of the 30th international conference on machine learning, vol 28(3), pp 1058–1066
Hinton GE, Srivastava N, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov RR (2012). Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors. arXiv: 1207.0580
Fei J, Fang H, Yin Q, Yang C, Wang D (2018) Restricted stochastic pooling for convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the 10th international conference on internet multimedia computing and service, Article No. 24. https://doi.org/10.1145/3240876.3240919
Zhai S, Wu H, Kumar A, Cheng Y, Lu Y, Zhang Z, Feris R (2017) S3Pool: pooling with stochastic spatial sampling.arXiv:1611.05138v1
Song Z, Liu Y, Song R, Chen Z, Yang J, Zhang C, Jiang Q (2018) A sparsity-based stochastic pooling mechanism for deep convolutional. Neural Netw 105:340–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.05.015
Shi Z, Ye Y, Wu Y (2016) Rank-based pooling for deep convolutional neural networks. Neural Netw 83:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2016.07.003
Tong Z, Aihara K, Tanaka G (2016) A hybrid pooling method for convolutional neural networks, ICONIP 2016, Part II (LNCS), vol 9948pp. 454–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46672-9_51
Zhang Y, Shi B (2017) Improving pooling method for regularization of convolutional networks based on the failure probability density. Optik 145:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.07.045
Bulo S, Kontschieder P (2014) Neural decision forests for semantic image labelling. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.18
Lee C-Y, Gallagher PW, Tu Z (2015) Generalizing pooling functions in convolutional neural networks: mixed, gated, and tree. arXiv:1509.08985
Kumar A (2018) Ordinal pooling networks: for preserving information over shrinking feature maps. arXiv:1804.02702
Kolesnikov A, Lampert CH (2016) Seed, expand and constrain: three principles for weakly-supervised image segmentation. LNCS 9908:695–711. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_42
Hu Y, Wang B, Lin S (2017) FC4 fully convolutional color constancy with confidence-weighted pooling. Proc Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 1:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.43
Zhang Y-D, Pan Ch, Chen X, Wang F (2018) Abnormal breast identification by nine-layer convolutional neural network with parametric rectified linear unit and rank-based stochastic pooling. J Comput Sci 27:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2018.05.005
Qian Y, Woodland PC (2016) Very deep convolutional neural networks for robust speech recognition. arXiv:1610.00277v1
Abdel-Hamid O, Mohamed A-R, Jiang H, Penn G. (2012) Applying convolutional neural networks concepts to hybrid NN-HMM model for speech recognition. In: Proceedings of international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, pp 4277–4280. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2012.6288864
Sainath T, Mohamed A, Kingsbury B, Ramabhadran B (2013) Deep convolutional neural networks for LVCSR. In: Proceedings of international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing. https://doi.org/10.1109/ASRU.2013.6707749
Waibel A, Hanazawa T, Hinton G, Shikano K, Lang K (1989) Phoneme recognition using time-delay neural networks. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 37(3):328–339. https://doi.org/10.1109/29.21701
Deng L, Abdel-Hamid O, Yu D (2013) A deep convolutional neural network using heterogeneous pooling for trading acoustic invariance with phonetic confusion. In Proceedings of international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, pp 6669–6673. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6638952
Williams T, Li R (2018) Wavelet pooling for convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations, vol 6
Rippel O, Snoek J, Adams RP (2015) Spectral representations for convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.03767
Xu Y, Kong Q, Wang W, Plumbley MD (2018) Large-scale weakly supervised audio classification using gated convolutional. Neural Netw. arXiv:1710.00343v1
Wang Z, Lan Q, Huang D, Wen M (2016) Combining FFT and spectral-pooling for efficient convolution neural network model. In: Proceeding 2nd International conference on artificial intelligence and industrial engineering, vol 133. https://doi.org/10.2991/aiie-16.2016.47
Zhang H, Ma J (2018) Hartley spectral pooling for deep learning. arXiv:1810.04028v1
Smith JS, Wilamowski BM (2018) Discrete cosine transform spectral pooling layers for convolutional neural networks, artificial intelligence and soft computing. ICAISC 2018 (Lecture notes in computer science), vol. 10841. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91253-0_23
Springenberg JT, Dosovitskiy A, Brox T, Riedmiller M (2015) Striving for simplicity: the all convolutional net. In: Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations. arXiv:1412.6806v3
Li S, Li W, Cook C, Zhu C, Gao Y (2017) A fully trainable network with RNN-based pooling. arXiv:1706.05157
Sabour S, Frosst N, Hinton G (2018) Matrix capsules with EM routing. In: Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations. https://doi.org/10.13140/rg.2.2.27416.44800
Tsai Y-H, Hamsici OC, Yang M-H (2015) Adaptive region pooling for object detection. In Proceedings of 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 731–739. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298673
Cherian A, Gould S (2018) Second-order temporal pooling for action recognition. arXiv:1704.06925
Girdhar R, Ramanan D (2017) Attentional pooling for action recognition. arXiv:1711.01467v3
Wang P, Cao Y, Shen C, Liu L, Shen HT (2015) Temporal pyramid pooling based convolutional neural networks for action recognition. arXiv:1503.01224
Song S, Cheung N-M, Chandrasekhar V, Mandal B (2018) Deep adaptive temporal pooling for activity recognition. arXiv:1808.07272
Cherian A, Fernando B, Harandi M, Gould S (2017) Generalized rank pooling for activity recognition. Proc Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 1:1581–1590. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.172
Fernando B, Gavves E, Oramas J, Ghodrati A, Tuytelaars T (2017) Rank pooling for action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Int 39(4):773–787. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2558148
Fernando B, Gould S (2017), Discriminatively learned hierarchical rank pooling networks. arXiv:1705.10420v1
Wang P, Li W, Gao Z, Tang C, Ogunbona P (2018) Depth pooling based large-scale 3D action recognition with convolutional neural networks. arXiv:1804.01194
Kar A, Rai N, Sikka K, Sharma G (2017) AdaScan: adaptive scan pooling in deep convolutional neural networks for human action recognition in videos. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.604
Suárez-Paniagua V, Segura-Bedmar I (2018) Evaluation of pooling operations in convolutional architectures for drug-drug interaction extraction. BMC Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-018-2195-1
Girshick R (2015) Fast R-CNN. In: International conference on computer vision, pp 1440–1448. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169
Gulcehre C, Cho K, Pascanu R, Bengio Y (2014) Learned-norm pooling for deep feed forward and recurrent neural networks. arXiv:1311.1780v7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akhtar, N., Ragavendran, U. Interpretation of intelligence in CNN-pooling processes: a methodological survey. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 879–898 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04296-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04296-5