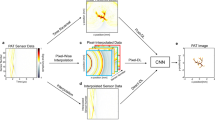
Abstract
Endoscopic photoacoustic tomography (EPAT) is a rapidly developing catheter-based imaging technique to provide cross-sectional images of anatomical, functional and molecular data of tubular objects. The scanning geometry of the ultrasonic detector is enclosed in the cavity resulting in highly restricted acquisition of photoacoustically induced acoustic pressures. Thus, data-incompleteness is an important factor that causes degradation of the image quality. This work presents a method to solve the acoustic inverse problem of EPAT from incomplete measurements associated with the image formation process. This method combines the traditional variational iteration with convolutional neural network (CNN), in which the forward operator and adjoint operator of imaging are excluded from the network training and are embedded into each layer of the structural unit. The gradient information is utilized to reduce the influence of incomplete measurements on the image quality. The network is trained unit by unit in an adaptive way to achieve fast convergence. Our numerical results conducted on various data sets showed that the trained network is robust to the sampling rate of the measured data. Also, it is able to provide a generalization that can work across various noise levels in the data. In addition, a robust peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity (SSIM) improvement obtained in the reconstructed images has been demonstrated in comparison with conventional TR reconstruction, CS reconstruction and post-processing by U-net.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miranda C, Marschall E, Browning B, Smith BS (2020) Side-viewing photoacoustic waveguide endoscopy. Photoacoustics 19(9):100167
Poudel J, Yang L, Anastasio MA (2019) A survey of computational frameworks for solving the acoustic inverse problem in three-dimensional photoacoustic computed tomography. Phys Med Biol 64(14):14TR01
Javaherian A, Holman S (2019) Direct quantitative photoacoustic tomography for realistic acoustic media. Inverse Prob 35:084004
Sheu YL, Chou CY, Hsieh BY (2011) Image reconstruction in intravascular photoacoustic imaging. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 58(10):2067–2077
Ambartsoumian G, Kunyansky L (2014) Exterior/interior problem for the circular means transform with applications to intravascular imaging. Inverse Probl Imaging 8(2):339–359
Sun Z, Han D, Yuan Y (2016) 2-D image reconstruction of photoacoustic endoscopic imaging based on time-reversal. Comput Biol Med 76:60–68
Sheu YL, Chou CY, Hsieh BY et al (2010) Application of limited-view image reconstruction method to intravascular photoacoustic tomography. Proc SPIE Int Conf Photons Plus Ultrasound Imaging And Sens 7564:75640B
Bu S, Yamakaway M, Shiina T (2010) Interpolation method for model-based 3-D planar photoacoustic tomography reconstruction. Proc 3rd Biomed Eng Int Conf 129–132.
Javaherian A, Holman S (2017) A multi-grid iterative method for photoacoustic tomography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36(3):696–706
Liu X, Peng D (2016) Regularized iterative weighted filtered back-projection for few-view data photoacoustic imaging. Comput Math Methods Med 2016:9732142
Syed TA, Krishnan VP, Sivaswamy J (2016) Numerical inversion of circular arc radon transform. IEEE Trans Comput Imaging 2(4):540–549
Jin W, Yuanyuan W (2017) An efficient compensation method for limited-view photoacoustic imaging reconstruction based on gerchberg–papoulis extrapolation. Appl Sci 7(5):505
Arridge S, Beard P, Betcke M et al (2016) Accelerated high-resolution photoacoustic tomography via compressed sensing. Phys Med Biol 61(24):8908
Haltmeiera M, Sandbichler M, Berer T et al (2018) A sparsification and reconstruction strategy for compressed sensing photoacoustic tomography. J Acoust Soc Am 143:3838–3848
Antholzer S, Schwab J, Bauer-Marschallinger J et al (2019) (2019) NETT regularization for compressed sensing photoacoustic tomography. Proc SPIE Int Conf Photons Plus Ultrasound Imaging Sens 10878:108783
Gao M, Si G, Bai Y et al (2020) Graphics processing unit accelerating compressed sensing photoacoustic computed tomography with total variation. Appl Opt 59(3):712–719
Sun Z, Yan X (2020) Image reconstruction based on compressed sensing for sparse-data endoscopic photoacoustic tomography. Comput Biol Med 116:103587
Ji Y, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Liu M (2021) CNN-based encoder-decoder networks for salient object detection: a comprehensive review and recent advances. Inf Sci 546:835–857
Połap D, Woźniak M (2019) Bacteria shape classification by the use of region covariance and convolutional neural network. Proceedings of 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Budapest, Hungary, N-19459, 14–19 July 2019
Woźniak M, Wieczorek M, Siłka J, Połap D (2020) Body pose prediction based on motion sensor data and recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans Ind Inf. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.3015934
Wang G, Ye JC, Mueller K, Fessler JA (2018) Image reconstruction is a new frontier of machine learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37(6):1289–1296
Wei W, Zhou B, Połap D, Woźniak M (2019) A regional adaptive variational PDE model for computed tomography image reconstruction. Pattern Recogn 92:64–81
Lucas A, Iliadis M, Molina R, Katsaggelos AK (2018) Using deep neural networks for inverse problems in imaging: beyond analytical methods. IEEE Signal Process Mag 35(1):20–36
Kelly B, Matthews TP, Anastasio MA (2017) Deep learning-guided image reconstruction from incomplete data. Proceedings of 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA
Waibel DJE (2018) Photoacoustic image reconstruction to solve the acoustic inverse problem with deep learning. Master's thesis, University of Heidelberg
Haltmeier M, Antholzer S, Schwab J et al (2018) (2018) Photoacoustic image reconstruction via deep learning. Proc SPIE Int Conf Photons Plus Ultrasound Imaging Sens 10494:104944U
Antholzer S, Haltmeier M, Schwab J et al (2019) Deep learning for photoacoustic tomography from sparse data. Inverse Probl Sci Eng 27(7):987–1005
Schwab J, Antholzer S, Haltmeier M (2019) Learned backprojection for sparse and limited view photoacoustic tomography. Proc SPIE Int Conf on Photons Plus Ultrasound Imaging Sens 10878:1087837
Sun Z, Yan X (2020) A deep learning method for limited-view intravascular photoacoustic image reconstruction. J Med Imaging Health Inform 10(11):2707–2713
Farnia P, Mohammadi M, Najafzadeh E et al (2020) High-quality photoacoustic image reconstruction based on deep convolutional neural network: towards intra-operative photoacoustic imaging. Biomed Phys Eng Express 6(4):045019
Antholzer S, Schwab J, Haltmeier M (2018) Deep learning versus l1-minimization for compressed sensing photoacoustic tomography. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS). Kobe, Japan, 22–25 Oct 2018
Awasthi N, Prabhakar KR, Kalva SK et al (2019) PA-Fuse: deep supervised approach for the fusion of photoacoustic images with distinct reconstruction characteristics. Biomed Opt Express 10(5):2227–2243
Oktem O, Adler J (2017) Solving ill-posed inverse problems using iterative deep neural networks. Inverse Prob 33(12):124007
Hauptmann A, Lucka F, Betcke M et al (2018) Model based learning for accelerated, limited-view 3D photoacoustic tomography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37(6):1382–1393
Jonas A, Ozan O (2018) Learned primal-dual reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37(6):1322–1332
Boink YE, Manohar S, Brune C (2020) A partially-learned algorithm for joint photo-acoustic reconstruction and segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(1):129–139
Li H, Schwab J, Antholzer S et al (2020) NETT: solving inverse problems with deep neural networks. Inverse Prob 36(6):065005
Guan S, Khan AA, Sikdar S et al (2020) Limited-view and sparse photoacoustic tomography for neuroimaging with deep learning. Sci Rep 10:8510
Davoudi N, Deán-Ben XL, Razansky D (2019) Deep learning optoacoustic tomography with sparse data. Nature Mach Intell 1(10):453–460
McCann MT, Jin KH, Unser M (2017) Convolutional neural networks for inverse problems in imaging: a review. IEEE Signal Process Mag 34(6):85–95
Treeby BE, Cox BT (2010) K-wave: MATLAB toolbox for the simulation and reconstruction of photoacoustic wave fields. J Biomed Opt 15(2):1–12
Jacques SL (2014) Coupling 3D monte carlo light transport in optically heterogeneous tissues to photoacoustic signal generation. Photoacoustics 2(4):137–142
Sun Z, Yuan Y, Han D (2017) A computer-based simulator for intravascular photoacoustic images. Comput Biol Med 81:176–187
Sun Z, Zheng L (2018) Reconstruction of optical absorption coefficient distribution in intravascular photoacoustic imaging. Comput Biol Med 97:37–49
Pan SJ, Yang Q (2010) A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(10):1345–1359
Ravishankar S, Ye JC, Fessler JA (2020) Image reconstruction: from sparsity to data-adaptive methods and machine learning. Proc IEEE 108(1):86–109
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Nature Science Foundations of China (no. 62071181).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None conflicts of interest declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Wang, X. & Yan, X. An iterative gradient convolutional neural network and its application in endoscopic photoacoustic image formation from incomplete acoustic measurement. Neural Comput & Applic 33, 8555–8574 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05607-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05607-x