Abstract
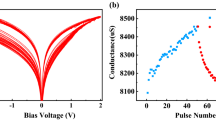
In this paper, a Competitive Neural Network circuit based on voltage-controlled memristors is proposed, of which the synapse structure is one memristor (1M). The designed circuit consists of the forward calculation part and the weight updating part. The forward calculation part is designed according to the winner-take-all mechanism, in which the m-LIF model and PMOS transistors with switching characteristics are combined to achieve the lateral inhibition. The weight updating part is designed based on the Hebbian learning rule. By using the voltage controlled switches, only the synaptic memristors connected to the winner output neuron obtained from the forward calculation part are adjusted. The whole circuit does not require the participation of CPU, FPGA or other microcontrollers, providing the possibility to realize computing-in-memory and parallel computing. We perform simulation experiments of unsupervised online learning of 5*3 pixels patterns and 28*28 pixels patterns based on the designed circuit in PSPICE. The changing trend of the network weights during the training phase and the high recognition accuracy in the recognition phase verify the network can effectively learn and recognize different patterns.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidhuber J (2015) Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Netw 61:85
Ji Y, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Liu M (2021) CNN-based encoder-decoder networks for salient object detection: A comprehensive review and recent advances. Inf Sci 546:835
Poulos J, Valle R (2021) Character-based handwritten text transcription with attention networks. Neural Comput Appl 33(16):10563–10573
Chen HY, Chen CC, Hwang WJ (2017) An efficient hardware circuit for spike sorting based on competitive learning networks. Sensors 17(10):2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102232
Hasan R, Taha TM (2017) Memristor crossbar based winner take all circuit design for self-organization. In: Proceedings of the neuromorphic computing symposium. ACM, pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1145/3183584.3183622
Wu LS, Jain L (2007) Size invariant shape recognition by modulated competitive neural circuit. Int J Inf Commun Technol 1(1):76. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJICT.2007.013319
Chang CY, Lin SY, Jeng M (2005) Using a two-layer competitive hopfield neural network for semiconductor wafer defect detection. In: IEEE international conference on automation science and engineering. IEEE, pp 301–306. https://doi.org/10.1109/coase.2005.1506786
Gong S, Yang S, Guo Z, Huang T (2019) Global exponential synchronization of memristive competitive neural networks with time-varying delay via nonlinear control. Neural Process Lett 49(1):103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-017-9777-1
Merolla PA, Arthur JV, Alvarez-Icaza R et al (2014) A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 345(6197):668. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254642
Eberhardt SP, Daud T, Kerns D, Brown TX, Thakoor A (1991) Competitive neural architecture for hardware solution to the assignment problem. Neural Netw 4(4):431. https://doi.org/10.1016/0893-6080(91)90039-8
Oniga S, Tisan A, Attila B, Lung C (2007) Hardware implementation of simple competitive artificial neural networks with neuron parallelism. In: Proceedings of regional conference on embedded and ambient systems, RCEAS, pp 27–32
Asai T, Ohtani M, Yonezu H (1999) Analog integrated circuits for the Lotka–Volterra competitive neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 10(5):1222. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.788661
Fang Y, Cohen MA, Kincaid TG (2010) Dynamic analysis of a general class of winner-take-all competitive neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 21(5):771. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2010.2041671
Hollis PW, Paulos JJ (1990) Artificial neural networks using MOS analog multipliers. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 25(3):849. https://doi.org/10.1109/4.102684
Chua L (1971) Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans Circuit Theory 18(5):507. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337
Strukov DB, Snider GS, Stewart DR, Williams RS (2008) The missing memristor found. Nature 453(7191):80. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06932
Zhou Z, Yan X, Zhao J et al (2019) Synapse behavior characterization and physical mechanism of a TiN/SiO x/p-Si tunneling memristor device. J Mater Chem C 7(6):1561. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TC04903C
Cantley KD, Subramaniam A, Stiegler HJ, Chapman RA, Vogel EM (2011) Hebbian learning in spiking neural networks with nanocrystalline silicon TFTs and memristive synapses. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 10(5):1066. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2011.2105887
Ohno T, Hasegawa T, Tsuruoka T, Terabe K, Gimzewski JK, Aono M (2011) Short-term plasticity and long-term potentiation mimicked in single inorganic synapses. Nat Mater 10(8):591. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3054
Jo SH, Chang T, Ebong I, Bhadviya BB, Mazumder P, Lu W (2010) Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett 10(4):1297. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl904092h
Zhao L, Hong Q, Wang X (2018) Novel designs of spiking neuron circuit and STDP learning circuit based on memristor. Neurocomputing 314:207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.06.062
Pedretti G, Milo V, Ambrogio S et al (2017) Memristive neural network for on-line learning and tracking with brain-inspired spike timing dependent plasticity. Sci Rep 7(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05480-0
Hu S, Liu Y, Liu Z, Chen T, Wang J, Yu Q, Deng L, Yin Y, Hosaka S (2015) Associative memory realized by a reconfigurable memristive Hopfield neural network. Nat Commun 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8522
Garbin D, Vianello E, Bichler O, Rafhay Q, Gamrat C, Ghibaudo G, DeSalvo B, Perniola L (2015) HfO 2-based OxRAM devices as synapses for convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 62(8):2494. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2015.2440102
Li C, Wang Z, Rao M, Belkin D, Song W, Jiang H, Yan P, Li Y, Lin P, Hu M et al (2019) Long short-term memory networks in memristor crossbar arrays. Nat Mach Intell 1(1):49. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-018-0001-4
Prezioso M, Mahmoodi M, Bayat FM, Nili H, Kim H, Vincent A, Strukov D (2018) Spike-timing-dependent plasticity learning of coincidence detection with passively integrated memristive circuits. Nat Commun 9(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07757-y
Qu L, Zhao Z, Wang L, Wang Y (2020) Efficient and hardware-friendly methods to implement competitive learning for spiking neural networks. Neural Comput Appl 32:13479–13490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04755-4
Hong Q, Yan R, Wang C, Sun J (2020) Memristive circuit implementation of biological nonassociative learning mechanism and its applications. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2020.3018777
Yan X, Wang J, Zhao M, Li X, Wang H, Zhang L, Lu C, Ren D (2018) Artificial electronic synapse characteristics of a Ta/Ta2O5-x/Al2O3/InGaZnO4 memristor device on flexible stainless steel substrate. Appl Phys Lett 113(1):013503. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5027776
Hansen M, Zahari F, Kohlstedt H, Ziegler M (2018) Unsupervised Hebbian learning experimentally realized with analogue memristive crossbar arrays. Sci Rep 8(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27033-9
Yu S, Gao B, Fang Z, Yu H, Kang J, Wong HSP (2013) Stochastic learning in oxide binary synaptic device for neuromorphic computing. Front Neurosci 7:186. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2013.00186
Serb A, Bill J, Khiat A, Berdan R, Legenstein R, Prodromakis T (2016) Unsupervised learning in probabilistic neural networks with multi-state metal-oxide memristive synapses. Nat Commun 7(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12611
Jiang Y, Huang P, Zhu D et al (2018) Design and hardware implementation of neuromorphic systems with RRAM synapses and threshold-controlled neurons for pattern recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 65(9):2726. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2018.2812419
Biolek Z, Biolek D, Biolkova V (2009) SPICE model of memristor with nonlinear dopant drift. Radioengineering 18(2):210
Kvatinsky S, Friedman EG, Kolodny A, Weiser UC (2012) TEAM: threshold adaptive memristor model. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 60(1):211. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2012.2215714
Zhang Y, Wang X, Li Y, Friedman EG (2016) Memristive model for synaptic circuits. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 64(7):767. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2016.2605069
Li Y, Zhong Y, Xu L, Zhang J, Xu X, Sun H, Miao X (2013) Ultrafast synaptic events in a chalcogenide memristor. Sci Rep 3:1619. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01619
Li Y, Zhong Y, Zhang J, Xu L, Wang Q, Sun H, Tong H, Cheng X, Miao X (2014) Activity-dependent synaptic plasticity of a chalcogenide electronic synapse for neuromorphic systems. Sci Rep 4:4906. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04906
Hebb DO (2005) The organization of behavior: a neuropsychological theory. Taylor and Francis, London
Chu M, Kim B, Park S, Hwang H, Jeon M, Lee BH, Lee BG (2015) Neuromorphic hardware system for visual pattern recognition with memristor array and CMOS neuron. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(4):2410–2419. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2014.2356439
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61876209 and in part by the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant 2017YFC1501301.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Hong, Q. & Wang, X. Memristor-based circuit implementation of Competitive Neural Network based on online unsupervised Hebbian learning rule for pattern recognition. Neural Comput & Applic 34, 319–331 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06361-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06361-4