Abstract
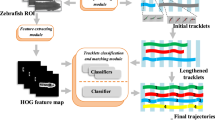
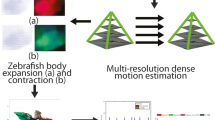
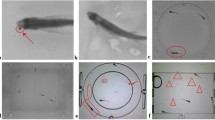
Zebrafish is a useful animal model for studying human diseases such as muscle disorders. However, manual monitoring of fish motion is time-consuming and prone to subjective variations. In this paper, an automatic fish motion analytics framework is proposed. The proposed framework could be exploited to help validate zebrafish models of transgenic zebrafish that express human genes carrying mutations which lead to muscle disorders, thus affecting their ability to swim normally. To differentiate between wild-type (normal) and transgenic zebrafish, the proposed framework consists of two approaches to exploit discriminative spatial–temporal kinematic features which are extracted to represent zebrafish movements. First, the proposed approach studies precise quantitative measurements of motor movement abnormalities using a camera with the capability to record videos with high frames rates (up to 1,000 frames per second). This differs from previous works, which only tracked each fish as a single point over time. Second, the proposed approach studies multi-view spatial–temporal swimming trajectories. This differs from previous works which typically only considered single-view analysis of fish swimming trajectories. The proposed motion features are then incorporated into a supervised classification approach to identify abnormal fish movements. Experimental results have shown that the proposed approach is capable of differentiating between wild-type and transgenic zebrafish, thus helping to validate the zebrafish models.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, N.S.: An Introduction to Kernel and nearest neighbors nonparametric regression. Am. Stat. 46, 175–185 (1992)
Beyan, C., Fisher, R.B.: Detecting abnormal fish trajectories using clustered and labelled data. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Confrence on Image Processing, Sept 2013, Melbourne, Australia, pp. 1476–1480 (2013)
Cachat, J., Stewart, A., Utterback, E., Hart, P., Gaikwad, S., Wong, K., Kyzar, E., Wu, N., Kalueff, A.V.: Three-dimensional neurophenotyping of adult zebrafish behavior. PLoS ONE 6(3), 1–14 (2011)
Cachat, J.M., Stewart, A., Utterback, E., Kyzar, E., Hart, P.C., Carlos, D., Gaikwad, S., Hook, M., Rhymes, K., Kalueff, A.V.: Deconstructing adult zebrafish behavior with swim trace visualizations. Zebrafish Neurobehav Protocols 51, 191–201 (2011)
Cario, C.L., Farrell, T.C., Milanese, C., Burton, E.A.: Automated measurement of zebrafish larval movement. J. Physiol. 589(15), 3703–3708 (2011)
Chang, C.-C., Lin, C.-J.: LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2(3), 1–27 (2011)
Cheng, W., Tian, J., Burgunder, J-M., Hunziker, W., Eng, H-L.: Myotonia congenita-associated mutations in chloride channel-1 affect zebrafish body wave swimming kinematics. PLoS ONE 9(8), e103445 (2014)
Fisher, R.B., Beyan, C.: Detection of abnormal fish trajectories using a clustering based hierarchical classifier. In: Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference, Bristol, UK, Sept 2013, pp. 21.1-21.11 (2013)
Fontaine, E., Lentink, D., Kranenbarg, S., Muller, U., Leeuwen, J., Barr, A.H., Burdick, J.W.: Automated visual tracking for studying the ontogeny of zebrafish swimming. J. Exp. Biol. 211, 1305–1316 (2008)
Friedman, J.H., Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: Additive logistic regression: a statistical view of boosting. Ann. Stat. 28, 337–407 (2000)
Greena, J., Collins, C., Kyzar, E.J., Pham, M., Roth, A., Gaikwad, S., Cachat, J., Stewart, A.M., Landsman, S., Grieco, F., Tegelenbosch, R., Noldus, L., Kalueff, A.V.: Automated high-throughput neurophenotyping of zebrafish social behavior. J. Neurosci. Methods 210(2), 266–271 (2012)
Liu, T.: A quantitative zebrafish phenotyping tool for developmental biology and disease modeling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 24(1), 126–129 (2007)
Martineau, P.R., Mourrain, P.: Tracking zebrafish larvae in group: status and perspectives. Methods 62(3), 292–303 (2013)
McClenahan, P., Troup, M., Scott, E.K.: Fin-tail coordination during escape and predatory behavior in larval zebrafish. PLoS ONE 7(2), 1–11 (2012)
Mikut, R., Dickmeis, T., Driever, W., Geurts, P., Hamprecht, F., Kausler, B.X., Ledesma-Carbayo, M.J., Marée, R., Mikula, K., Pantazis, P., Ronneberger, O., Santos, A., Stotzka, R., Strähle, U., Peyriéras, N.: Automated processing of zebrafish imaging data: a survey. Zebrafish 10(3), 401–421 (2013)
Mitchell, T.M.: Machine Learning. McGraw Hill, Maidenhead (1997)
Rosemberg, D.B., Rico, E.P., Mussulini, B.H.M., Piato, A.L., Calcagnotto, M.E., Bonan, C.D., Dias, R.D., Blaser, R.E., Souza, D.O., de Oliveira, D.L.: Differences in spatio-temporal behavior of zebrafish in the open tank paradigm after a short-period confinement into dark and bright environments. PLoS ONE 6(5), e19397 (2011)
Schaefer, A.T., Claridge-Chang, A.: The surveillance state of behavioral automation. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 22(1), 170–178 (2012)
Serra-Toro, C., Montoliu, R., Traver, V.J., Hurtado-Melgar, I.M., Nunez-Redo, M., Cascales, P.: Assessing water quality by video monitoring fish swimming behavior. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, Aug 2010, pp. 428–431 (2010)
Shortis, M.R., Ravanbakhsh, M., Shafait, F., Harvey, E.S., Mian, A., Seager, J.W., Culverhouse, P.F., Cline, D.E., Edgington, D.R.: A review of techniques for the identification and measurement of fish in underwater stereo-video image sequences. In: SPIE Conference on Videometrics, Range Imaging, and Applications XII, Munich, Germany, May 2013, pp. 1–10 (2013)
Spampinato, C., Palazzo, S.: Hidden Markov models for detecting anomalous fish trajectories in underwater footage. In: IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, Sept 2012, Santander, UK, pp. 1–6 (2012)
Spampinato, C., Giordano, D., Salvo, S.D., Chen-Burger, Y.-H.J., Fisher, R.B., Nadarajan, G.: Automatic fish classification for underwater species behavior understanding. In: Proceedings of ACM International Workshop on Analysis and Retrieval of Tracked Events and Motion in Imagery Streams, Firenze, Italy, Oct 2010, pp. 45–50 (2010)
Spampinato, C., Palazzo, S., Boom, B., Ossenbruggen, J., Kavasidis, I., Salvo, R.D., Lin, F.-P., Giordano, D., Hardman, L., Fisher, R.B.: Understanding fish behavior during typhoon events in real-life underwater environments. Multimed. Tools Appl. 70(1), 199–236 (2014)
Stewart, A.M., Gaikwad, S., Kyzar, E., Kalueff, A.V.: Understanding spatio-temporal strategies of adult zebrafish exploration in the open field test. Brain Res. 1451, 44–52 (2012)
Tian, J., Eng, H.-L.: Stochastic multiple fish tracking using motion and shape consistency. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Consumer Electronics, Singapore, June 2011, pp. 268–271 (2011)
Tian, J., Eng, H.-L.: Regularized high temporal resolution fish motion synthesis. In: IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, Singapore, April 2013, pp. 37–41 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Satpathy, A., Ng, E.S. et al. Motion analytics of zebrafish using fine motor kinematics and multi-view trajectory. Multimedia Systems 22, 713–723 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-014-0441-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-014-0441-6