Abstract
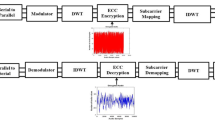
Owing to the rapid development and advancements in the field of networks and communication, sharing of multimedia contents over insecure networks has become vital. The confidentiality of audio signals is predominantly needed in military and intelligence bureau applications. The proposed algorithm addresses this issue by encrypting audio signal using chaotic maps in spatial and transform domain. Discrete Fourier transform (DFT), discrete cosine transform (DCT) and integer wavelet transform (IWT) approaches are considered for the experiment. The algorithm involves three-layer security of confusion and diffusion in the spatial domain, and confusion in the transform domain. The confusion in the transform domain is equivalent to diffusion in the spatial domain. Different sizes of audio samples are considered to validate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme. Experimental results prove that the DFT-assisted encryption scheme is more efficient than the DCT- and IWT-based methods because the DFT scheme employs effective diffusion through reversible phase coding. Effectiveness of the proposed method is substantiated using various metrics. Correlation coefficients arrive significantly closer to zero; number of samples changes rate (NSCR) value is at 100% and scrambling degree close to 1. Besides, the proposed scheme has a larger keyspace higher than 2128. Thus, the proposed algorithm has the potency to withstand the statistical, differential and brute force attacks.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engel, D., Stütz, T., Uhl, A.: A survey on JPEG2000 encryption. Multimed. Syst. 15, 243–270 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-008-0150-0
Fallahpour, M.: Secure logarithmic audio watermarking scheme based on the human auditory system. Multimed. Syst. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-013-0325-1
Yan, D., Wang, R., Yu, X., Zhu, J.: Steganography for MP3 audio by exploiting the rule of window switching. Comput. Secur. 31, 704–716 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2012.04.006
Sadek, M.M., Khalifa, A.S., Mostafa, M.G.M.: Video steganography: a comprehensive review. Multimed. Tools Appl. 74, 7063–7094 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-014-1952-z
Fallahpour, M., Megias, D.: High capacity audio watermarking using FFT amplitude interpolation. IEICE Electron. Express. 6, 1057–1063 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1587/elex.6.1057
Cheddad, A., Condell, J., Curran, K., Mc Kevitt, P.: Digital image steganography: survey and analysis of current methods. Signal Processing. 90, 727–752 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.08.010
Cox, I.J., Miller, M.L., Bloom, J.A., Fridrich, J., Kalker, T. eds: Preface to the first edition. In: Digital watermarking and steganography (second edition), pp. xv–xviii. Morgan Kaufmann, Burlington (2008)
Lian, S.: Multimedia content encryption. Tech. Appl. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420065282
Abuturab, M.R.: Color image security system based on discrete Hartley transform in gyrator transform domain. Opt. Lasers Eng. 51, 317–324 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2012.09.008
Madain, A., Abu Dalhoum, A.L., Hiary, H., Ortega, A., Alfonseca, M.: Audio scrambling technique based on cellular automata. Multimed. Tools Appl. 71, 1803–1822 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-012-1306-7
Ye, G.: Image scrambling encryption algorithm of pixel bit based on chaos map. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 31, 347–354 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2009.11.008
Zhou, N., Zhang, A., Zheng, F., Gong, L.: Novel image compression-encryption hybrid algorithm based on key-controlled measurement matrix in compressive sensing. Opt. Laser Technol. 62, 152–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2014.02.015
Dworkin, M.J., Barker, E.B., Nechvatal, J.R., Foti, J., Bassham, L.E., Roback, E., Dray Jr., J.F.: Announcing the advanced encryption standard (AES). Technol. Lab. Natl. Inst. Stand. 2009, 8–12 (2001)
Socek, D., Magliveras, S., Ćulibrk, D., Marques, O., Kalva, H., Furht, B.: Digital video encryption algorithms based on correlation-preserving permutations. Eurasip J. Inf. Secur. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/52965
McDevitt, T., Leap, T.: Multimedia cryptology. Cryptologia. 33, 142–150 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/01611190802300408
Mosa, E., Messiha, N.W., Zahran, O., Abd El-Samie, F.E.: Chaotic encryption of speech signals. Int. J. Speech Technol. 14, 285–296 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-011-9103-7
Wang, Y., Wong, K.-W., Liao, X., Chen, G.: A new chaos-based fast image encryption algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 11, 514–522 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2009.12.011
Rajaram, G.: Audio encryption using higher dimensional chaotic map. Int. J. Recent Trends Eng. 1, 103–107 (2009)
Ghasemzadeh, A., Esmaeili, E.: A novel method in audio message encryption based on a mixture of chaos function. Int. J. Speech Technol. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-017-9452-y
Belmeguenai, A., Ahmida, Z., Ouchtati, S., Djemii, R.: A novel approach based on stream cipher for selective speech encryption. Int. J. Speech Technol. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-017-9439-8
Farsana, F.J., Gopakumar, K.: A novel approach for speech encryption : Zaslavsky map as Pseudo random number generator. Procedia Procedia Comput. Sci. 93, 816–823 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2016.07.302
Eldin, S.M.S., Khamis, S.A., Hassanin, A.-A.I.M., Alsharqawy, M.A.: New audio encryption package for TV cloud computing. Int. J. Speech Technol. 18, 131–142 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-014-9253-5
Rao, R.: Efficient audio encryption algorithm for online applications using hybrid transposition and multiplicative non binary system. In: Presented at the (2013)
Sheela, J., Kaggere, S., Tandur, S.: A novel audio cryptosystem using chaotic maps and DNA encoding. J. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2017, 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2721910
Wang, H., Hempel, M., Peng, D., Wang, W., Sharif, H., Member, S., Chen, H.: Index-based selective audio encryption for wireless multimedia sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 12, 215–223 (2010)
Kwon, G.-R., Wang, C., Lian, S., Hwang, S.: Advanced partial encryption using watermarking and scrambling in MP3. Multimed. Tools Appl. 59, 885–895 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-011-0771-8
Farsana, F.J., Devi, V.R., Gopakumar, K.: Applied computing and informatics an audio encryption scheme based on fast walsh hadamard transform and mixed chaotic keystreams. Appl. Comput. Informatics. 2019, 1–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aci.2019.10.001
Yang, Y.G., Tian, J., Sun, S.J., Xu, P.: Quantum-assisted encryption for digital audio signals. Optik (Stuttg). 126, 3221–3226 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.07.082
Lima, J.B., da Silva Neto, E.F.: Audio encryption based on the cosine number transform. Multimed. Tools Appl. 75, 8403–8418 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2755-6
Alwahbani, S., Bashier, E.: Speech scrambling based on chaotic maps and one time pad. In: Presented at the (2013)
Liu, H., Kadir, A., Li, Y.: Audio encryption scheme by confusion and diffusion based on multi-scroll chaotic system and one-time keys. Optik (Stuttg). 127, 7431–7438 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.05.073
Ballesteros, D., Renza, D., Camacho, S.: High Scrambling degree in audio through imitation of an unintelligible signal. In: Presented at the (2016)
Belazi, A., Khan, M., Abd, A.A., Belghith, E.S.: Efficient cryptosystem approaches: S-boxes and permutation—substitution-based encryption. Nonlinear Dyn. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3046-0
Sathiyamurthi, P., Ramakrishnan, S.: Speech encryption using chaotic shift keying for secured speech communication. Eurasip J. Audio Speech Music Process. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13636-017-0118-0
Chang, D., Li, Z., Wang, M., Zeng, Y.: A novel digital programmable multi-scroll chaotic system and its application in FPGA-based audio secure communication. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 88, 20–29 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2018.03.007
Acknowledgements
Authors wish to acknowledge SASTRA Deemed University, Thanjavur, India for extending infrastructural support to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Wu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshmi, C., Ravi, V.M., Thenmozhi, K. et al. Con(dif)fused voice to convey secret: a dual-domain approach. Multimedia Systems 26, 301–311 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-019-00644-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-019-00644-6