Abstract
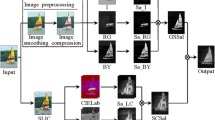
With the advancement of time, the computer vision systeams are focusing on mimicking the human visual system. In this manuscript, we tried to develop a model which works at improving both the detection accuracy and computation time. First, two double opponent color based features and twelve directional edge features using Gabor filter are computed. Then the most dominant feature pertaining to the salient object is extracted using principal component analysis to form the saliency map. Further, a threshold is applied on the saliency map to detect the salient object present in the image. This threshold selection is a vital procedure. We mapped the Ising model of ferromagnetism to the salient object detection problem by employing an optimization problem for this threshold selection. Experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms the existing models in terms of detection accuracy and also takes less computation time in comparison to many methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itti, L., Koch, C., Niebur, E.: A model of saliency based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20, 1254–1259 (1998)
Borji, A., Cheng, M., Jiang, H., Li, J.: Salient object detection: a survey. arXiv 1411, 5878 (2014)
Li, Z., Itti, L.: Saliency and gist features for target detection in satellite images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20, 2017–2029 (2011)
Graefe, R., Efenberger, W.: A novel approach for the detection of vehicles on freeways by real time vision. Intell. Veh. 1996, 363–368 (1996)
Itti, L.: Models of bottom up and top down visual attention. California Institute of Technology, Pasadena (2000)
Karssemeijer, N.: Detection of stellate distortions in mammograms. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 15, 611–619 (2006)
Santella, A., Agrawala, M., Decarlo, D., Salesin, D., Cohen, M.: Gaze based interaction for semi-automatic photo cropping. In: Proceedings of Conference Human Factors in Computing Systems pp. 771–780 (2006)
Rother, C., Bordeaux, L., Hamadi, Y., Blake, A.: Autocollage. ACM Siggraph 25, 847–852 (2006)
Koch, C., Ullman, S.: Shifts in selective visual attention: towards the underlying neural circuitry. Hum. Neurobiol. 4, 219–227 (1985)
Bruce, N.D.B., Tsotsos, J.K.: Saliency Based on Information Maximization. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 18, 155–162 (2006)
Han, J., Ngan, K.N., Li, M.J., Zhang, H.J.: Unsupervised extraction of visual attention objects in color images. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol. 16, 141–145 (2006)
Meur, O.L., Callet, P.L., Barba, D., Thoreau, D.: A coherent computational approach to model bottom up visual attention. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28, 802–817 (2006)
Harel, J., Koch, C., Perona, P. (2007)Graph based visual saliency. In:Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information and Processing Systems pp. 545–552 (2007)
Hou, X., Zhang, L.: Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach.In: Proceedings in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 1–8 (2007)
Yu, Z., Wong, H.S.: A rule based technique for extraction of visual attention regions based on real time clustering. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 9, 766–784 (2007)
Zhang, L., Tong, M.H., Marks, T.K., Shan, H., Cottrell, G.W.: SUN: A Bayesian framework for saliency using natural statistics. J. Vis. 8, 1–20 (2008)
Liu, T., Yuan, Z., Sun-Wang, J., Zheng, N., Tang, X., Shum, H.Y.: Learning to Detect A Salient Object. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33, 353–366 (2011)
Achanta, R., Hemamiz, S., Estraday, F., Susstrunk S.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection.In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 1597–1604 (2004)
Achanta, R., Susstrunk S.: Saliency detection using maximum symmetric surround. In: Proceedings in International Conference on Image Processing pp. 2653–2656 (2010)
Zhang, W., Wu, Q.M.J., Wang, G., Yin, H.: An Adaptive Computational Model for Salient Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 12, 300–315 (2010)
Goferman, S., Zelnik-Manor, L., Tal, A.: Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34, 1915–1926 (2012)
Liu, Z., Shi, R., Shen, L., Xue, Y., Ngan, K.N., Zhang, Z.: Unsupervised salient object segmentation based on kernel density estimation and two-phase graph cut. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 14, 1275–1289 (2012)
Shen, X., Wu Y.: A unified approach to salient object detection via low rank matrix recovery. In: Proceedings in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 853–860 (2012)
Vikram, T.N., Tscherepanow, M., Wrede, B.: A saliency map based on sampling an image into random rectangular regions of interest. Pattern Recogn. 45, 3114–3124 (2012)
İmamoğlu, N., Lin, W., Fang, Y.: A saliency detection model using low-level features based on wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 15, 96–105 (2013)
Singh, N., Agrawal, R.K.: Combination of Kullback-Leibler divergence and Manhattan distance measures to detect salient objects. SIVIP (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-013-0457-y
Singh, N., Arya, R., Agrawal, R.K.: A novel approach to combine features for salient object detection using constrained particle swarm optimization. Pattern Recogn. 47, 1731–1739 (2014)
Liu, Z., Zou, W., Meur, O.L.: Saliency tree: a novel saliency detection framework. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23, 1937–1952 (2014)
Zhu, L., Klein, D.A., Frintrop, S., Cao, Z., Cremers, A.B.: A multisize super pixel approach for salient object detection based on multivariate normal distribution estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23, 5094–5107 (2014)
Peng, P., Shao, L., Han, J., Han, J.: Saliency-aware image-to-class distances for image classification. Neurocomputing 166, 337–345 (2015)
Jiang, H., Wang, J., Yuan, Z., Wu, Y., Zheng, N., Li, S.: Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition pp. 2083–2090 (2013)
Fu, H, Cao X., Tu Z.: Cluster-Based Co-Saliency Detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (2013)
Zhao, R., Wanli, O., Hongsheng, L., Xiaogang, W.: Saliency detection by multi-context deep learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1265–1274 (2015)
Lin, Y., Kong, S., Wang, D. and Zhuang, Y.: Saliency detection within a deep convolutional architecture. In Workshops at the Twenty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2014)
Zhang, D., Han, J., Han, J., Shao, L.: Cosaliency detection based on intrasaliency prior transfer and deep intersaliency mining. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(6), 1163–1176 (2016)
Li, G. and Yu, Y.: Deep contrast learning for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 478–487 (2016)
Xie, Y., Lu, H., Yang, M.-H.: Bayesian saliency via low and mid level cues. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22, 1689–1698 (2013)
Qin, Y., Lu, H., Xu Y., Wang H.E.: Saliency detection via cellular automata. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp.110–119 (2015)
Singh, N., Arya, R., Agrawal, R.K.: A novel position prior using fusion of rule of thirds and image center for salient object detection. Multimed. Tools Appl.d 76(8), 10521–10538 (2017)
Singh, N., Arya, R., Agrawal, R.K.: A convex hull approach in conjunction with Gaussian mixture model for salient object detection. Digit. Signal Process. 55, 22–31 (2016)
Singh, N., Arya, R., Agrawal, R.K.: Performance enhancement of salient object detection using super pixel based Gaussian mixture model. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77, 1–19 (2017)
Singh, N., Mishra, K.K., Bhatia, S.: SEAM an improved environmental adaptation method with real parameter coding for salient object detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08678-z
Chen, S., Tan, X., Wang, B., Huchuan, Lu, Xuelong, Hu, Yun, Fu: Reverse attention for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 3763–3776 (2020)
Zhang, L., Wu, J., Wang, T., Borji, A., Wei, G., & Lu, H.: A Multistage Refinement Network for Salient Object Detection. IEEE transactions on image processing: a publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society (2020)
Wold, S., Esbensen, K., Geladi, P.: Principal component analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2(1–3), 37–52 (1987)
Ising, E.: Beitrag zur theorie des ferromagnetismus. Zeitschrift für Physik A Hadrons Nucl. 31(1), 253–258 (1925)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Y. Zhang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N. Saliency threshold: a novel saliency detection model using Ising’s theory on Ferromagnetism (STIF). Multimedia Systems 26, 397–411 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-020-00650-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-020-00650-z