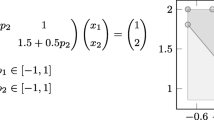Abstract
The paper considers systems of linear interval equations, i.e., linear systems where the coefficients of the matrix and the right hand side vary between given bounds. We focus on symmetric matrices and consider direct methods for the enclosure of the solution set of such a system. One of these methods is the interval Cholesky method, which is obtained from the ordinary Cholesky decomposition by replacing the real numbers by the related intervals and the real operations by the respective interval operations. We present a method by which the diagonal entries of the interval Cholesky factor can be tightened for positive definite interval matrices, such that a breakdown of the algorithm can be prevented. In the case of positive definite symmetric Toeplitz matrices, a further tightening of the diagonal entries and also of other entries of the Cholesky factor is possible. Finally, we numerically compare the interval Cholesky method with interval variants of two methods which exploit the Toeplitz structure with respect to the computing time and the quality of the enclosure of the solution set.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neumaier A (1990) Interval methods for systems of equations Encyclopedia Math Appl 37. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Alefeld G, Herzberger J (1983) Introduction to interval computations. Academic Press, New York
Garloff J (2009) Interval Gaussian elimination with pivot tightening. SIAM J Matrix Anal Appl 30: 1761–1772
Alefeld G, Mayer G (1993) The Cholesky method for interval data. Linear Algebra Appl 194: 161–182
Alefeld G, Mayer G (2009) New criteria for the feasibility of the Cholesky method with interval data. SIAM J Matrix Anal Appl 30: 1392–1405
Rohn J (1994) Positive definiteness and stability of interval matrices. SIAM J Matrix Anal Appl 15: 175–184
Białas S, Garloff J (1984) Intervals of P-matrices and related matrices. Linear Algebra Appl 58: 33–41
Gantmacher FR (1977) The theory of matrices, vol 1. Chelsea Publishing, New York
Johnson CR, Horn RA (1985) Matrix analysis, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rohn J (1993) Inverse interval matrix. SIAM J Numer Anal 30: 864–870
Hertz D (1992) The extreme eigenvalues and stability of real symmetric interval matrices. IEEE Trans Autom Control 37: 532–535
Rohn J (1998) Bounds on the eigenvalues of interval matrices. ZAMM Z Angew Math Mech Suppl 78(3): S1049–S1050
Hladík M, Daney D, Tsigaridas E (2010) Bounds on real eigenvalues and singular values of interval matrices. SIAM J Matrix Anal Appl 31: 2116–2129
Garloff J (2010) Pivot tightening for the interval Cholesky method. Proc Appl Math Mech 10: 549–550
Dembo A (1988) Bounds on the extreme eigenvalues of positive-definite Toeplitz matrices. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 34: 352–355
Ma EM, Zarowski CJ (1995) On lower bounds for the smallest eigenvalue of a Hermitian positive-definite matrix. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 41: 539–540
Sun W (2000) Lower bounds of the minimal eigenvalue of a Hermitian positive definite matrix. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 46: 2760–2762
Rosen KH (2000) Handbook of discrete and combinatorial mathematics, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Mukherjee BN, Maiti SS (1988) On some properties of positive definite Toeplitz matrices and their possible applications. Linear Algebra Appl 102: 211–240
Berenhaut KS, Bandyopadhyay D (2005) Monotone convex sequences and Cholesky decomposition of symmetric Toeplitz matrices. Linear Algebra Appl 403: 75–85
Rump SM (1999) INTLAB—INTerval LABoratory. In: Csendes T (ed) Developments in reliable computing. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 77–104
Bareiss EH (1969) Numerical solution of linear equations with Toeplitz and vector Toeplitz matrices. Numer Math 13: 404–424
Zohar S (1974) The solution of a Toeplitz set of linear equations. J ACM 21: 272–276
Trench WF (1964) An algorithm for the inversion of finite Toeplitz matrices. SIAM J Appl Math 12: 515–522
Garloff J (1986) Solution of linear equations having a Toeplitz interval matrix as coefficient matrix. Opuscula Math 2: 33–45
Dimitrov D (2011) Investigations of pivot tightening for the interval Cholesky method and of the solution of Toeplitz systems of linear interval equations. Master thesis, University of Applied Sciences/HTWG Konstanz, Konstanz
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
On the occasion of the 100th anniversary of Cholesky’s method on Dec. 2, 2010 (see http://math.univ-lille1.fr/~brezinsk/cholNUMA.pdf).
This submission is related to SCAN 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garloff, J. Pivot tightening for direct methods for solving symmetric positive definite systems of linear interval equations. Computing 94, 97–107 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-011-0159-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-011-0159-7