Abstract
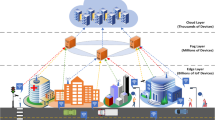
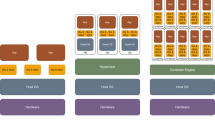
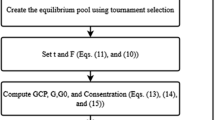
We address in this paper the task-scheduling in cloud computing. This problem is known to be \({\mathcal {NP}}\)-hard due to its combinatorial aspect. The main role of our model is to estimate the time needed to run a set of tasks in cloud and in turn reduces the processing cost. We propose a genetic approach for modelling and optimizing a task-scheduling problem in cloud computing. The experimental results demonstrate that our solution successfully competes with previous task-scheduling algorithms. For this, we develop a decision support system based on the core of CloudSim. In terms of processing cost, the obtained results show that our approach outperforms previous scheduling methods by a significant margin. In terms of makespan, the obtained schedules are also shorter than those of other algorithms.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Jain S (2014) Efficient optimal algorithm of task-scheduling in cloud computing environment. Int J Comput Trends Technol 9(7):344–349
Alkhanak EN, Lee SP, Reza R, Parizi RM (2015) Cost optimization approaches for scientific workflow scheduling in cloud and grid computing: a review, classifications, and open issues. J Syst Softw. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2015.11.023
Berwal M, Kant C (2015) Load balancing in cloud computing using task-scheduling. Int J Adv Res Comput Commun Eng. doi:10.17148/IJARCCE.2015.4737
Calheiros RN, Ranjan R, Beloglazov A, De Rose CAF, Buyya R (2011) CloudSim: a toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud computing environments and evaluation of resource provisioning algorithms. Softw Pract Exper 41:23–50. doi:10.1002/spe.995
Downey Allen B (1996) Predicting queue times on space-sharing parallel computers. University of California at Berkeley, Berkeley
Gao Y, Guan H, Qi Z, Hou Y, Liu L (2013) A multi-objective ant colony system algorithm for virtual machine placement in cloud computing. J Comput Syst Sci. doi:10.1016/j.jcss.2013.02.004
Garey MR, Johnson DS (1979) Computers and intractability: a guide to the theory of NP-completeness. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco
Goyal T, Agrawal A (2013) Host scheduling algorithm using genetic algorithm in cloud computing environment. IJRET 1(1):7–12
Grandinetti L, Pisacane O, Sheikhalishahi M (2013) An approximate \(\epsilon \)-constraint method for a multi-objective job scheduling in the cloud. Future Gener Comput Syst 29:1901–1908. doi:10.1016/j.future.2013.04.023
Jungck K, Rahman SM (2011) Cloud computing avoids downfall of application service providers. Int J Inf Technol Converg Serv. doi:10.5121/ijitcs.2011.1301
Kaleeswaran A, Ramasamy V, Vivekanandan P (2013) Dynamic scheduling of data using genetic algorithm in cloud computing. Int J Adv Eng Technol 5(2):327–334
Kumar P, Verma A (2012) Independent task-scheduling in cloud computing by improved genetic algorithm. Int J Adv Res Comput Sci Softw Eng. doi:10.1145/2345396.2345420
Kumar P, Anandarangan V, Reshma A (2015) An approach to workflow scheduling using priority in cloud computing environment. Int J Comput Appl 109(11):32–38
Li W et al (2013) Resource virtualization and service selection in cloud logistics. J Netw Comput Appl. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2013.02.019i
Malawski M, Figiela K, Nabrzyski J (2013) Cost minimization for computational applications on hybrid cloud infrastructures. Future Gener Comput Syst 29:1786–1794. doi:10.1016/j.future.2013.01.004
Mell P, Grance T (2011) The NIST definition of cloud computing. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg
Mohammadi F, Jamali S, Bekravi M (2014) Survey on job scheduling algorithms in cloud computing. Int J Emerg Trends Technol Comput Sci (IJETTCS) 3(2):151–154
Pasha N, Agarwal A, Rastogi R (2014) Round robin approach for VM load balancing algorithm in cloud computing environment. Int J Adv Res Comput Sci Softw Eng 4(5):34–39
Patil SD, Mehrotra SC (2012) Resource allocation and scheduling in the cloud. Int J Emerg Trends Technol Comput Sci (IJETTCS) 1(1):47–52
Ramanjeet K (2015) A review of computing technologies: distributed, utility, cluster, grid and cloud computing. Int J Adv Res Comput Sci Softw Eng 5(2):144–148
Savitha P, Reddy J (2013) A review work on task-scheduling in cloud computing using genetic algorithm. Int J Sci Technol Res 2(8):241–245
Sbaa A, El Bejjet R, Medromi H (2013) Architecture design of a virtualized embedded system. Int J Comput Sci Eng 5(01):15–23
Sheikhalishahi M, Wallace RM, Grandinetti L, Vazquez-Poletti JL, Guerriero F (2015) A multi-dimensional job scheduling. Future Gener Comput Syst. doi:10.1016/j.future.2015.03.014
Tiwari A, Verma A (2015) An energy efficient algorithm using improved minmin technique. Int J Innovat Res Comput Commun Eng. doi:10.15680/IJIRCCE.2015.0312148
Tsai J-T, Fang J-C, Chou J-H (2013) Optimized task-scheduling and resource allocation on cloud computing environment using improved differential evolution algorithm. Comput Oper Res. doi:10.1016/j.cor.2013.06.012
Xu Y, Li K, Hu J, Li K (2014) A genetic algorithm for task-scheduling on heterogeneous computing systems using multiple priority queues. Inf Sci 270:255–287. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2014.02.122
Yoosefi M, Rahmani AM (2014) Tasks scheduling algorithm with predefined dead line and considering the balance factor. Int J Comput Sci Netw Solut 2(8):1–14
Zeng L et al (2015) An integrated task computation and data management scheduling strategy for workflow applications in cloud environments. J Netw Comput Appl. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2015.01.001
Zhang F, Cao J, Li K, Khan SU (2013) Multi-objective scheduling of many tasks in cloud platforms. Future Gener Comput Syst. doi:10.1016/j.future.2013.09.006
Zhu Z, Zhang G (2015) Evolutionary multi-objective workflow scheduling in cloud. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst. doi:10.1109/TPDS.2015.2446459
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aziza, H., Krichen, S. Bi-objective decision support system for task-scheduling based on genetic algorithm in cloud computing. Computing 100, 65–91 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-017-0566-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-017-0566-5