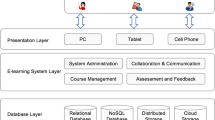
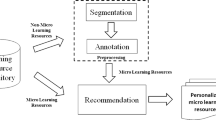
Abstract
As the e-learning area matures, there are a growing number of e-learning content providers that produce and distribute material that covers a large range of topics, differs in quality and is represented in various formats. Lately, different devices and various network technologies allow extensive user access to educational content almost anywhere, anytime and from any device. Ubiquitous e-learning has the potential to provide continuous and context-based, educational material to human learners anytime, anywhere and on any device. Since each person has different expectations related to the content, the performance of the delivery and display of that content, it is desirable for an ubiquitous e-learning environment to provide user-oriented personalisation of e-learning material. However very often there are multiple sources of e-learning material at various web locations (open corpus resources) that cover the same topic, but differ in terms of quality, formatting and even cost. It is very difficult for learners to select the content that best suits their interests and goals, characteristics of the device used and delivery network as well as their cost budget. This paper proposes an innovative ubiquitous e-learning environment called Performance-based E-learning Adaptive Cost-efficient Open Corpus frameworK (PEACOCK) that provides support for the selection and distribution of personalised e-learning rich media content (e.g. multimedia, pictures, graphics and text) to e-learners such as it will best suit users’ interests and goals, meet their formatting preferences and cost constraints, while considering the limitations introduced by the end-user devices and the delivery networks to the user. PEACOCK’s main goal is to maximise the users’ e-learning experience and increase their learning satisfaction and learning outcome.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bersin J (2004) E-learning research year in review and predictions for 2005. In: What works in e-learning newsletter. Bersin & Associates, Oakland
Stephen Abram (2003) A primer on e-learning...The framework, the market, the players, vol 12, issue 2. KMWorld Magazine, San Jose
Interactive Services, http://www.interactiveservices.com/
Ossidian, http://www.ossidian.com/
De Bra P, Calvi L (1998) AHA! An open adaptive hypermedia architecture. New Rev Hypermedia Multimedia J 4:115–139
De Bra P (2002) Adaptive educational hypermedia on the web. Commun ACM J 45(5):60–61
Brusilovsky P, Sosnovsky S, Shcherbinina O (2005) User modeling in a distributed e-learning architecture. In: Ardissono L, Brna P, Mitrovic A (eds) Lecture notes in artificial intelligence 3538. Springer, Berlin, pp 387–391
Weber G, Brusilovsky P (2001) ELM-ART: an adaptive versatile system for web based instruction. Artif Intell Educ J, Special Issue on Adaptive and Intelligent Web-based Educational Systems 12(4):351–384
Ng M, Hall W, Maier P, Armstrong R (2002) The application and evaluation of adaptive hypermedia techniques in web-based medical education. Assoc Learn Technol J 10(3):19–40
Conlan O, Wade V, Bruen C, Gargan M (2002) Multi-model, metadata driven approach to adaptive hypermedia services for personalized e-learning. In: Proceedings of second international conference on adaptive hypermedia and adaptive web-based systems (AH 2002), Malaga, Spain, pp100–111
Papanikolaou KA, Grigoriadou M, Kornilakis H, Magoulas GD (2003) Personalizing the interaction in a web-based educational hypermedia system: the case of INSPIRE. User Model User Adapt Interact J 13(3):213–267
Triantafillou E, Pomportsis A, Georgiadou E (2002) AESCS: adaptive educational system base on cognitive styles. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on adaptive hypermedia and adaptive web based systems (AH’2002), workshop on adaptive systems for web-based education, Malaga, Spain, pp10–20
Gütl C, Pivec M, Trummer C, García-Barrios VM, Mödritscher F, Pripfl J, Umgeher M (2005) AdeLE (Adaptive e-Learning with Eye-Tracking): theoretical background, system architecture and application scenarios. EURODL II, September, http://www.eurodl.org/materials/contrib/2005/Christian_Gutl.htm
Pivec M, Pripfl J, Trummer C (2005) Adaptable e-learning by means of real-time eye-tracking. In: Kommers P, Richards G (eds) Proceedings of world conference on educational multimedia, hypermedia and telecommunications, Montreal, Canada, pp 4037–4041
Yatani K, Sugimoto M, Kusunoki F (2004) Musex: a system for supporting children’s collaborative learning in a museum with PDAs. In: Proceedings of the wireless and mobile technologies in education, 2nd IEEE Intl. Workshop on Wireless and Mobile Technologies in Education (WMTE’04), pp109–113
Lancaster University, the guide project: overview http://www.guide.lancs.ac.uk/overview.html
Becking D, Betermieux S, Bomsdorf B, Feldmann B, Heuel E, Langer P, Schlageter G (2005) How to match mobile learning resources with learners current needs: the didactic profiling, proceedings of HCI 2005, Las Vegas
IBM Workplace Collaborative Learning v2.5, http://www.lotus.com/lotus/offering3.nsf
SkillSoft, http://www.skillsoft.com
PulseLearning, http://www.pulselearning.com
IEEE 1484.12.1-2002 (2002) Draft Standard for Learning Object Metadata, IEEE Learning Technology Standards Committee
MERLOT—Multimedia Educational Resource for Online Learning and Teaching, http://www.merlot.org
SmartForce, http://www.smartforce.com
Dolog P, Nejdl W (2003) Personalisation in ELENA: how to cope with personalisation in distributed e-learning networks. SINN03 Conference, Oldenburg, Germany, www.elena-project.org
Muntean CH, Muntean G-M, McManis J, Cristea AI (2006) Authoring model for quality of experience-aware adaptive hypermedia systems. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on adaptive hypermedia and adaptive web-based systems (AH2006), A3EH: the 4th international workshop on authoring of adaptive and adaptable educational hypermedia, Dublin, Ireland, pp 325–334
Muntean CH, Muntean G-M, McManis J, Cristea AI (2007) Quality of experience—LAOS: create once, use many, use anywhere. Int J Learn Technol, Special issue on Authoring Adaptive and Adaptable Hypermedia, 2007
Cristea AI, Mooij A (2003) LAOS: layered WWW AHS authoring model and their corresponding algebraic operators. In: Proceedings of the W3C Int. World Wide Web Conference (WWW’03), Alternate Track on Education, Budapest, Hungary
Muntean CH, McManis J (2006) Fine grained content-based adaptation mechanism for providing high end-user quality of experience with adaptive hypermedia systems. In: Proceedings of the W3C Int. World Wide Web Conference, Edinburgh, UK, pp 53–62
Muntean G-M (2006) Efficient delivery of multimedia streams over broadband networks using QOAS. IEEE Trans Broadcast J 52(2):230–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muntean, C.H., Muntean, GM. Open corpus architecture for personalised ubiquitous e-learning. Pers Ubiquit Comput 13, 197–205 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-007-0189-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-007-0189-5