Abstract
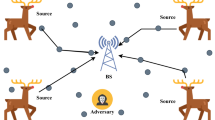
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are widely deployed to collect data in military and civilian applications today. Due to the open nature of a WSN, it is relatively easy for an adversary to eavesdrop and trace packets in order to capture the receiver. Therefore, location privacy, particularly the location privacy of the sink node, requires ultimate protection because of its critical position in WSNs. In this paper, we propose a sink location privacy protection scheme by injecting fake packets, but every real packet is still routed along its shortest path. The fake packets are routed to some random destinations and some fake sinks in order to provide the path diversity. It is difficult for an attacker to distinguish the real packets from the fake packets. Thus, the chance of finding the real sink by packet-tracing attack is reduced. Privacy analysis shows that the sink location privacy can be protected better with higher successful probability. We examine the packet travel delay, safe time, and energy consumption by both mathematical analysis and simulations.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz IF, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, Cayirci E (2002) Wireless sensor networks: a survey. Comput Netw 38(4):393–422
Li N, Zhang N, Das SK, Thuraisingham B (2009) Privacy preservation in wireless sensor networks: a state-of-the-art survey. Ad Hoc Netw 7(8):1501–1514. doi:10.1016/j.adhoc.2009.04.009
Kusdaryono A, Lee KO, Lee Y (2011) A clustering protocol with mode selection for wireless sensor network. JIPS. 7(1):29–42
Deng J, Han R, Mishra S (2004) Intrusion tolerance and anti-traffic analysis strategies for wireless sensor networks. In: DSN ‘04: Proceedings of the 2004 international conference on dependable systems and networks. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, pp 637–646. doi:10.1109/DSN.2004.1311934
Jian Y, Chen SG, Zhang Z, Zhang L (2008) A novel scheme for protecting receiver’s location privacy in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun 7(10):3769–3779. doi:10.1109/T-WC.2008.070182
Deng J, Han R, Mishra S (2005) Countermeasures against traffic analysis attacks in wireless sensor networks. First international conference on security and privacy for emerging areas in communications networks, pp 113–126. doi:10.1109/SECURECOMM.2005.16
Ponomarchuk Y, Seo DW (2010) Intrusion detection based on traffic analysis and fuzzy inference system in wireless sensor networks. JoC. 1(1):35–42
Li XF, Wang XY, Zheng N, Wan ZG, Gu M (2009) Enhanced location privacy protection of base station in wireless sensor networks. 2009 fifth international conference on mobile ad-hoc and sensor networks, pp 457–464. doi:10.1109/MSN.2009.19
Kamat P, Zhang Y, Trappe W, Ozturk C (2005) Enhancing source location privacy in sensor network routing. 25th IEEE international conference on distributed computing systems (ICDCS’05), pp 599–608. doi:10.1109/ICDCS.2005.31
Deng J, Han R, Mishra S (2006) Decorrelating wireless sensor network traffic to inhibit traffic analysis attacks. Pervasive Mob Comput 2(2):159–186. doi:10.1016/j.pmcj.2005.12.003
Hong XY, Wang P, Kong JJ, Zheng QW, Liu J (2005) Effective probabilistic approach protecting sensor traffic. In: Military communications conference, pp 169–175. doi:10.1109/MILCOM.2005.1605681
Jian Y, Chen SG, Zhang Z, Zhang L (2007) Protecting receiver-location privacy in wireless sensor networks. In: INFOCOM 2007. 26th IEEE international conference on computer communications, pp 1955–1963. doi:10.1109/INFCOM.2007.227
Chen HL, Lou W (2010) From nowhere to somewhere: protecting end-to-end location privacy in wireless sensor networks. Performance computing and communications conference (IPCCC), 2010 IEEE 29th international, pp 1–8. doi:10.1109/PCCC.2010.5682341
Biswas S, Mukherjee S, Mukhopadhyaya K (2007) A countermeasure against traffic analysis based base station detection in WSN. International conference on high performance computing, pp 1–5
Ngai ECH (2009) On providing sink anonymity for sensor networks. In: IWCMC ‘09: Proceedings of the 2009 international conference on wireless communications and mobile computing. New York, NY, pp 269–273. doi:10.1145/1582379.1582439
Ngai ECH, Rodhe I (2009) On providing location privacy for mobile sinks in wireless sensor networks. In: MSWiM ‘09: Proceedings of the 12th ACM international conference on modeling, analysis and simulation of wireless and mobile systems, pp 116–123. doi:10.1145/1641804.1641825
Ngai ECH (2009) On providing sink anonymity for sensor networks. In: IWCMC ‘09: Proceedings of the 2009 international conference on wireless communications and mobile computing. New York, NY, pp 269–273. doi:10.1145/1582379.1582439
Li Y, Ren J (2010) Source-location privacy through dynamic routing in wireless sensor networks. In: INFOCOM: 2010 Proceedings IEEE, pp 1–9. doi:10.1109/INFCOM.2010.5462096
Kang L (2009) Protecting location privacy in large-scale wireless sensor networks. In: ICC’09: IEEE international conference on communications, pp 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2009.5199372
Xi Y, Schwiebert L, Shi W (2006) Preserving source location privacy in monitoring-based wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings 2nd international workshop on security in systems and networks, pp 8–15. doi:10.1109/IPDPS.2006.1639682
Nezhad AA, Makrakis D, Miri A (2007) Anonymous topology discovery for multihop wireless sensor networks. In: Q2SWinet ‘07: Proceedings of the 3rd ACM workshop on QoS and security for wireless and mobile networks. New York, NY, pp 78–85, doi:10.1145/1298239.1298254
Chow CY, Mokbel MF, He T (2011) A privacy-preserving location monitoring system for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 10(1):94–107. doi:10.1109/TMC.2010.145
Kumar D, Aseri TC, Patel RB (2011) Multi-hop communication routing (MCR) protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. IJITCC 1(2):130–145. doi:10.1504/IJITCC.2011.039281
Imani M, Taheri M, Naderi M (2010) Security enhanced routing protocol for ad hoc networks. JoC. 1(1):43–48
Wang SJ, Tsai YR, Shen CC, Chen PY (2010) Hierarchical key derivation scheme for group-oriented communication systems, IJITCC. 1(1):66–76. doi:10.1504/IJITCC.2010.035227
Yang WB, Zhu WT (2010) Protecting source location privacy in wireless sensor networks with data aggregation. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on ubiquitous intelligence and computing (UIC) 2010, pp 252–266. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-16355-5_22
Li Y, Ren J (2009) Preserving Source-Location Privacy in Wireless Sensor Nerworks. In: SECON’09: 6th annual IEEE communications society conference on sensor, mesh and ad hoc communications and networks, pp 1–9. doi:10.1109/SAHCN.2009.5168962
Fall K, Varadhan K (2003) The ns manual. http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns
Yoo DS, Choi SS (2010) Medium access control with dynamic frame length in wireless sensor networks. In:JIPS. 6(4):501–510
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61173179 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, L., Kang, L., Shang, P. et al. Protecting the sink location privacy in wireless sensor networks. Pers Ubiquit Comput 17, 883–893 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-012-0539-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-012-0539-9