Abstract
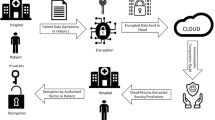
As a more ubiquitous concept, smart health (s-health) is the context-aware complement of mobile health within smart cities, and it has made an increasing number of people turn to cloud-based services. In a practical s-health system, security and privacy issues are of great importance and have to be addressed. In this paper, we propose a secure s-health system which realizes fine-grained access control on s-health cloud data and hence ensures users’ privacy protection. The key technique is a promising cryptographic primitive called ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption. In order to trace malicious behaviors in the proposed s-health system, two kinds of key abuse problems are considered: malicious key sharing among colluding users and key escrow problem of the semi-trusted authority. In the proposed s-health system, any malicious behavior of a user including illegal key sharing can be traced. For the semi-trusted authority, it can be accountable for its misbehavior including illegal key re-distribution. Particularly, the proposed system supports large universe and attributes do not need to be pre-specified during the system initialization phase. Besides, our system is proven fully secure in the random oracle model and it allows any monotonic access policies. Theoretical analysis and experimental results indicate that the proposed s-health system is suitable for smart city environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The expression “weak public” is similar to the term “partial public” in [9], in which only private user traceability is realized.
References
Solanas A, Patsakis C, Conti M, Vlachos IS, Ramos V, Falcone F, Postolache O, Pérez-Martínez PA, Di Pietro R, Perrea DN et al (2014) Smart health: a context-aware health paradigm within smart cities. IEEE Commun Mag 52(8):74–81
Sahai A, Waters B (2005) Fuzzy identity-based encryption. In: Cramer R (ed) Advances in cryptology-EUROCRYPT’05, volume 3494 of lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 557–557
Goyal V, Pandey O, Sahai A, Waters B (2006) pages 89–98. In: Proceedings of the 13th ACM conference on computer and communications security, CCS’06. ACM, New York
Lewko A, Waters B (2011) Unbounded hibe and attribute-based encryption. In: Advances in cryptology–EUROCRYPT’11. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 547–567
Lewko A, Okamoto T, Sahai A, Takashima K, Waters B (2010) Fully secure functional encryption: Attribute-based encryption and (hierarchical) inner product encryption. In: Gilbert H (ed) Advances in cryptology-EUROCRYPT’10, volume 6110 of lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 62–91
Li JX, Ren K, Kim K (2009) A2be: Accountable attribute-based encryption for abuse free access control. IACR Cryptol ePrint Archive 2009:118
Liu Z, Cao ZF, Wong DS (2013) White-box traceable ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption supporting any monotone access structures. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 8(1):76–88
Liu Z, Cao Z, Wong DS (2013) cp-abe: Blackbox traceable how to catch people leaking their keys by selling decryption devices on ebay. In: Proceedings of the 2013 ACM SIGSAC conference on computer and communications security. ACM, New York, pp 475–486
Ning J, Cao Z, Dong X, Wei L, Lin X (2014) Large universe ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption with white-box traceability. In: Computer security-ESORICS’14. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 55–72
Deng H, Wu Q, Qin B, Mao J, Liu X, Zhang L, Shi W (2014) Who is touching my cloud. In: Computer security-ESORICS’14. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 362–379
Ning J, Dong X, Cao Z, Wei L (2015) Accountable authority ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption with white-box traceability and public auditing in the cloud. In: Computer security–ESORICS’15. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 270–289
Liu Z, Wong DS (2015) Practical ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption: Traitor tracing, revocation, and large universe. In: Applied cryptography and network security–ACNS’15. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 127–146
Zhang X, Jin C, Li C, Wen Z, Shen Q, Fang Y, Wu Z (2015) Ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption with user and authority accountability. In: Security and privacy in communication networks. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 500–518
Liu Z, Wong DS (2015) Traceable cp-abe on prime order groups: Fully secure and fully collusion-resistant blackbox traceable. In: International conference on information and communications security. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 109–124
Li Y, Dai W, Ming Z, Qiu M (2016) Privacy protection for preventing data over-collection in smart city. IEEE Trans Comput 65(5):1339–1350
Lomotey RK, Deters R (2014) Using a cloud-centric middleware to enable mobile hosting of web services: mhealth use case. Person Ubiquit Comput 18(5):1085–1098
Guo P, Wang J, Li B, Lee S (2014) A variable threshold-value authentication architecture for wireless mesh networks. J Internet Technol 15(6):929–936
Shen J, Tan H, Wang J, Wang J, Lee S (2015) A novel routing protocol providing good transmission reliability in underwater sensor networks. J Internet Technol 16(1):171–178
Xia Z, Wang X, Sun X, Wang Q (2015) A secure and dynamic multi-keyword ranked search scheme over encrypted cloud data. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 27(2):340–352
Ren Y, Shen J, Wang J, Han J, Lee S (2015) Mutual verifiable provable data auditing in public cloud storage. J Internet Technol 16(2):317–323
Bethencourt J, Sahai A, Waters B (2007) Ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption. In: IEEE symposium on security and privacy. IEEE, pp 321–334
Cheung L, Newport C (2007) Provably secure ciphertext policy abe. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM conference on computer and communications security, CCS’07. ACM, NY, USA, pp 456– 465
Nishide T, Yoneyama K, Ohta K (2008) Abe with partially hidden encryptor-specified access structure. In: Bellovin S (ed) Proceedings of applied cryptography and network security–ACNS’08, volume 5037 of lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 111–129
Lai J, Deng RH, Li Y (2012) Expressive cp-abe with partially hidden access structures. In: Proceedings of the 7th ACM symposium on information, computer and communications security, ASIACCS’12. ACM, New York, pp 18–19
Zhang Y, Chen X, Li J, Wong DS, Li H (2013) Anonymous attribute-based encryption supporting efficient decryption test. In: Proceedings of the 8th ACM symposium on information, computer and communications security, ASIACCS’13. ACM, New York, pp 511–516
Zhang Y, Chen X, Li J, Wong DS, Li H, You I (2017) Ensuring attribute privacy protection and fast decryption for outsourced data security in mobile cloud computing. Inf Sci 379:42–61
Zhang Y, Li J, Chen X, Li H (2016) Anonymous attribute-based proxy re-encryption for access control in cloud computing. Secur Commun Netw 9(14):2397–2411
Yu S, Wang C, Ren K, Lou W (2010) Attribute based data sharing with attribute revocation. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM symposium on information, computer and communications security, ASIACCS’10. ACM, New York, pp 261–270
Balu A, Kuppusamy K (2014) An expressive and provably secure ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption. Inf Sci 276:354–362
Zhang Y, Zheng D, Chen X, Li J, Li H (2014) Computationally efficient ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption with constant-size ciphertexts. In: Provable security, ProvSec’14. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 259–273
Li J, Huang X, Li J, Chen X, Xiang Y (2014) Securely outsourcing attribute-based encryption with checkability. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 25(8):2201–2210
Shi Y, Zheng Q, Liu J, Han Z (2015) Directly revocable key-policy attribute-based encryption with verifiable ciphertext delegation. Inf Sci 295:221–231
Zhang Y, Zheng D, Chen X, Li J, Li H (2016) Efficient attribute-based data sharing in mobile clouds. Pervasive Mob Comput 28:135–149
Rouselakis Y (2013) Practical constructions and new proof methods for large universe attribute-based encryption. In: Proceedings of the practical ACM SIGSAC conference on computer and communications security, CCS’13. ACM, New York, p 2013
Okamoto T, Takashima K (2010) Fully secure functional encryption with general relations from the decisional linear assumption. In: Rabin T (ed) Advances in cryptology-CRYPTO’10, volume 6223 of lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 191–208
Li J, Ren K, Zhu B, Wan Z (2009) Privacy-aware attribute-based encryption with user accountability. In: Samarati P (ed) Proceedings of the international information security conference. ISC’09, volume 5735 of lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 347–362
Yu S, Ren K, Lou W, Li J (2009) Defending against key abuse attacks in kp-abe enabled broadcast systems. In: Chen Y (ed) Proceedings of the 5th international conference on security and privacy in communication networks. Securecomm’09, volume 19 of lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 311–329
Li J, Huang Q, Chen X, Chow SSM, Wong DS, Xie D (2011) Multi-authority ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption with accountability. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM symposium on information, computer and communications security, ASIACCS’11. ACM, New York, pp 386–390
Liu Z, Cao Z, Wong DS (2015) Traceable cp-abe: how to trace decryption devices found in the wild. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 10(1):55–68
Zhang Y, Li J, Zheng D, Chen X, Li H (2016) Accountable large-universe attribute-based encryption supporting any monotone access structures. In: Australasian conference on information security and privacy, ACISP’16. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 509–524
Boneh D, Goh E-J, Nissim K (2005) Evaluating 2-dnf formulas on ciphertexts. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 325–341
Schnorr C-P (1989) Efficient identification and signatures for smart cards. In: Advances in cryptology-CRYPTO’89 proceedings. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 239–252
Bellare M, Goldreich O (1992) On defining proofs of knowledge. In: Advances in cryptology-CRYPTO’92. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 390–420
Beimel A (1996) Secure schemes for secret sharing and key distribution. PhD thesis, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology Faculty of computer science
Boneh D, Boyen X (2004). In: Short signatures without random oracles. In Advances in cryptology-EUROCRYPT’04. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 56–73
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61402366, 61472091, 61472472, and 61272037), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province (No. 2015JQ6236, 2013JZ020), Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (No. 15JK1686), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-13-0946), Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (No. 20130203110004), and Distinguished Young Scholars Fund of Department of Education, Guangdong Province (No. Yq2013126). Yinghui Zhang is supported by New Star Team of Xi’an University of Posts and Telecommunications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
A preliminary version of this paper appears in ACISP 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, J., Zheng, D. et al. Towards privacy protection and malicious behavior traceability in smart health. Pers Ubiquit Comput 21, 815–830 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-017-1047-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-017-1047-8