Abstract
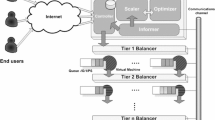
The scenario in which services are obtained by combining sub services is of a great importance. Reliability and fault tolerance are important concerns in the design of such distributed systems. This paper proposes a framework for designing robust client–server tier systems. First, we suggest implementing robust tier automata for each tier τ i used by the processors that the tier contains. The robust tier automata are useful abstractions that allow distribution of the tier’s tasks (and its stubs) in a way that ensures availability, consistency, and recovery in the presence of faults. Then we suggest an active tier framework in which the computation of a user request progresses on several paths in the tier system; those paths may intersect, leaving footprints for each other. And last, we propose the super tier architecture, which correlates equivalent tiers in order to gain more robustness and load balancing. We present and analyze optimistic, pessimistic, and semi-optimistic approaches for computing over the active tier system with super tiers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attiya H., Welch J.: Distributed Computing. McGraw-Hill, New York (1998)
Box, D., Ehnebuke, D., Kakivaya, G., Layman, A., Mendelson, N., Nielsen, H.F., Thatte, S., Winer, D.: Simple object access protocol (SOAP) 1.1. W3C (2000)
Baldoni R., Marchetti C.: Three-tier replication for FT-CORBA infrastructures. Softw. Pract. Exp. 33(7), 767–797 (2003)
Birman K., van Renesse R.: Reliable Distributed Computing with the Isis Toolkit. IEEE Computer Society Press, New York (1994)
Cristian F.: Synchronous atomic broadcast for redundant broadcast channels. J. Real Time Syst. 2, 195–212 (1990)
Cristian, F., Aghili, H., Strong, R., Dolev, D.: Atomic broadcast: from simple message diffusion to Byzantine agreement. In: Proceedings of the 15th international symposium on fault-tolerant computing, pp. 200–206. Ann Arbor, MI (1985)
Computability Theory Course Caltech, http://www.its.caltech.edu/~jclemens/courses/03ma117c/handouts/handout3.pdf, Springer (2003)
Chandra T., Toueg S: Unreliable failure detectors for reliable distributed systems. J. ACM 43(2), 225–267 (1996)
Dolev S.: Self-Stabilization. MIT Press, Cambridge (2000)
Dolev, S., Gilbert, S., Lynch, N.A., Shvartsman, A., Welch, J.: GeoQuorum: implementing atomic memory in ad hoc networks. In: 17th International Conference on Principles of DIStributed Computing, pp. 306–320. Springer, Heidelberg, LNCS:2848, (DISC 2003) (2003)
Dolev, S., Gilbert, S., Lynch, N.A., Schiller, E., Shvartsman, A., Welch, J.: Virtual mobile nodes for mobile ad hoc networks. In: International Conference on Principles of DIStributed Computing (DISC 2004) (2004)
Dekel E, Goft G: ITRA: inter-tier relationship architecture for end-to-end QoS. J. Supercomput. 28(1), 43–70 (2004)
Dolev, S., Segala, R., Shvartsman, A.: Dynamic load balancing with group communication. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Colloquium on Structural Information and Communication Complexity, (SIROCCO 1999), pp. 111–125 (1999)
DeMichiel, L.G., Yalcinalp, L.U., Krisham, S.: Enterprise JavaBeans Specification, Version 2.0, Proposed Final Draft. Sun Microsyst (1999)
Erl T.: Service-oriented Architecture: Concepts, Technology, and Design. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2005)
Foster, I., Kesselman, C., Tuecke, S.: The anatomy of the grid: enabling scalable virtual organizations. Int. J. Supercomput. Appl. (2001)
Hawthorne, M.J., Perry, D.E.: Applying design diversity to aspects of system architectures and deployment configurations to enhance system dependability. DSN 2004 Workshop on Architecting Dependable Systems, (DSN-WADS 2004) (2004)
Hazan, E., Safra, S., Schwartz, O.: On the hardness of approximating k-dimensional matching. Electronic Colloquium on Computational Complexity, Report No. 20 (2003)
Intel, “Building a Better e-Business Infrastructure: N-tier Architecture Improves Scalability, Availability and Ease of Integration”, Intel e-Business Center white paper. http://www.intel.com/eBusiness/pdf/busstrat/industry/wp012302.pdf.
Kemme, B., Jiménez-Peris, R., Patiño-Martinez, M., Salas, J.: Exactly once interaction in a multi-tier architecture. VLDB workshop on design, implementation, and deployment of database replication (2005)
Lamport L.: Time, clocks and the ordering of events in a distributed system. Commun. ACM 21(7), 558–565 (1978)
Lamport L.: The part-time parliament. ACM Trans Comput Syst 16(2), 133–169 (1978)
G. Lorriman, Introduction to multi-tier N-tier 3-tier architecture. http://www.undu.com/Articles/010131f.html, 2000
Lynch N.A.: Distributed algorithms. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Mateo (1996)
Object Management Group: Description of New OMA Reference Model, OMG Document ab/96-05-02 (1996)
Object Management Group: Fault Tolerant CORBA Specification 1.0. OMG Document ptc/00-04-04 (2000)
Papadimitriou C.: Computational complexity. Addison Wesley, Reading (1994)
Plasil, F., Stal, M.: An architectural view of distributed objects and components in CORBA, Java RMI and COM/DCON”. Softw. Concepts. Tools. 19(1), Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
White, D.R., Neman, M.: Fast approximation algorithms for finding node-independent paths in networks. Research Report 01-07-035. Santa Fe Institute (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An extended abstract of this work was presented in the IEEE International Conference on Software Science Technology and Engineering, pp. 23–33, February 2005.
Shlomi Dolev was partially supported by IBM Faculty Award, NSF grant 0098305, the Israeli Ministry of Defense, the Israeli Ministry of Trade and Industry, and the Rita Altura Trust Chair in Computer Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dolev, S., Gersten, O. A framework for robust active super tier systems. Int J Softw Tools Technol Transfer 12, 53–67 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10009-008-0096-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10009-008-0096-8