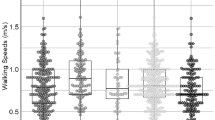
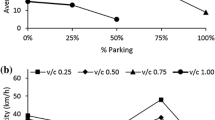
Abstract
We propose a new version of our pedestrian simulator, CrowdWalk, with a flexible framework to control and to enhance detailed behaviors of pedestrians and changes of conditions of environments. To provide a simulation framework of pedestrian dynamics to satisfy conflicting requests, scalability and flexibility, we add a new functionality to control simulation conditions by Ruby script inside of the simulation to CrowdWalk. The new functionality enables to change simulation environments and agent behaviors during the simulation. Using this facility, we can carry out various simulations uniformly without changes of source codes of the simulator itself.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helbing D, Molnar P (1995) Social force model for pedestrian dynamics. Phys Rev E 51(5):4282–4286
Johansson A, Helbing D, Shukla PK (2007) Specification of the social force pedestrian model by evolutionary adjustment to video tracking data. Adv Complex Syst 10(2):271–288. doi:10.1142/S0219525907001355
Karkin I, Grachev V, Skochilov A, Zverev V (2010) “flowtech” and “evatech”: Two computer-simulation methods for evacuation calculation. In: Klingsch WWF, Rogsche C, Schadschneider A, Schreckenberg M (eds) Pedestrian and evacuation dynamics 2008. Springer, Berlin, pp 537–545. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-04504-2_47
Laemmel G, Plaue M (2014) Getting out of the way—collision-avoiding pedestrian models compared to the realworld—. In: Weidmann U, Kirsch U, Schreckenberg M (eds) Pedestrian and evacuation dynamics 2012. Springer International Publishing, Berlin, pp 1275–1289. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-02447-9_105
Nishinari K, Suma Y, Yanagisawa D, Tomoeda A, Kimura A, Nishi R (2008) Toward smooth movement of crowds. In: Klingsch WWF, Rogsche C, Schadschneider A, Schreckenberg M (eds) Pedestrian and evacuation dynamics 2008. Springer, Berlin, pp 293–308. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-04504-2_26
Noda I, Ito N, Izumi K, Yamashita T, Mizuta H, Kamada T, Murase Y, Yoshihama S, Hattori H (2015) Roadmap for multiagent social simulation on hpc. In: Kurihara S, Hattori H (eds) Proc. of DOCMAS-WEIN 2015
Soeda S, Yamashita T, Noda I (0008) Network based pedestrian simulator. In: Proc. of 7th international symposium on new technologies for urban safety of mega cities in Asia, p. ??? Center for Public Safety Research, Tsinghua University (2008)
Tome P, Bonzon F, Merminod B, Aminian K (2010) Improving pedestrian dynamics modeling using fuzzy logic. In: Klingsch WWF, Rogsche C, Schadschneider A, Schreckenberg M (eds) Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics 2008. Springer, Berlin, pp 503–508 (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-04504-2_42
Yamashita, T., Matsushima, H., Noda, I.: Exhaustive analysis with a pedestrian simulation environment for assistant of evacuation planning. In: Prof. of PED 2014, pp. SE05–3 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.trpro.2014.09.047
Yamashita T, Soeda, Noda I (2011) Verification of evacuation plan by exhaustive testing with evacuation simulation netmas. In: Proc. of SICE Annual Conference 2011, pp WeA06–03. SICE
Zanlungo, F., Ikeda, T., Kanda, T.: Social force model with explicit collision prediction. EPL (Europhysics Letters) 93(6), 68,005 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JST CREST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the 21st International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics, Beppu, Oita, January 20–22, 2016.
About this article
Cite this article
Noda, I., Yamashita, T. Pedestrian simulator with flexible framework to enhance detailed behavior and environmental change. Artif Life Robotics 22, 308–315 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-017-0371-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-017-0371-4