Abstract
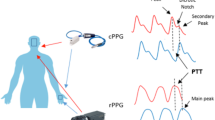
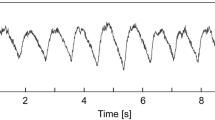
In this paper, we investigate the possibility of using image-based pulse transit time (iPTT) to estimate blood pressure using an RGB (red, green, blue)-camera video taken from the face only. It is generally known that there is a correlation between iPTT and blood pressure. iPTT refers to the difference between the times when a pulse wave reaches two different parts of the body. Therefore, it is possible to estimate blood pressure without contact, with iPTTs obtained from the RGB camera. However, this method requires simultaneous capture of images of the face and palm. Recording of such videos is limited by the subject’s posture. Hence, it is very difficult to achieve blood pressure estimation in a real-world environment. To solve these problems, this study examined whether it is possible to measure pulse wave propagation based on a single part of the body. The results showed that there was a time difference between the pulse waves at the forehead and the chin, thus it was possible to measure iPTT using only the face. Pulse waves were obtained from the chin and forehead, and the correlations between iPTT and blood pressure from the acquired pulse waves were examined. The results showed a negative correlation between these iPTT measures and blood pressure. The results suggest that simple, non-contact blood pressure estimation will be possible in the future.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mukkamala R, Hahn JO, Inan OT, Mestha LK, Kim CS, Töreyin H, Kyal S (2015) Toward ubiquitous blood pressure monitoring via pulse transit time: theory and practice. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng 62(8):1879–1901
Jeong IC, Finkelstein J (2016) Introducing contactless blood pressure assessment using a high speed video camera. J Med Syst 40(4):77
Verkruysse W, Svaasand LO, Nelson JS (2008) Remote plethysmographic imaging using ambient light. Opt Express 16(26):21434–21445
Yang Y, Liu C, Yu H, Shao D, Tsow F, Tao N (2016) Motion robust remote photoplethysmography in CIELab color space. J Biomed Opt 21(11):117001
Mcduff D, Gontarek S, Picard R (2014) Improvements in remote cardiopulmonary measurement using five band digital camera. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(10):2593–2601
Poh M, Mcduff D, Picard R (2011) Advancements in noncontact, multiparameter physiological measurements using a webcam. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(1):7–11
Shao D, Yang Y, Liu C, Tsow F, Yu H, Tao N (2014) Noncontact monitoring breathing pattern, exhalation flow rate and pulse transit time. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(11):2760–2767
Fukunishi M, Kurita K, Yamamoto S, Tsumura N (2017) Non contact video based estimation of heart rate variability spectrogram from hemoglobin composition. Artif Life Robot 22:457–463
Tsumura N, Ojima N, Sato K, Shiraishi M, Shimizu H, Nabeshima H, Akazaki S, Hori K, Miyake Y (2003) Image-based skin color and texture analysis/synthesis by extracting hemoglobin and melanin information in the skin. ACM Trans Graph 22:770–779
Hayashi K, Nagasawa S, Naruo Y, Okumura A (1980) Mechanical properties of human cerebral arteries. Biorheology 17(3):211–218
Fukunishi M, Yonezawa T, Okada G, Kurita K, Yamamoto S, Tsumura N (2017) Remote measurement of pulse transit time based on fluctuation of hemoglobin component. J Pac Area Longev Med Soc No.13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, R., Ogawa-Ochiai, K. & Tsumura, N. Non-contact method of blood pressure estimation using only facial video. Artif Life Robotics 25, 343–350 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-020-00622-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-020-00622-6